Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus BioBricks
From 2012.igem.org
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
!Derived from | !Derived from | ||
!Reference | !Reference | ||
| - | ! | + | !BioBrick |
|- | |- | ||
!pSB<sub>Bs</sub>1C-<i>lacZ</i> | !pSB<sub>Bs</sub>1C-<i>lacZ</i> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
|pAC6 | |pAC6 | ||
|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11902727 Stülke ''et al''.] | |[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11902727 Stülke ''et al''.] | ||
| - | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823021 BBa_K823021 | + | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823021 BBa_K823021] |
|- | |- | ||
!pSB<sub>Bs</sub>4S | !pSB<sub>Bs</sub>4S | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
|pDG1731 | |pDG1731 | ||
|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8973347 Guérout-Fleury ''et al.''] | |[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8973347 Guérout-Fleury ''et al.''] | ||
| + | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823022 BBa_K823022] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!pSB<sub>Bs</sub>1C | !pSB<sub>Bs</sub>1C | ||
| Line 58: | Line 59: | ||
|pDG1662 | |pDG1662 | ||
|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8973347 Guérout-Fleury ''et al.''] | |[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8973347 Guérout-Fleury ''et al.''] | ||
| + | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823023 BBa_K823023] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!pSB<sub>Bs</sub>4S-P<sub><i>Xyl</i></sub> | !pSB<sub>Bs</sub>4S-P<sub><i>Xyl</i></sub> | ||
| Line 66: | Line 68: | ||
|pXT | |pXT | ||
|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11069659 Derré ''et al.''] | |[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11069659 Derré ''et al.''] | ||
| + | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823024 BBa_K823024] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!pSB<sub>Bs</sub>3C-<i>luxABCDE</i> | !pSB<sub>Bs</sub>3C-<i>luxABCDE</i> | ||
| Line 74: | Line 77: | ||
|pAH328 | |pAH328 | ||
|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20709900 Schmalisch ''et al''.] | |[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20709900 Schmalisch ''et al''.] | ||
| + | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823025 BBa_K823025] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!pSB<sub>Bs</sub>0K-P<sub><i>spac</i></sub> | !pSB<sub>Bs</sub>0K-P<sub><i>spac</i></sub> | ||
| Line 82: | Line 86: | ||
|pDG148 | |pDG148 | ||
|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11728721 Joseph ''et al.''] | |[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11728721 Joseph ''et al.''] | ||
| + | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823026 BBa_K823026] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!pSB<sub>Bs</sub>2E | !pSB<sub>Bs</sub>2E | ||
| Line 90: | Line 95: | ||
|pAX01 | |pAX01 | ||
|[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11274134 Härtl ''et al.''] | |[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11274134 Härtl ''et al.''] | ||
| + | |[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823027 BBa_K823027] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 11 September 2012

The LMU-Munich team is exuberantly happy about the great success at the World Championship Jamboree in Boston. Our project Beadzillus finished 4th and won the prize for the "Best Wiki" (with Slovenia) and "Best New Application Project".
[ more news ]

