Team:Tokyo Tech/Projects/PHAs/index.htm
From 2012.igem.org
(→Achivement) |
(→What is PHA?) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[File:tokyotech PHA whatsPHA.png|350px|thumb|right|fig1]] | [[File:tokyotech PHA whatsPHA.png|350px|thumb|right|fig1]] | ||
Polyhydroixyalkanoates(PHAs) are biological polyester synthesized by a wide range of bacteria, and can be produced by fermentation from renewable carbon sources such as sugars and vegetable oils. These polyesters are biodegradable thermoplastics and elastomers, which exhibit interesting material properties. Bacteria produce PHAs for the storage of carbon and energy. When the bacteria can’t get enough nutrients from outside, these PHAs will be degraded and used as energy source. This function is quite similar to the one of lipid in human body. PHAs are also a kind of bio plastics, which can be biodegraded a lot faster than fossil-fuel plastics in the environment. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is the most common type of PHAs. P(3HB) is synthesized by the enzymes coded in the gene of PHA synthesis (phaC1-A-B1) from Ralstonia eutropha H16. | Polyhydroixyalkanoates(PHAs) are biological polyester synthesized by a wide range of bacteria, and can be produced by fermentation from renewable carbon sources such as sugars and vegetable oils. These polyesters are biodegradable thermoplastics and elastomers, which exhibit interesting material properties. Bacteria produce PHAs for the storage of carbon and energy. When the bacteria can’t get enough nutrients from outside, these PHAs will be degraded and used as energy source. This function is quite similar to the one of lipid in human body. PHAs are also a kind of bio plastics, which can be biodegraded a lot faster than fossil-fuel plastics in the environment. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is the most common type of PHAs. P(3HB) is synthesized by the enzymes coded in the gene of PHA synthesis (phaC1-A-B1) from Ralstonia eutropha H16. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:tokyotech PHA whatsPHA2.png|350px|thumb|right|fig2]] | ||
| + | Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is synthesized by three enzymes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The A gene encodes for the 393 amino acids protein, 3-ketothiolase (PhaA) | ||
| + | The B gene encodes for the 246 amino acids protein, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (PhaB) | ||
| + | The C gene encodes for the 589 amino acids protein, PHA Synthase (PhaC) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The pathway and regulation of P(3HB) synthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16 is shown in Fig*. Acetyl CoA is metabolized from glucose by glycolysis and Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). At first, two molecules of acetyl-CoA are ligated to one molecule acetoacetyl-CoA by the action of 3-ketothiolase (coded in phaA). Acetoacetyl-CoA is transformed into (R)-3-hydroxybutyl-CoA by NADPH dependent acetoacetyl-CoA reductase(coded in phaB). P(3HB) polymers are then synthesized by the polymerization of (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA by the action of PHA synthase (PhaC). In most of the cases, PHA synthase determines the characteristic of PHA being synthesized in microorganism. | ||
=Production of PHAs by E.coli= | =Production of PHAs by E.coli= | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 22 September 2012
Contents |
Achivement
We made a new biobrick part and succeeded synthesizing Polyhydroixyalkanoates(PHAs). In our project, we designed rose silhouette to enhance the balcony scene of “Romeo and Juliet” by the synthesis of PHAs.
What is PHA?
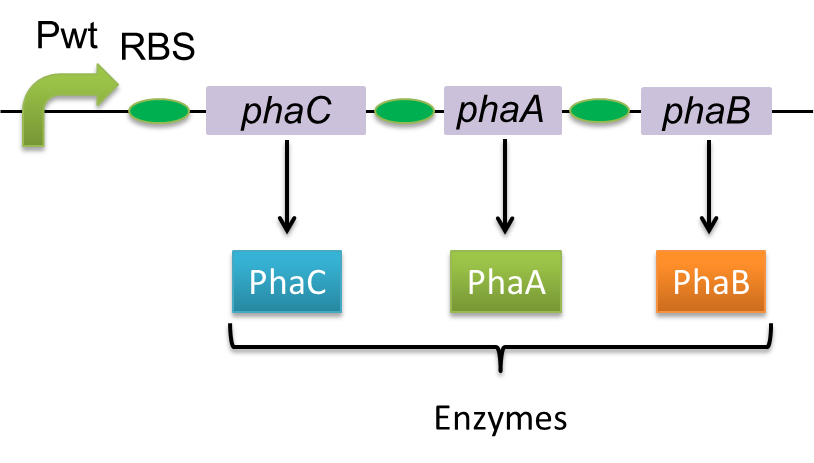
Polyhydroixyalkanoates(PHAs) are biological polyester synthesized by a wide range of bacteria, and can be produced by fermentation from renewable carbon sources such as sugars and vegetable oils. These polyesters are biodegradable thermoplastics and elastomers, which exhibit interesting material properties. Bacteria produce PHAs for the storage of carbon and energy. When the bacteria can’t get enough nutrients from outside, these PHAs will be degraded and used as energy source. This function is quite similar to the one of lipid in human body. PHAs are also a kind of bio plastics, which can be biodegraded a lot faster than fossil-fuel plastics in the environment. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is the most common type of PHAs. P(3HB) is synthesized by the enzymes coded in the gene of PHA synthesis (phaC1-A-B1) from Ralstonia eutropha H16.
Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is synthesized by three enzymes.
The A gene encodes for the 393 amino acids protein, 3-ketothiolase (PhaA) The B gene encodes for the 246 amino acids protein, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (PhaB) The C gene encodes for the 589 amino acids protein, PHA Synthase (PhaC)
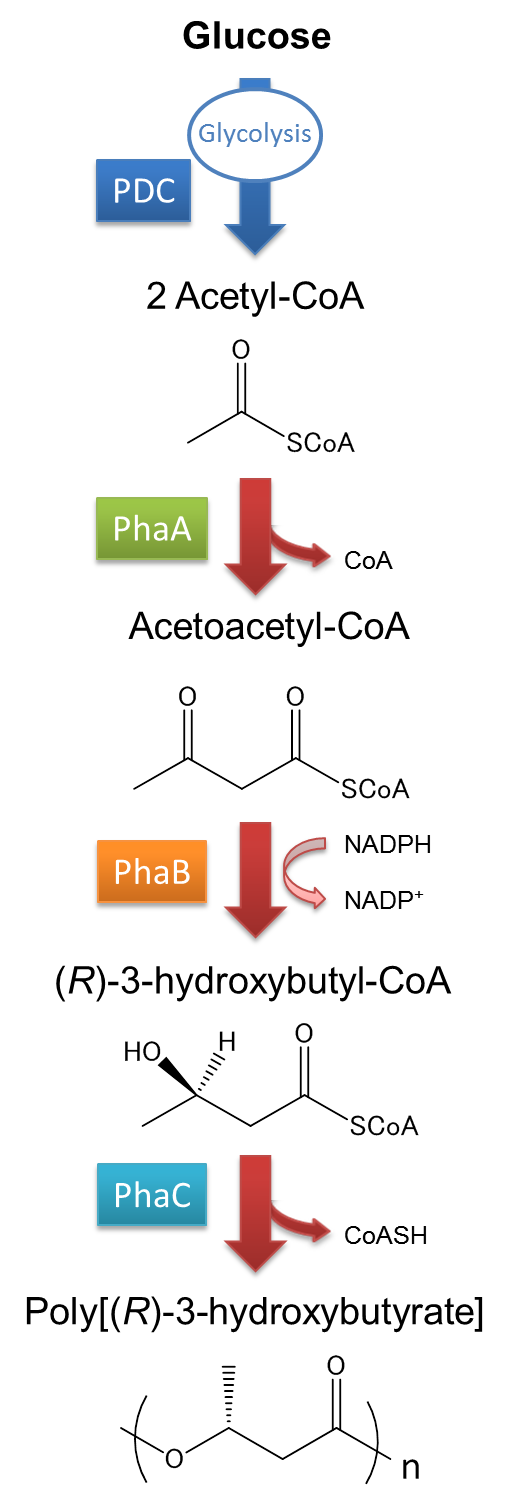
The pathway and regulation of P(3HB) synthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16 is shown in Fig*. Acetyl CoA is metabolized from glucose by glycolysis and Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). At first, two molecules of acetyl-CoA are ligated to one molecule acetoacetyl-CoA by the action of 3-ketothiolase (coded in phaA). Acetoacetyl-CoA is transformed into (R)-3-hydroxybutyl-CoA by NADPH dependent acetoacetyl-CoA reductase(coded in phaB). P(3HB) polymers are then synthesized by the polymerization of (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA by the action of PHA synthase (PhaC). In most of the cases, PHA synthase determines the characteristic of PHA being synthesized in microorganism.
Production of PHAs by E.coli
Text
DNA construction
Text
asssay
Text
(1)Nile Red
Text
(2)Nile Blue
Text
Perspective
Text
 "
"