Team:USP-UNESP-Brazil/Plasmid Plug n Play/Modeling
From 2012.igem.org
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<p>where <span class="math"><em>M</em></span> represents the concentration of recombinase monomers and <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>1</sub></span> and <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>−1</sub></span> represent the association and dissociation rate constant, respectively. As described in the above equation, there is only two possibilities of changing the concentration of the state <span class="math"><em>S</em></span>: it can increase (positive sign) if a molecule in the state <span class="math"><em>S</em><sub><em>a</em></sub></span> loses the monomer or it can decrease (negative sign) if a monomer binds the DNA.</p> | <p>where <span class="math"><em>M</em></span> represents the concentration of recombinase monomers and <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>1</sub></span> and <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>−1</sub></span> represent the association and dissociation rate constant, respectively. As described in the above equation, there is only two possibilities of changing the concentration of the state <span class="math"><em>S</em></span>: it can increase (positive sign) if a molecule in the state <span class="math"><em>S</em><sub><em>a</em></sub></span> loses the monomer or it can decrease (negative sign) if a monomer binds the DNA.</p> | ||
| + | |||
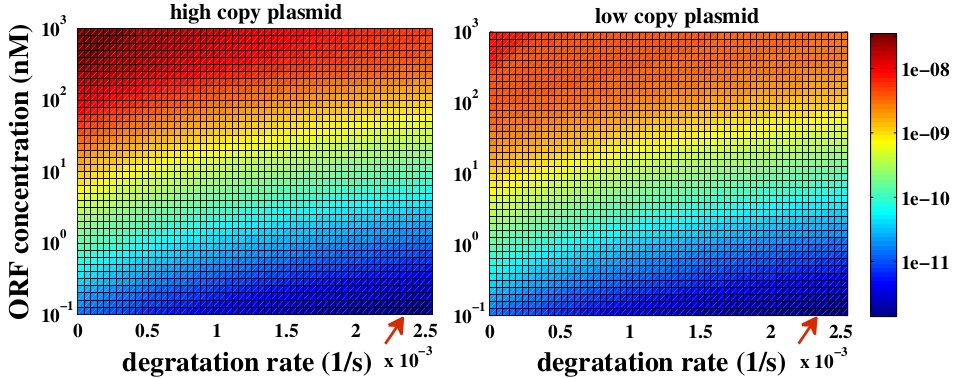
| + | <p>Using gel mobility shift assays it is possible to estimate the affinity of the monomer for their target site, represented by the parameters <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>−1</sub></span> and <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>1</sub></span>, as described by Ringrose et al <span class="citation"></span>. They also estimate, using the same proceeding, the parameters <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>−2</sub></span> and <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>2</sub></span> referring to the association and dissociation rate constant of the monomer for a target site when the neighbor site is already occupied by another monomer. Other parameters (<span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>34</sub></span>, <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>−34</sub></span>, <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>5</sub></span> and <span class="math"><em>k</em><sub>−5</sub></span>) were determined by the authors comparing the simulated and in vitro recombination data, see Table 1. The entire recombination reaction is illustrated in the figure .</p> | ||
{{:Team:USP-UNESP-Brazil/Templates/RImage | image=Table1_pplay.jpeg | caption=Table 1. Association and dissociation rate constants for FLP and Cre binding to DNA, obtained by [1]. | size=600px }} | {{:Team:USP-UNESP-Brazil/Templates/RImage | image=Table1_pplay.jpeg | caption=Table 1. Association and dissociation rate constants for FLP and Cre binding to DNA, obtained by [1]. | size=600px }} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<p>Our experimental design consists in a circularization of the ORF and its insertion in the plug and play plasmid. The whole process is illustrated in figure and the equations of our model are presented in the appendix.</p> | <p>Our experimental design consists in a circularization of the ORF and its insertion in the plug and play plasmid. The whole process is illustrated in figure and the equations of our model are presented in the appendix.</p> | ||
Revision as of 22:18, 21 September 2012
 Introduction
Introduction Project Overview
Project Overview Plasmid Plug&Play
Plasmid Plug&Play Associative Memory
Associative MemoryNetwork
 Extras
Extras
Contents |
Objective
In order to evaluate the feasibility of our project, we developed a mathematical model based on kinetic equations to simulate our experimental design. We considered important to approach this problem mathematically in order to evaluate some issues. Firstly, we evaluated the effect of linear DNA degradation of the ORF when inserted in bacteria after eletroporation. Secondly, we estimated the amount of ORF that should be amplified by PCR in order to optimize the recombination. We compared the results obtained using two recombination protein: CRE and FLP. Finally, we discuss methodologies to improve our design using the standard biological parts.
