Team:SJTU-BioX-Shanghai/Project/project1.1
From 2012.igem.org
AleAlejandro (Talk | contribs) (→Membrane Localization) |
AleAlejandro (Talk | contribs) (→Membrane Localization Test) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{Template:12SJTU_part_summary_head}} | {{Template:12SJTU_part_summary_head}} | ||
| - | To make membrane into a scaffold, we must first make sure that our device is directed to inner membrane of ''E.coli''. To achieve this goal, we used native inner membrane protein of ''E.coli'' and a well-studied signaling sequence as basic components to direct fusion protein onto inner membrane. To | + | To make membrane into a scaffold, we must first make sure that our device is directed to inner membrane of ''E.coli''. To achieve this goal, we used native inner membrane protein of ''E.coli'' and a well-studied signaling sequence as basic components to direct fusion protein onto inner membrane. To justify this construction strategy, we constructed a novel testing fusion protein and conducted two tests to determine the localization of the engineered membrane protein. |
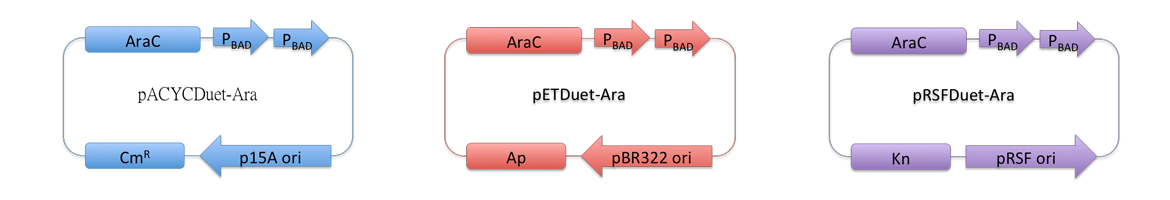
To express multiple large proteins at the same time in ''E.coli'', we reconstructed 3 compatible plasmids with araBAD promoter. | To express multiple large proteins at the same time in ''E.coli'', we reconstructed 3 compatible plasmids with araBAD promoter. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
To construct membrane assemblies, we must make sure that our device is directed to inner membrane of ''E.coli''. | To construct membrane assemblies, we must make sure that our device is directed to inner membrane of ''E.coli''. | ||
| - | The first step is to choose an membrane anchor upon which other components could be built. To avoid toxicity caused by foreign membrane proteins, we chose ''phosphatidylglycerol:: prolipoprotein diacylglyceryl transferase'' (Lgt) as | + | The first step is to choose an membrane anchor upon which other components could be built. To avoid toxicity caused by foreign membrane proteins, we chose ''phosphatidylglycerol:: prolipoprotein diacylglyceryl transferase'' (Lgt) as core component of fusion protein. Lgt is an inner membrane protein of ''E.coli'' with seven transmembrane segments and has been successfully overexpressed in ''E. coli'' without causing harm to cells. |
| - | SsDsbA is the signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent signaling sequence of DsbA. SsDsbA-tagged proteins are exported to the periplasm through the SRP pathway. With ssDsbA fused to the N-terminus, | + | SsDsbA is the signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent signaling sequence of DsbA. SsDsbA-tagged proteins are exported to the periplasm through the SRP pathway. With ssDsbA fused to the N-terminus, fusion proteins with Lgt are expected to be anchored onto inner membrane of ''E.coli'' (''Fig.2'' ). |