Bacillus BioBricks
We will create a toolbox of Bacillus BioBricks to contribute to the registry.
This Bacillus BioBrick Box contains Bacillus specific:
Bacillus Vectors
Here is a list of all the vectors we cloned and used. Please note that pMAD is not in a BioBrick standard, but it is a useful tool to knock out genes in Bacillus subtilis.
For the use of our vectors, please see our Protocols page. A general introduction to Bacillus subtilis and its integrative vectors can be found here. All vectors have ampicillin as E. coli resistance and RFP as selection marker.
| Name | E. coli res. | B. subt. res. | Insertion locus | Description | Derived from | Reference | BioBrick |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pSBBs1C-lacZ | Amp | Cam | amyE | with lacZ reporter gene | pAC6 | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11902727 Stülke et al.] | [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823021 BBa_K823021] |
| pSBBs4S | Amp | Spec | thrC | empty | pDG1731 | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8973347 Guérout-Fleury et al.] | [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823022 BBa_K823022] |
| pSBBs1C | Amp | Cam | amyE | empty | pDG1662 | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8973347 Guérout-Fleury et al.] | [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823023 BBa_K823023] |
| pSBBs4S-PXyl | Amp | Spec | thrC | with Xylose-inducible promoter | pXT | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11069659 Derré et al.] | [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823024 BBa_K823024] |
| pSBBs3C-luxABCDE | Amp | Cam | sacA | with luxABCDE reporter cassette | pAH328 | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20709900 Schmalisch et al.] | [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823025 BBa_K823025] |
| pSBBs0K-Pspac | Amp | Kan | replicative | with IPTG inducible promoter | pDG148 | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11728721 Joseph et al.] | [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823026 BBa_K823026] |
| pSBBs2E | Amp | MLS | lacA | empty | pAX01 | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11274134 Härtl et al.] | [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823027 BBa_K823027] |
The number in the vector's name codes for the insertion locus and the following letter for the Bacillus subtilis resistance gene according to the following table:
| Number | Insertion locus | Letter | Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | replicative | C | Chloramphenicol |
| 1 | amyE (amylase) | E | MLS (Erythromycin + Lincomycin) |
| 2 | lacA (laccase ?) | K | Kanamycin |
| 3 | sacA (saccase?) | S | Spectinomycin |
| 4 | thrC (threonine C) |
The concentrations of the antibiotics and the insertion tests can be found in our Protocol section.
The promoters we submit are:
Pveg, PliaI, PliaG, plepA, Pxyl, Pxyl+XylR
We also tested the [http://partsregistry.org/Promoters/Catalog/Anderson Anderson promoter collection] in Bacillus subtilis with pSBBs3C-luxABCDE. The data will be online in our Data section soon.
Furthermore we plan to submit reporter genes optimized for Bacillus subtilis, namely GFP, lacZ, luc and mKate.
Useful for the registry are also 5 tags in Freiburg Standard (cMyc, 10His, Flag, Strep, HA).
More details to come soon.
Bacillus Promoters
Another goal is to produce promoters of Bacillus subtilis in BioBrick mode and to evaluate them. These well-defined promoters will then be part of the Bacillus BioBrickBox which we will send to the registry, but they can also be useful in our project Beadzillus to express our fusion crust proteins on the outside of our spores. Therefore we will use different promoters which are the constitutive promoters from the [http://partsregistry.org/Promoters/Catalog/Anderson Anderson collection] from the Parts Registry, the constitutive promoters PliaG, Pveg and PlepA from B. subtilis as well as the inducible promoter PliaI from B. subtilis. For the characterization of the different promoters we will clone them upstream of reporter genes (lux operon, lacZ) to measure their activity in B. subtilis. Therefore we use e.g. the two reporter vectors from B. subtilis which are also part of the Bacillus BioBrickBox. One of the reporter vectors pSBBs3C-luxABCDE contains the lux operon as a reporter. This is why the activity of the promoter can be measured as luminescence with the plate reader (BioTek) which is a result of the expression of the luciferase. The second reporter vector used for the evaluation of the promoters is pSBBs1C-lacZ which contains the reporter gene lacZ. The promoter activity leads to the production of the enzyme beta-galactosidase which cleaves the substrate ONPG. The product is detectable with the photometer and refers to the promoter activity.
Promoter Evaluation