Model
The model we developed was based on the one proposed by Ringrose et al [1]. The authors introduced a model to describe a excision recombination reaction illustrated in Fig. 1. We used the parameters characterized by the authors in order to simulate our experimental design that consists in the circularization and insertion of the ORF in the plasmid. We also introduced a linear DNA degradation rate in the model in order to be more accurate in simulating in vivo process.
The first step when making a model based on kinetic equations is to determine the states or configurations of the system. In our context, we refer to S the linear ORF without any monomer bound and to Sa the linear ORF with one monomer bound, see Fig. . All four monomer sites (two sites per loxP) have the same affinity for the monomers, resulting in a symmetry in the system in terms of energy of association. Because of that, there is no need of distinguishing the site that the first monomer binds, referred as Sa. To represent the next state - the DNA bound by two monomers - we need to distinguish between two possibilities: there can be one monomer in each loxP, represented by Saa, or two monomers in the same loxP, represented by Sab. It is essential to distinguish these two states because the affinity of the monomers for the target site is different if there is already one monomer bound to the neighbor site. The following states representing the ligation of third and fourth monomer - referred as S3 and S4, respectively - have the same affinity and there is no need of distinguishing them.
The rate of change of each state over time was approached by using kinetic equations. To illustrate this process, we described the kinetic equation which refers to the change of the state S over time:
$\frac{d}{dt}[S] = k_{-1}[S_{a}] - k_{1}[S][M]$
where M represents the concentration of recombinase monomers and k1 and k−1 represent the association and dissociation rate constant, respectively. As described in the above equation, there is only two possibilities of changing the concentration of the state S: it can increase (positive sign) if a molecule in the state Sa loses the monomer or it can decrease (negative sign) if a monomer binds the DNA.
Using gel mobility shift assays it is possible to estimate the affinity of the monomer for their target site, represented by the parameters k−1 and k1, as described by Ringrose et al . They also estimate, using the same proceeding, the parameters k−2 and k2 referring to the association and dissociation rate constant of the monomer for a target site when the neighbor site is already occupied by another monomer. Other parameters (k34, k−34, k5 and k−5) were determined by the authors comparing the simulated and in vitro recombination data, see Table 1. The entire recombination reaction is illustrated in the figure .
Our experimental design consists in a circularization of the ORF and its insertion in the plug and play plasmid. The whole process is illustrated in figure and the equations of our model are presented in the appendix.
Estimation of the variables
In order to simulate our design, we first need to define the initial condition of our system, which consists in estimating the following variables:
[P]0 - initial concentration of the plug and play plasmids inside bacterium.
[M]0 - initial concentration of recombinase monomers.
[S]0 - initial concentration of ORF inside bacterium
To estimate the concentration of the variables, we need the volume of E coli. According to
Vec = 0. 7 * 10 − 15L
. Using this, it is possible to estimate the concentration of one molecule inside the bacterium in molar concentration (
1M = 1mol / 1L = 6 * 1023molecules / L
).
$[1 molecule] = 1 molecule/(0.7 10^{-15} L) = \frac{1}{6 10^{23}
0.7 10^{-15}}M \simeq 10^{-9} M = 1nM$
Plasmid concentration
According to it is expected approximately 100-300 plasmid inside the bacterium (high copy) and approximately 10 plasmids (low copy). So, using the equation we have:
$[P]_0 \simeq 100\hspace{0.1cm} nM (high copy)$
$[P]_0 \simeq 10\hspace{0.1cm} nM (lowcopy)$
Estimating Recombinase Concentration.
To estimate the concentration of recombinase we used a simple model:
$\begin{aligned}
&\frac{d}{dt}[mRNA] = \frac{k_{tran}}{V\hspace{0.1cm}n_{bp}} - k_{dRNA} [mRNA] \nn
&\frac{d}{dt}[Prot] = \frac{k_{trad}[mRNA]}{n_{aa}} - k_{dProt} [Prot] \nn\end{aligned}$
where the constant ktran represents the translation rate, V refers to the volume of bacterium, nbp refers to the number of base pairs of the protein, kdRNA represents the mRNA degradation rate, ktrad represents the traduction rate, naa the number of amino acids of the protein and kdProt the degradation rate of the protein.
