Team:LMU-Munich/Data/Knockout
From 2012.igem.org
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Knockouts of germination genes === | ===Knockouts of germination genes === | ||
| - | We induced our germination-mutant strains to sporulate in Difco sporulation media. We quantified the cells and spores per milliliter of each culture using a Neubauer cell counting chamber. Then we plated known dilutions of culture, and measured the germination rate of mutant spores in a germination assay (see [https://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Lab_Notebook/Protocols Protocols]). | + | <p align="justify">We induced our germination-mutant strains to sporulate in Difco sporulation media. We quantified the cells and spores per milliliter of each culture using a Neubauer cell counting chamber. Then we plated known dilutions of culture, and measured the germination rate of mutant spores in a germination assay (see [https://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Lab_Notebook/Protocols Protocols]). The germination assays were carried out several times, and yielded similar results each time. For these results, see "Mutant Germination Rates" graph.</p> |
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
|} | |} | ||
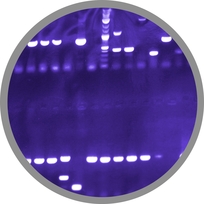
| - | The plate growth demonstrates the inability of our mutant spores to germinate. We can say that fewer than 1 out of 3x10^7 spores of strains B40, B41, B43, B46, and B47 germinated. | + | <p align="justify">The plate growth demonstrates the inability of our mutant spores to germinate. We can say that fewer than 1 out of 3x10^7 spores of strains B40, B41, B43, B46, and B47 germinated. |
| - | The plates below demonstrate the procedure of the germination assay. Plates here include those containing heated and unheated cultures, and show both germinable spores (B42) and spores unable to germinate (B47). | + | The plates below demonstrate the procedure of the germination assay. Plates here include those containing heated and unheated cultures, and show both germinable spores (B42) and spores unable to germinate (B47).</p> |
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | ||
Revision as of 09:05, 26 September 2012
The LMU-Munich team is exuberantly happy about the great success at the World Championship Jamboree in Boston. Our project Beadzillus finished 4th and won the prize for the "Best Wiki" (with Slovenia) and "Best New Application Project".
[ more news ]

Knockouts of germination genes
We induced our germination-mutant strains to sporulate in Difco sporulation media. We quantified the cells and spores per milliliter of each culture using a Neubauer cell counting chamber. Then we plated known dilutions of culture, and measured the germination rate of mutant spores in a germination assay (see Protocols). The germination assays were carried out several times, and yielded similar results each time. For these results, see "Mutant Germination Rates" graph.
|
The plate growth demonstrates the inability of our mutant spores to germinate. We can say that fewer than 1 out of 3x10^7 spores of strains B40, B41, B43, B46, and B47 germinated. The plates below demonstrate the procedure of the germination assay. Plates here include those containing heated and unheated cultures, and show both germinable spores (B42) and spores unable to germinate (B47).
|
 "
"






