Team:TU Darmstadt/Cooperation
From 2012.igem.org
(→Cooperation) |
(→Cooperation) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
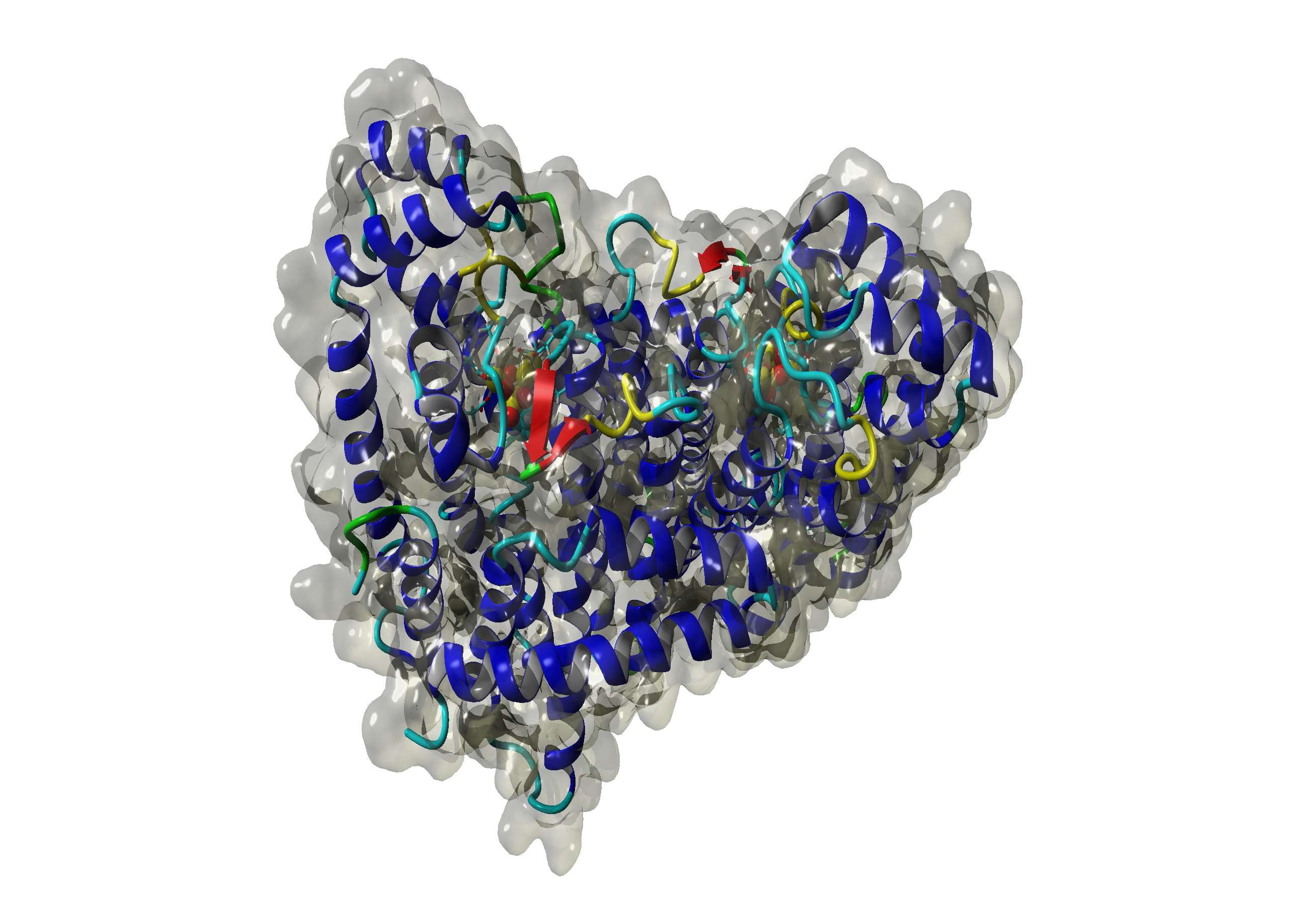
| - | The target sequence of the Saccharomyces HMG CoA Reduktase contains 536 residues in 1 molecule. Hence the target sequence was the only available information we identified modelling templates by running various PSI-BLAST iterations. We used [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1DQA 1DQA] chain A (Human Hmg-coa Reductase) and [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2R4F 2R4F] chain A (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a Reductase). Unfortunately, our hybrid model could not be improved by copying parts from other models. | + | The target sequence of the Saccharomyces HMG CoA Reduktase (SHMGR) contains 536 residues in 1 molecule. Hence the target sequence was the only available information we identified modelling templates by running various PSI-BLAST iterations. We used [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1DQA 1DQA] chain A (Human Hmg-coa Reductase) and [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2R4F 2R4F] chain A (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a Reductase). Unfortunately, our hybrid model could not be improved by copying parts from other models. <br> |
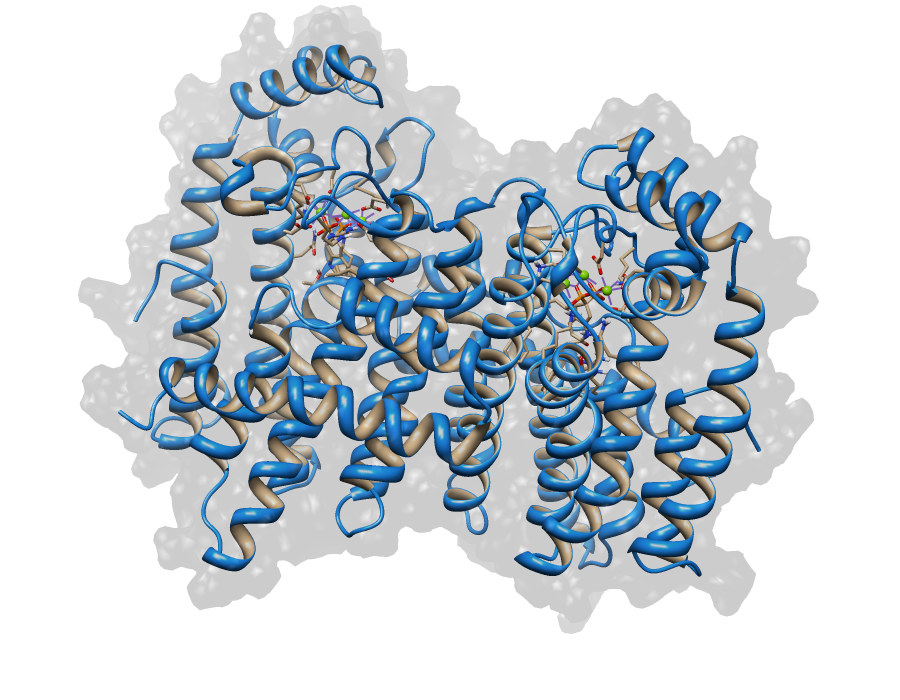
| + | The Sulfolobus GGPP Synthase (SGGPPS) sequence contains 262 residues in 1 molecule. As for the SHMGR we only were running various PSI-BLAST iterations. | ||
<gallery perrow="2" widths="400px" heights="300px" > | <gallery perrow="2" widths="400px" heights="300px" > | ||
| - | File:Sulfolobus_GGPP_Synthase.png|[[Aborted model of Sulfolobus GGPP Synthase]] | + | File:Sulfolobus_GGPP_Synthase.png|[[Aborted model of Sulfolobus GGPP Synthase (SGGPPS)]] |