The values of these constants were obtained in and are presented below:
$\begin{aligned}
&k_{degRNA} = 1/350 \hspace{0.1cm} (1/sec)\nn
&k_{transcription} = 40 \hspace{0.1cm} (bp/sec) \hspace{1.6cm} for\hspace{0.2cm} T7 \hspace{0.2cm} promoter\nn
&k_{translation} = 15 \hspace{0.1cm} (aa/sec) \nn
&k_{degProt} = 0.0167/60 \hspace{0.1cm} (Prot/sec)\hspace{0.3cm} Average\hspace{0.1cm}protein \hspace{0.1cm}degradation \nn
&n_{bp} = 1032 \hspace{3.6cm} for \hspace{0.1cm} CRE \nn
&n_{aa} = n_{bp}/3 = 344 \hspace{2.4cm} for \hspace{0.1cm} CRE \nn
&n_{bp} = 1119 \hspace{3.6cm} for \hspace{0.1cm} FLP \nn
&n_{aa} = n_{bp}/3 = 373 \hspace{2.4cm} for \hspace{0.1cm} FLP \nn\end{aligned}$
Once we want the concentration of the protein in the equilibrium state, both equations are equal to zero:
$\begin{aligned}
&\frac{d}{dt}[mRNA] = 0 \nn
&\frac{d}{dt}[Prot] = 0 \nn\end{aligned}$
and as a consequence:
$\begin{aligned}
&\frac{k_{tran}}{V.n_{bp}} - k_{dRNA} .[mRNA] = 0 \nn
&\frac{k_{trad}[mRNA]}{n_{bp}/3} - k_{dProt} [Prot] = 0 \nn\end{aligned}$
So, we have for both CRE and FLP recombinases:
$\begin{aligned}
[Prot] = \frac{k_{trad}.k_{tran}}{k_{dProt} .k_{dRNA} .n_{bp}^2/3 } \simeq 2000 \hspace{0.1cm}nM \hspace{0.3cm}(for \hspace{0.1cm}each
\hspace{0.1cm}plug \hspace{0.1cm}and \hspace{0.1cm}play \hspace{0.1cm}plasmid)\end{aligned}$
This result is an estimate of the amount of protein (CRE or FLP) produced by each plug and play plasmid and consequently, the total concentration should be higher than $2000 \hspace{0.1cm}nM$ and dependent of the kind of plug and play plasmid (high or low copy). Therefore, there is no significant change in the results presented here for concentrations higher than 2000 nM. This might occur because there are plenty of recombinase monomers to perform the recombination for concentrations higher than $2000 \hspace{0.1cm}nM$. Because of that, the following results are presented using $2000 \hspace{0.1cm}nM$ of monomer concentration.
ORF concentration
Estimating the ORF concentration inside the bacteria ([S]0) is not simple because we do not know the amount of DNA that will get inside the bacteria during eletroporation. Because of that, we introduced a variable - lets call c - so that [S]0 = c[So] represents the concentration, in average, of genes inside the bacteria. The variable [So] represents the concentration of the genes in the solution before eletroporation and c is a constant such that c ≤ 1. In the most optimist scenario we have c = 1 which means that during eletroporation the concentration of genes inside the bacteria becomes the same as in the solution.
We can relate the variable [So] with the amount of mass of DNA using the following relation:
$[So] = \frac{n_{mols}}{V}$
where
$n_{mols} = \frac{m_{dna}}{n_{bp}\hspace{0.1cm}m_{bp}\hspace{0.1cm}n_{av}}$
where mdna is the mass of DNA, nbp is the number of base pairs of the DNA, mbp is the mass of one base pair, V is the volume of the solution and nav is the Avogadro’s number.
The variables mdna and mpb should have the same unit. For example, if mdna is given in ng we have
$m_{bp} = \frac{650\hspace{0.1cm}10^{9}}{n_{av}} = \frac{650\hspace{0.1cm}10^{9}}{6\hspace{0.1cm}10^{23}} \simeq 10^{-12} \hspace{0.1cm} ng$
For a 800 bp gene and 50 μL of solution we have:
$n_{mols} = \frac{m_{dna}}{800\hspace{0.1cm}6 \hspace{0.1cm}10^{23}.10^{-12}} \simeq m_{dna} \hspace{0.1cm}2 \hspace{0.1cm}10^{-15}$
and
$[So] = \frac{m_{dna}\hspace{0.1cm}2\hspace{0.1cm}10^{-15}}{50\hspace{0.1cm}10^{-6}}
\simeq m_{dna}\hspace{0.1cm} 0.4\hspace{0.1cm} 10^{-10}\hspace{0.1cm} M = 0.04\hspace{0.1cm} m_{dna} \hspace{0.1cm}nM$
This means, for example, that in order to obtain 10 nM of concentration 250 ng of DNA are needed in a solution of 50μL.
