Team:Amsterdam/modeling/generaldesign
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Methylated bits over time) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
== Methylated bits over time == | == Methylated bits over time == | ||
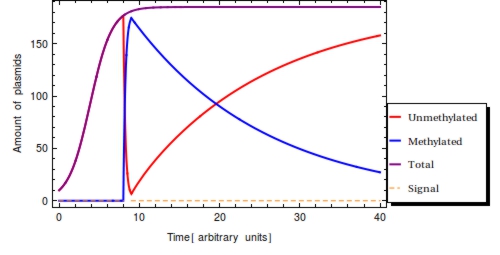
| - | Numerous copies of identical plasmids are often present in single cells and plasmids replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome (Scott 1984). A plasmid copy number (PCN) has been determined for all plasmids in the Parts Registry, which indicates a likely amount of copies of the plasmid to be present in each cell. Unlike | + | Numerous copies of identical plasmids are often present in single cells and plasmids replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome (Scott 1984). A plasmid copy number (PCN) has been determined for all plasmids in the Parts Registry, which indicates a likely amount of copies of the plasmid to be present in each cell. Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes do not copy DNA methylation patterns to the newly synthesized strand during DNA replication. This will lead to a dilution of the amount of ‘written’-plasmids over time, mostly due to cell replication and the ensuing binomial division of the plasmids in the parent cell among the two daughter cells. The ''volatility'' of this memory design seemed like a downside at first, but quickly opened our eyes to a very exciting feature of this system. By analyzing the fraction: |
<eqn>F(t) = \frac{\text{written plasmids}}{\text{written + unwritten plasmids}}</eqn> | <eqn>F(t) = \frac{\text{written plasmids}}{\text{written + unwritten plasmids}}</eqn> | ||
| - | at the time of memory read-out, the time at which the signal was registered by can be inferred. Using the here presented model, we will examine how this inferrance of signal detection time can be performed. Another goal of this model is to gain insight into the effects of the various parameters (e.g. plasmid replication and degradation rate) on | + | at the time of memory read-out, the time at which the signal was registered by can be inferred. |
| + | |||
| + | Using the here presented model, we will examine how this inferrance of signal detection time can be performed. Another goal of this model is to gain insight into the effects of the various parameters (e.g. plasmid replication and degradation rate) on <math>F(t)</math>. As this model has the sole purpose of clarifying the desired system behaviour, it is okay for units in this model to be dimensionless. | ||
== Model definition == | == Model definition == | ||
Revision as of 06:08, 21 September 2012
 "
"