| - | File:Saccharomyces_HMG_CoA_Reduktase.png|[[Aborted model of Saccharomyces HMG CoA Reduktase]] | + | File:Saccharomyces_HMG_CoA_Reduktase.png|[[Aborted model of Saccharomyces HMG CoA Reduktase (SHMGR)]] |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 17:41, 26 September 2012
Cooperation
Capacity for teamwork is one major feature and character of the iGEM competition. Since we first met team frankfurt at the Achema our paths crossed on several occasions. During these occasions we came up with the idea to give them support by modelling their enzymes. The simulations group performed modelling studies for three enzymes of the Frankfurt iGEM Team.
For the Saccharomyces HMG CoA Reductase and Sulfolobus GGPP Synthase we were not able to build homology models, but their Saccharomyces FPP Synthase (SFPPS) worked out. The results for the successful developed SFPPS and the two other enzymes can be seen in the following pictures.
FPP Synthase move klein.gif
|
|
The target sequence of the Saccharomyces HMG CoA Reduktase (SHMGR) contains 536 residues in 1 molecule. Hence the target sequence was the only available information we identified modelling templates by running various PSI-BLAST iterations. We used [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1DQA 1DQA] chain A (Human Hmg-coa Reductase) and [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2R4F 2R4F] chain A (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a Reductase). Unfortunately, our hybrid model could not be improved by copying parts from other models.
The Sulfolobus GGPP Synthase (SGGPPS) sequence contains 262 residues in 1 molecule. As for the SHMGR we only were running various PSI-BLAST iterations.
 "
"