Results
Bacteria use enzymes for linear DNA degradation as a defense mechanism against exogenous DNA. Because of that, we first evaluated whether the degradation is an important effect in our design.
To answer this question, a degradation rate of linear DNA (kd) was added to the model. Since we did not find any reference about the value of kd for E. coli we considered kd as a free parameter. Despite of the fact we do not have a good estimative of this parameter, it is well known that linear DNA degradation rate is lower than RNA degradation rate (kdRNA). So, we varied the parameter from zero to values close to kdRNA.
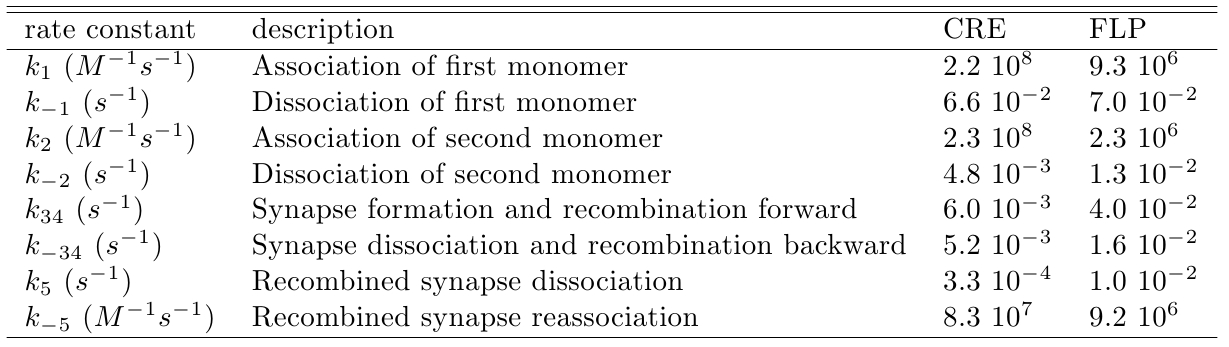
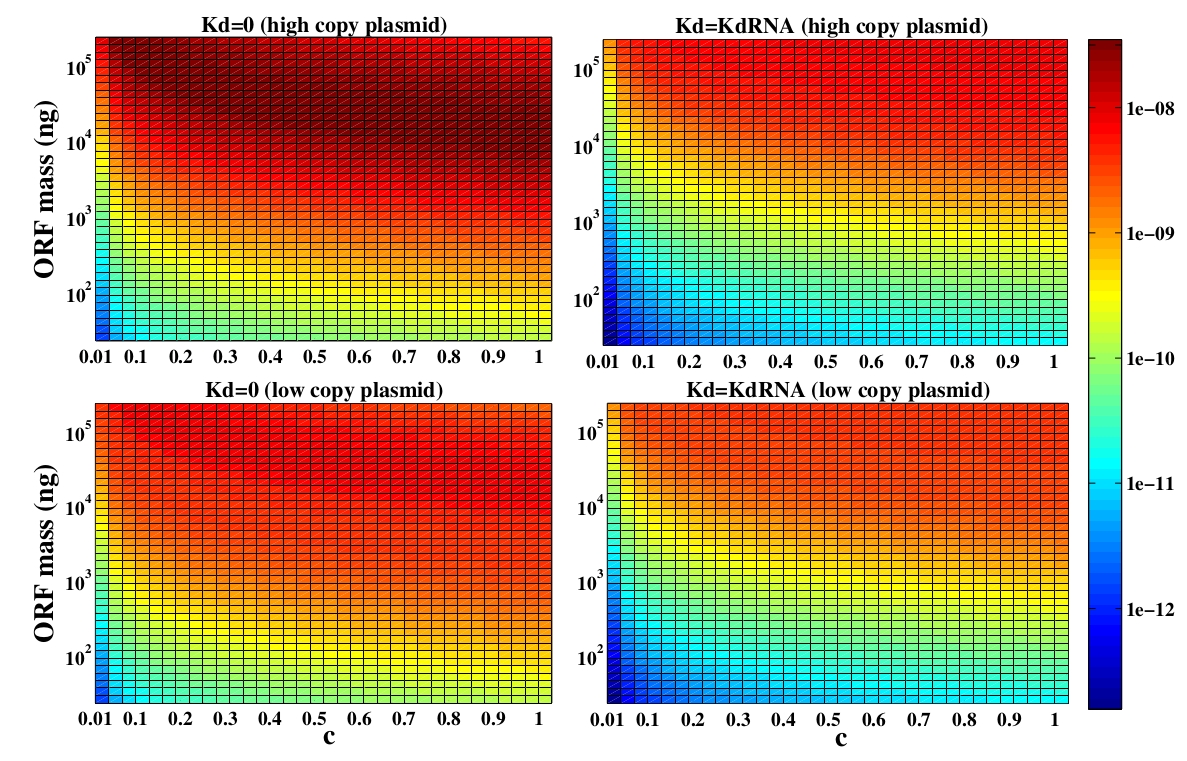
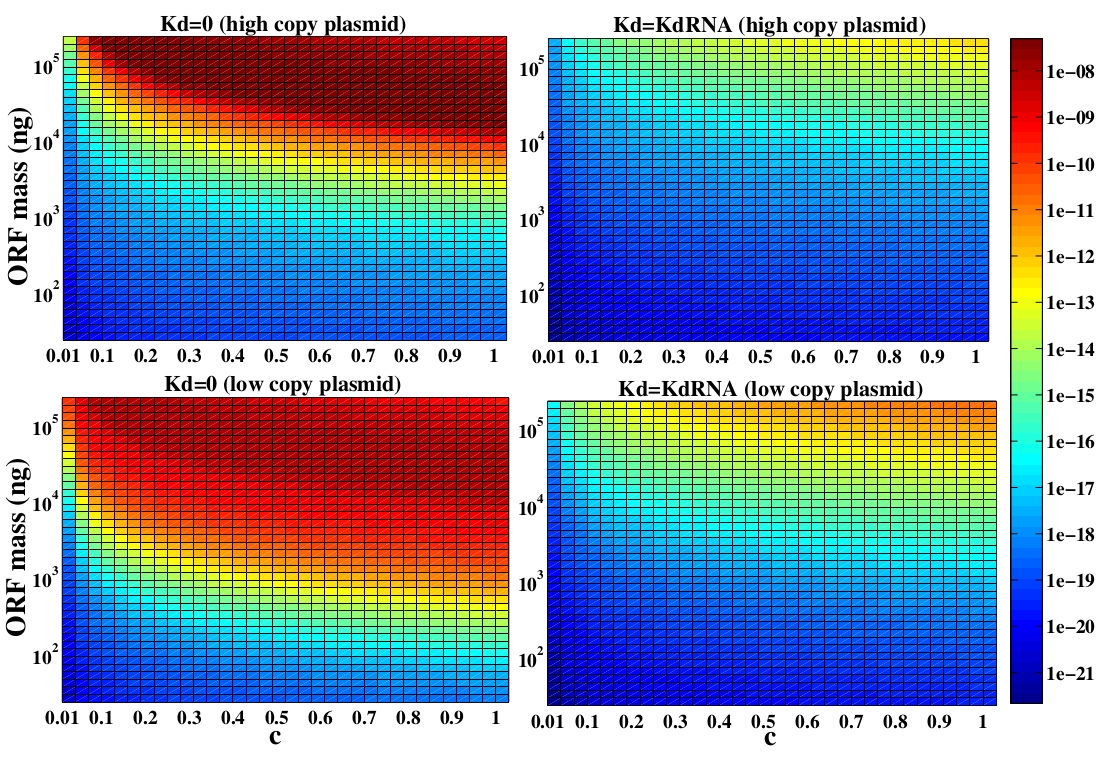
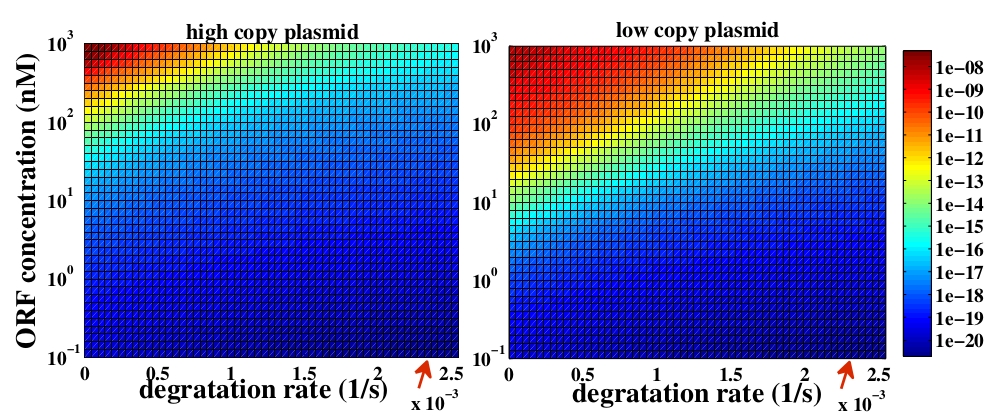
The variable we are interested in optimizing is the concentration of the plug and play plasmids with the ORF inserted. This variable is presented as a function of the degradation rate kd and ORF concentration in figure and , for CRE and FLP, respectively. The value of RNA degradation rate is indicated by a red arrow.
