Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/project3
From 2012.igem.org
Huanan1991 (Talk | contribs) |
Huanan1991 (Talk | contribs) (→Acceleration Modeling) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{Template:12SJTU_part_summary_head}} | {{Template:12SJTU_part_summary_head}} | ||
| - | + | *State of Art | |
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model. | In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mathematical modeling is a useful tool for understanding how a bio-system works and how to improve it. We build a mathematical model mainly based on the mechanism of the involved biochemical reaction. Here we focus on the dynamic process of membrane protein cluster in order to reveal how the system works over time. | ||
| + | *Aim | ||
PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, or elasticity. Defined by the PDE, the variable describing the phenomena can be solved according to different boundary values. | PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, or elasticity. Defined by the PDE, the variable describing the phenomena can be solved according to different boundary values. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Achievements | ||
| + | |||
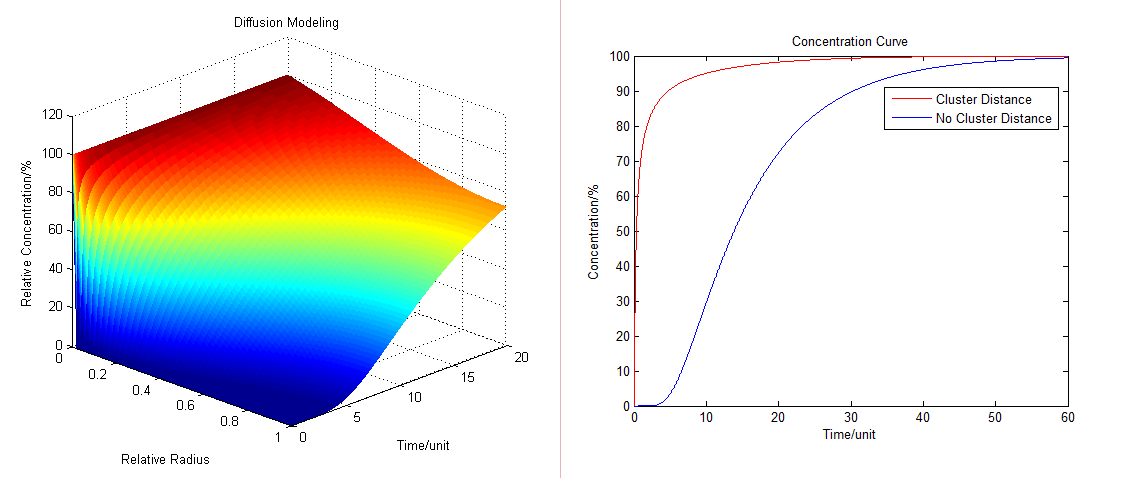
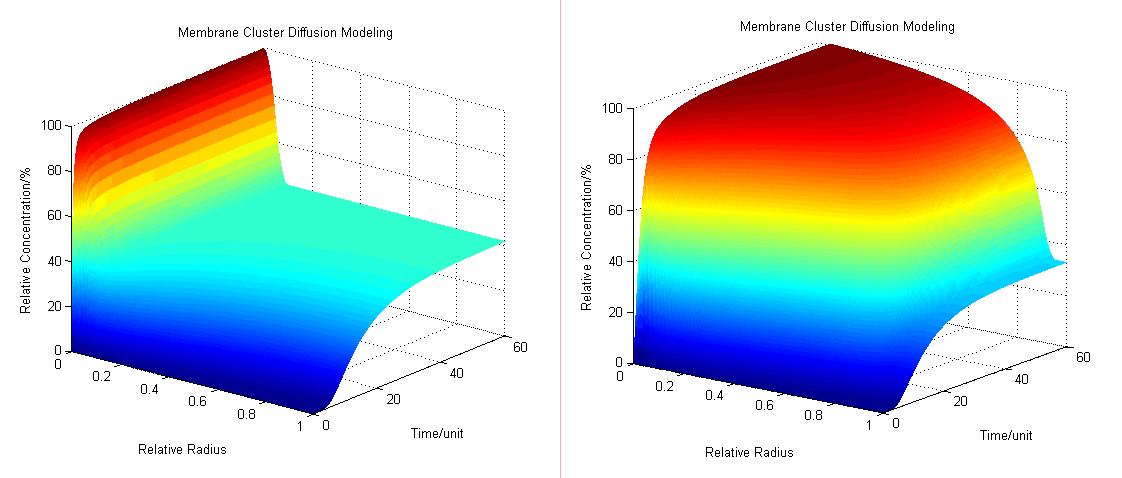
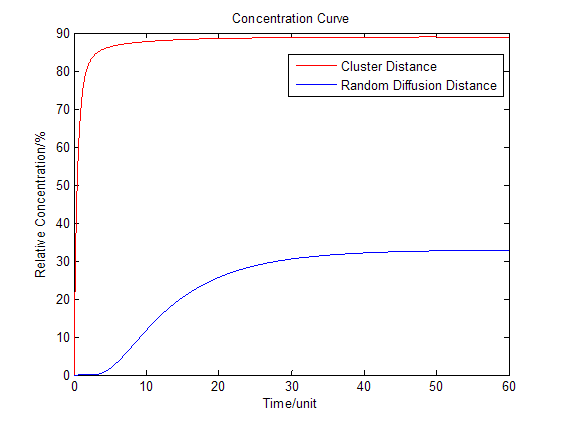
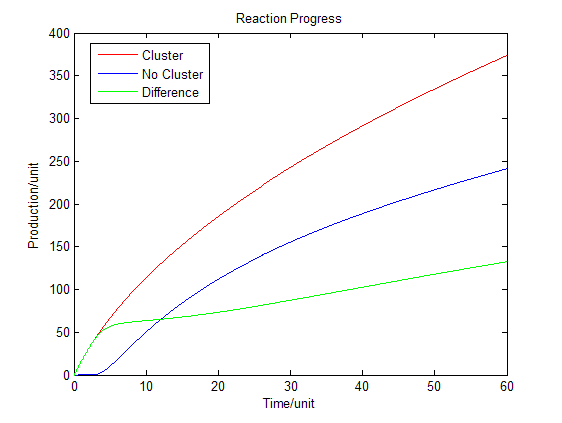
| + | Based on diffusion equation, by solving it under different boundary values, we found that the cluster system can increase production significantly. | ||
{{Template:12SJTU_part_summary_foot}} | {{Template:12SJTU_part_summary_foot}} | ||
===Basic Assumptions=== | ===Basic Assumptions=== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 47: | ||
:4. Each our membrane device occupies an area of membrane, adjacent to the others. Because each device is the same as others, the diffusion of the products out of the area can be regarded as reflected by the imaginary barrier, which means the normal derivative at the edge of the area is 0. | :4. Each our membrane device occupies an area of membrane, adjacent to the others. Because each device is the same as others, the diffusion of the products out of the area can be regarded as reflected by the imaginary barrier, which means the normal derivative at the edge of the area is 0. | ||
:5. The enzyme can be regarded as a thermal source, producing the molecular at a rate of v. | :5. The enzyme can be regarded as a thermal source, producing the molecular at a rate of v. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
==Acceleration Model== | ==Acceleration Model== | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 26 September 2012
| ||
|
 "
"