Flexible linker FL3 is introduced between each crucial protein domain to ensure the proper function of them. | Flexible linker FL3 is introduced between each crucial protein domain to ensure the proper function of them. | ||
| - | [[Image:12SJTU_proteinconstruction.jpg|thumb|700px|center|''Fig.2'' : Construction | + | [[Image:12SJTU_proteinconstruction.jpg|thumb|700px|center|''Fig.2'' : Construction details of membrane assemblies]] |
==Membrane Localization Test== | ==Membrane Localization Test== | ||
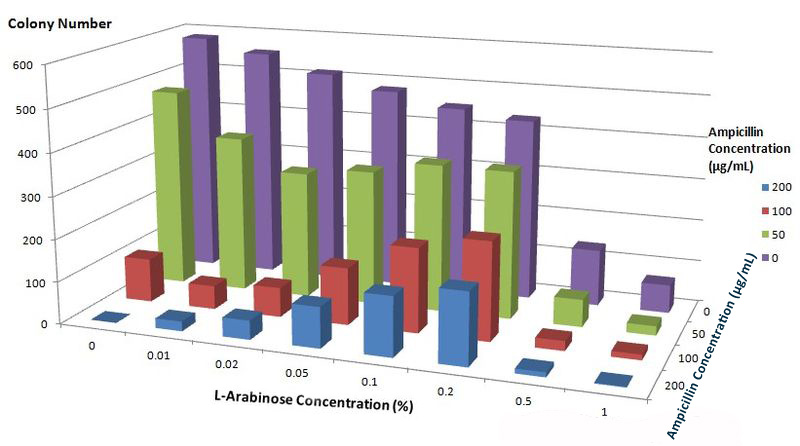
| - | To justify the localization ability of fusion membrane proteins mentioned above, we constructed a novel fusion protein called '''BlaLG'''. β-lactamase is fused to the N-terminus of Lgt and GFP is fused to the C-terminus of Lgt. The fusion protein in under control of araBAD promoter (''Fig.3'' ). | + | To justify the localization ability of fusion membrane proteins mentioned above, we constructed a novel fusion protein called '''BlaLG'''([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K771401 BBa_K771401]). β-lactamase is fused to the N-terminus of Lgt and GFP is fused to the C-terminus of Lgt. The fusion protein in under control of araBAD promoter (''Fig.3'' ). |
[[Image:12SJTU-project1-1.png|thumb|700px|center|''Fig.3'' : Details of fusion protein BlaLG for membrane localization]] | [[Image:12SJTU-project1-1.png|thumb|700px|center|''Fig.3'' : Details of fusion protein BlaLG for membrane localization]] | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
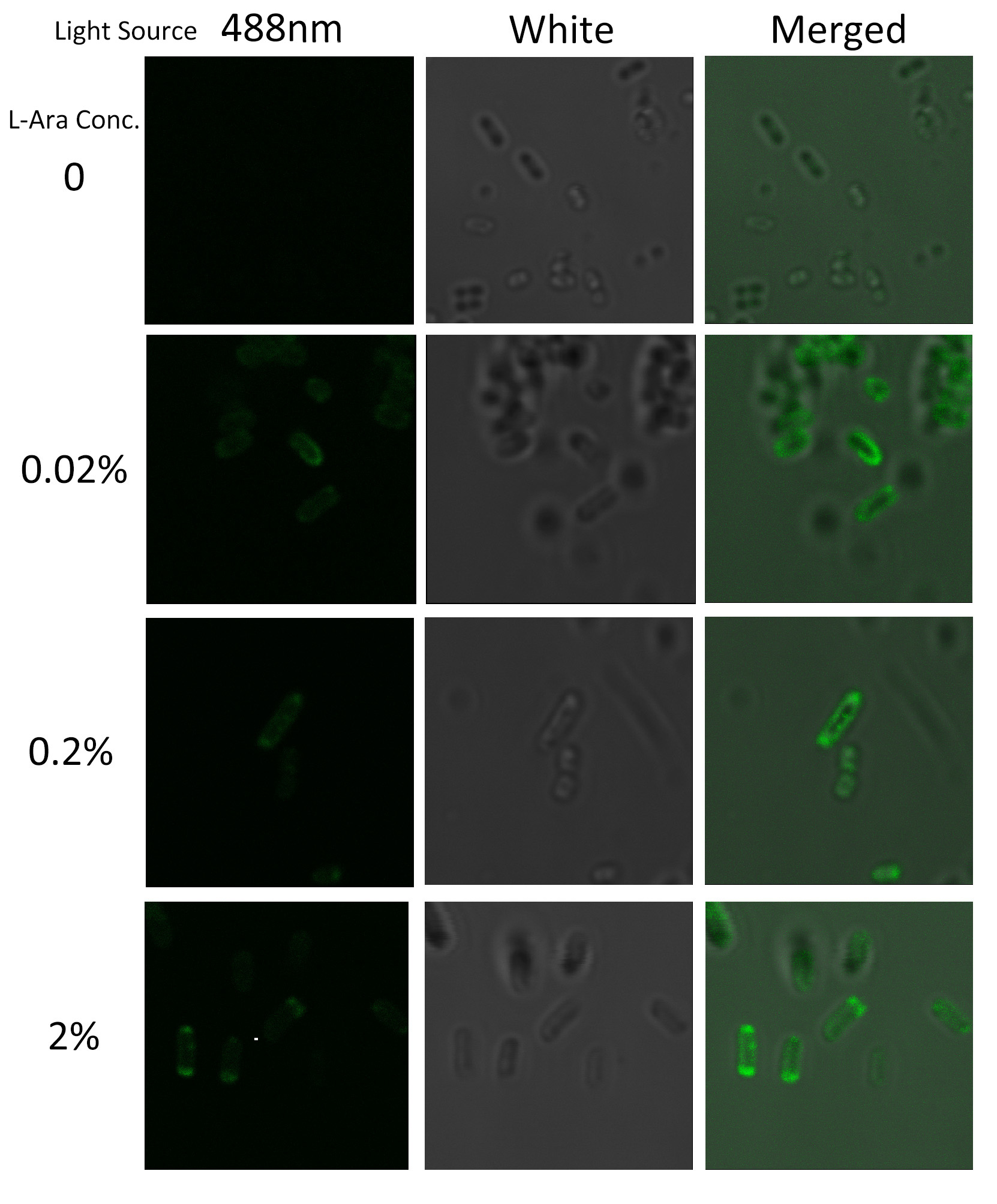
Under laser confocal microscope, we can observe the location of green fluorescence, thus to confirm the exact subcellular localization of the fusion protein BlaLG. | Under laser confocal microscope, we can observe the location of green fluorescence, thus to confirm the exact subcellular localization of the fusion protein BlaLG. | ||
[[Image:12SJTU_MLGFP.jpg|thumb|500px|center|''Fig.4'' :Bacteria carrying BlaLG induced at different concentration of L-arabinose.]] | [[Image:12SJTU_MLGFP.jpg|thumb|500px|center|''Fig.4'' :Bacteria carrying BlaLG induced at different concentration of L-arabinose.]] | ||
| + | |||
It is observed that green fluorescence intensity of ''E.coli'' margin is higher than that of cytoplasm. ''Fig.4'' proves that BlaLG has been localized to membrane. | It is observed that green fluorescence intensity of ''E.coli'' margin is higher than that of cytoplasm. ''Fig.4'' proves that BlaLG has been localized to membrane. | ||
Latest revision as of 02:57, 27 October 2012
| ||
|
 "
"