To get a set of promoters with different strength we chose several promoters. They can be divided in three different groups: the constitutive promoters from the [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J23100 Anderson collection] from the Parts Registry, the constitutive promoters PliaG, Pveg and PlepA from B. subtilis, and the inducible promoter PliaI from B. subtilis. For the characterization of the different promoters, they were all cloned upstream of reporter genes (lux operon, lacZ) to measure their activity in B. subtilis by regarding the gene expression of the reporter gene.
Anderson promoters
The first group of promoters evaluated are the promoters of the Anderson collection which we call Anderson promoters. They have already been measured in Escherichia coli and they all showed a constitutive behavior but with a different strength. In this project, these Anderson promoters were measured in B. subtilis. As they have already been evaluated in E. coli, they were already in the Parts Registry in the vector where they are fused to the Red fluorescent protein (RFP). For evaluation they were cut out of the vector and then first cloned in BioBrick standard in the empty vector pSB1C3 to send them to the registry. In addition, eleven (J23100,J23101, J23102, J23103, J23106, J23107, J23113, J23114, J23115, J23117, J23118) of the nineteen promoters of the Anderson collection were successfully cloned in the reporter vector pSBBs3C-luxABCDE from the BioBrickBox containing the lux operon as a reporter for promoter activity. The gene expression which correlates to the promoter activity leads to the expression of the lux operon with the luciferase. The luminescence which is produced by the luciferase can be measured with the plate reader (BioTek). To measure the activity not only with the lux reporter operon, four promoters were cloned into the reporter vector pSBBs1C-lacZ to do beta-galactosidase assays and then to compare the results of the strength of these promoters in B. subtilis.
Constitutive promoters from B. subtilis
The second group of promoters are constitutive promoters from B. subtilis. We will evaluate the promoters PliaG, Pveg and PlepA. Therefore we will use the reporter vectors pSBBs3C-luxABCDE and pSBBs1C-lacZ to evaluate the promoters with different reporters, the lux operon and the lacZ gene. Therefore the promoters will be amplified from the genome of B. subtilis with primers that conatin the restriction sites of the BioBrick standard. Then these constitutive promoters will be cloned into the empty vector pSB1C3 to send them to the registry as well as the two reporter vectors to evaluate their strength in B. subtilis.
Inducible promoters from B. subtilis
The last group of promoters consists of inducible promoters of B. subtilis e.g. PliaI. They are useful to decide when to turn on gene expression because these promoters need an inducer to start transcription. PliaI can be induced by antibiotics which interact with the lipidII cycle, e.g. bacitracin. In this project this promoter is evaluated like the constitutive promoters with the reporter vector pSBBs3C-luxABCDE which contains the lux operon as a reporter and with the vector pSBBs1C-lacZ which contains the lacZ reporter gene. Therefore the promoters will be amplified from the genome of B. subtilis with primers that contain the restriction sites of the BioBrick standard. Then these inducible promoters will be cloned into the empty vector pSB1C3 to send them to the registry as well as the two reporter vectors to evaluate their strength in B. subtilis. To turn the promoter on we have to add an inducer.
Bacillus Reporters
We designed some reporters that are commonly used in B. subtilis or are codon optimized versions of popular reporter genes. All reporters have a modified iGEM Freiburg standard ([http://partsregistry.org/Help:Assembly_standard_25 RCF 25]) pre- and suffix for assembly of in-frame fusion proteins. Our prefix also includes the B. subitlis optimized RBS.
prefix: GAATTCCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATAAGGAGGAACTACTATGGCCGGC
suffix: ACCGGTTAATACTAGTAGCGGCCGCTGCAGT
- GFP
We took a gfp derivate of the Bacillus subtilis plasmids pGFPamy and added the BioBrick compatiple pre- and suffix of the Freiburg standard (Assembly 25).
- mKate
We synthesized this rfp derivate with a codon-optimized version for the use in B. subtilis with pre- and suffix of the Freiburg standard
- LacZ
This lacZ gene is derived from the Bacillus reporter vector pAC6. It is constructed in the Freiburg Standard (Assembly 25) for in-frame fusion proteins. It also includes a Shine-Dalgarno Sequence optimized for Bacillus subtilis translation.
BioBrick Name: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823019 BBa_K823019]
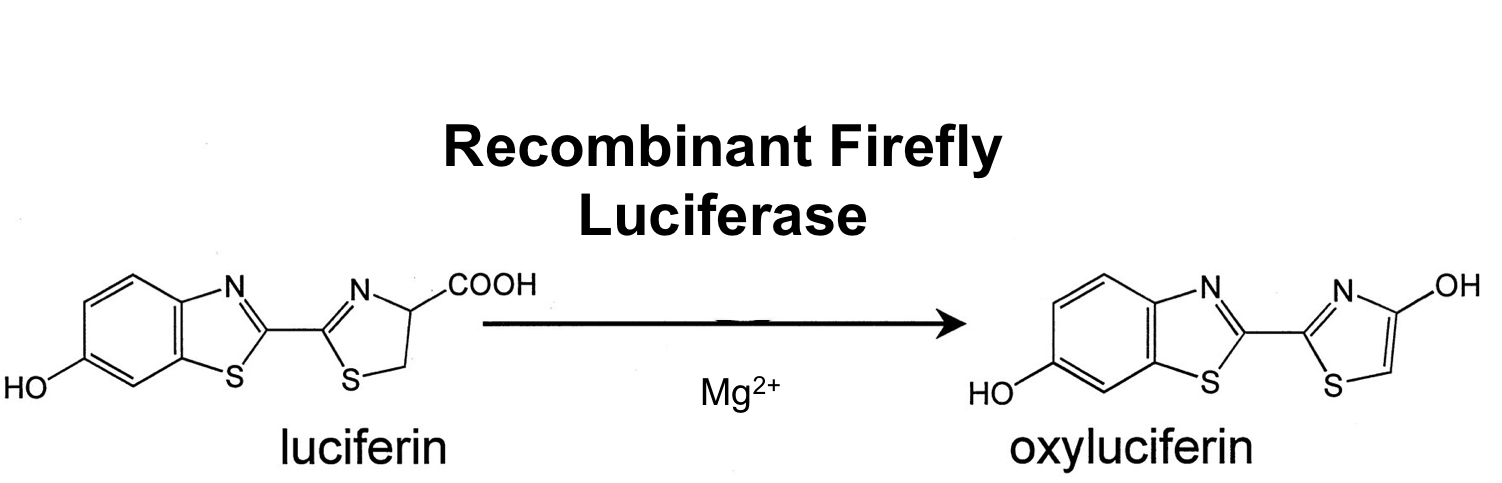
- luc
We synthesized this luciferase for luminescence assays with luciferin as substrate.
Project Navigation
| +--+--+--+--+--+--+-- | +--+--+--+--+-- | +--+--+--+--+--+-- | +--+--+--+--+--+-- |

Bacillus BioBrickBOX |

SporeCoat FusionProteins |

Germination STOP |
 "
"