The concentration of plasmids with the ORF inserted as a function of ORF mass in concentration and c (the fraction of ORF concentration that enters in the bacteria) for CRE recombinase. We suppose that eletroporation was done in a solution of 50 μL.
The concentration of plasmids with the ORF inserted as a function of degradation rate and ORF concentration for CRE recombinase. The red arrow indicates the RNA degradation rate kdRNA = 0. 0023 1 / s.
For CRE recombinase, linear DNA degradation do not play a fundamental role in this process and could even be disregarded, figure . This may occur because the circularization of linear DNA by recombinases is faster than the degradation of it. For FLP, however, linear DNA degradation is an important effect and must be taken in account, figure . This occurs because the association of the first and second monomers for CRE is significantly higher than for FLP.
In the following analysis we evaluated the concentration of plasmids with the ORF as a function of the mass of ORF in the solution during eletroporation and the variable c (the fraction of ORF concentration that enters in the bacteria), Figs and . We are interested in concentrations of plug and play plasmids with the ORF inserted higher than 1 nM which means that, in average, there will be at least one plasmid with the ORF in the bacterium, represented by the red region on the Figs. and . According to our results an amount of 10000 ng of DNA might be satisfactory when using CRE. Nevertheless, when using FLP this amount might not be enough and the amount needed is highly dependent of the linear DNA degradation rate.
One possible strategy to improve the recombination without increasing this amount of DNA is to reduce the volume of the solution before eletroporation, which increase the ORF concentration in the solution. Values lower than 10000 ng of DNA may also be satisfactory since the ORF has a antibiotics resistance gene and once the ORF had been inserted the bacteria tend to keep and replicate the plasmid.
Discussion
In order to identify differences between FLP and CRE, we compared the two enzymes in two analyses. Firstly, we evaluated performance of those enzymes inthe Our results point to an obvious choice of CRE-lox recombination system since it is less affected by DNA degradation and improves the insertion of the ORF compared with FLP-FRT system.
An important point In our model we have considered all lox sites as loxP. However, there are mutated loxP and a combination of them can improve the insertion of ORF. The main mutated loxP are lox66 and lox71 We did not introduced the lox66 and lox71 in the model for two main reasons: there are no references about the values of rate constants for altered loxP and we prefer to keep the simplicity and clarity of the model. In order to take these variables in consideration, would be necessary more equations and extra hypothesis.
Although we did not consider the mutated loxP, we can make some considerations about it. The insertion reaction is favored over the excision reaction by roughly fivefold using mutated recombination, when using CRE recombinases . This occur because the double mutated loxP has a very low affinity for the CRE monomers. So, an intuitive conclusion is that the combination we chose may optimize the insertion of the ORF in the plasmid. Nevertheless, this conclusion could be false because the altered loxP demands more time in the circularization step since it has a lower association constant for CRE recombinase. This extra amount of time could be such that the degradation of linear DNA plays a fundamental role in the process. However, as it is illustrated in figure , in the case of CRE recombinases, the degradation of linear DNA is not a fundamental variable and it may not interfere. Because of that, the combination of mutated loxP we have chosen must optimize the amount of ORF inserted in the plasmid.
 "
"