Team:Wageningen UR/InsideModification
From 2012.igem.org
(→CCMV with a negative interior) |
(→CCMV with coils on the inside) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
'''Results''' | '''Results''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first PCR went well. We used two dilutions of the backbone to ensure we have a rather pure PCR product. The backbone is still visible in sample II. Due to a pipetting mistake the positive control shows no result at all. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | [[File:CCMV wt K-coil PCR step1|350px|center|thumb|''Figure 2: PCR step I CCMV wt + K-coil'']] | ||
===CCMV with a negative interior=== | ===CCMV with a negative interior=== | ||
Revision as of 20:05, 25 September 2012
Contents |
Inside Modifications
Introduction
Since virus-like particles (VLPs) lack genetic content, they enclose an empty space. This space can be filled with proteins such as antibiotics, hormones, and all sorts of pharmaceuticals. Modifications on the inside of the VLPs can increase binding affinity to the loaded substance. The first modifications we pursue is adding the K-coil to the protein subunits at any location that is exposed on the inside of the VLP. In our case, this is a fusion to the N-terminal. The coils will facilitate strong attachment to the substance which has to carry the opposite coil.
The second modification we aim to make is a change in the interior's charge, which is another way to open up more options for loading our VLPs. Normally, the interior of a VLP is positively charged, facilitating interaction with negatively charged DNA/RNA molecules. By changing the amino acid sequence that is located on the interior of a VLP, the positive charge can be changed into a negative charge. A VLP with a negatively charged interior can be loaded with all sorts of positively charged molecules, such as polymeres, metals, etc.
Our aims:
Construct a Virus-Like Particle that has coils exposed on the inside.
Construct a Virus-Like Particle that has a negatively charged interior.
CCMV with coils on the inside
The Cowpea Chlorotic Mottle Virus (CCMV) VLP is one of the best candidates for drug delivery, since it is tolerant of high temperatures and stable at a certain pH range. Next to that, the wild-type CCMV VLP is not specific for mammalian cells in vivo. Because of the promising properties of the CCMV VLPs, we decided to place coiled-coils on the interior. Since the N-terminus of the CCMV coat protein is folded to the inside of the VLP, this was the logic place to attach the coil. Attachment of coiled-coils allows the fusion of a range of molecules, which are immobilized on the inside of the VLP [2].
Methods
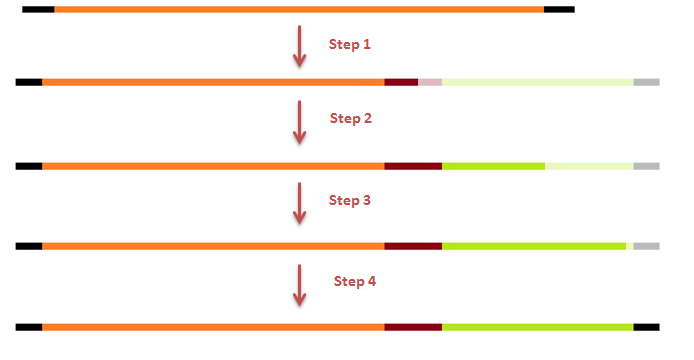
The attachment of the K-coil to the N-terminus of the CCMV wt VLP subunits was carried out in 3 subsequent PCR steps. Unluckily, the primer of the first step was not designed correctly, resulting in a frameshift over the entire VLP, making this construct useless. We discovered this on the 18th of September, when receiving the sequencing results of a similar experiment the attachment of the PnA-system to the outside of the CCMV Δ26 mutant.
Results
The first PCR went well. We used two dilutions of the backbone to ensure we have a rather pure PCR product. The backbone is still visible in sample II. Due to a pipetting mistake the positive control shows no result at all.
CCMV with a negative interior
One of the modifications that was performed on the CCMV VLP was to give the interior a negative charge. Whilst the wild-type CCMV VLP can not be loaded with positively charged substances, this modified version can [3]. One very interesting feature of these modified VLPs is that they can be loaded with positive ions like metals. Addition of iron ions to a solution containing these modified VLPs at a pH of 6.5 results in oxidative hydrolysis of the iron on the inside of the VLPs, creating paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles [3]. In figure 1 a schematic overview can be seen.
Methods
Constructing a CCMV VLP with a negative charge was facilitated by 3 subsequent PCR steps, see figure 2 Luckily. This construct was finished in august and we were able to place an IPTG promoter combined with an RBS site in front of it.
Results
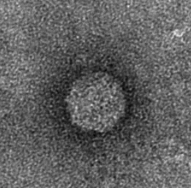
The next step was to produce VLPs with this new construct, which succeeded. In figure 2 a highly magnified image is shown of such a VLP with a negative interior.
As a proof of concept, the CCMV VLPs with a negative interior were loaded with iron ions and monitored using electron microscopy. Unluckily, the samples were highly contaminated, which made it impossible to pinpoint any present VLPs. This contamination was possibly cause by the addition of iron to the samples. In figure 2 an image is shown of such a sample in which there is lots of contamination.
Hepatitis B
Deletions as well as modifications to the C-terminal of the Hepatitis B core protein are possible since this part of the protein is not important for VLP formation [1]. Knowing this we can assume that the fusion of a K-coil to the C-terminal will lead to the formation of a VLP with a coil presented on the inside.
To obtain the maximal amount of space in the VLP capsule we decided to delete a part of the C-terminal that is normally used for DNA binding and not required for VLP folding. After looking at protein folding predictions it was decided to add a short flexible linker between coil and core protein instead.
Methods
This modification was carried out in 4 PCR steps extending our construct one step at a time.
Results:
After some problems with the last step of the PCR reaction a product with the correct length was obtained (see journal week18). Unfortunately the ligation into a vector and transformation with E. coli did not succeed yet.
References
1. Beterams, G., Böttcher B., & Nassal M. (15. Sept 2000). Packaging of up to 240 subunits of a 17 kDa nuclease into the interior of recombinant hepatitis B virus capsids. FEBS Lett., S. 169-76.
2. Minten, I.J., et al., Controlled encapsulation of multiple proteins in virus capsids. J Am Chem Soc, 2009. 131(49): p. 17771-3.
3. Douglas, T., et al., Protein Engineering of a Viral Cage for Constrained Nanomaterials Synthesis. Adv. Mater., 2002. 14, No. 6. March 18. p. 415-18.
 "
"