Team:LMU-Munich/Data/differentiation
From 2012.igem.org
Franzi.Duerr (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- Include the next line at the beginning of every page --> | <!-- Include the next line at the beginning of every page --> | ||
| - | {{:Team:LMU-Munich/Templates/Page Header|File: | + | {{:Team:LMU-Munich/Templates/Page Header|File:Bacillus in urban culture.jpg}} |
| + | [[File:Bacillus introduction banner.resized WORDS.JPG|620px|link=]] | ||
| - | + | [[File:Bacilluss_Intro.png|100px|right|link=]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[File:Bacilluss_Intro.png|100px|right]] | + | |
| - | + | ||
===Differentiation=== | ===Differentiation=== | ||
| - | + | <br> | |
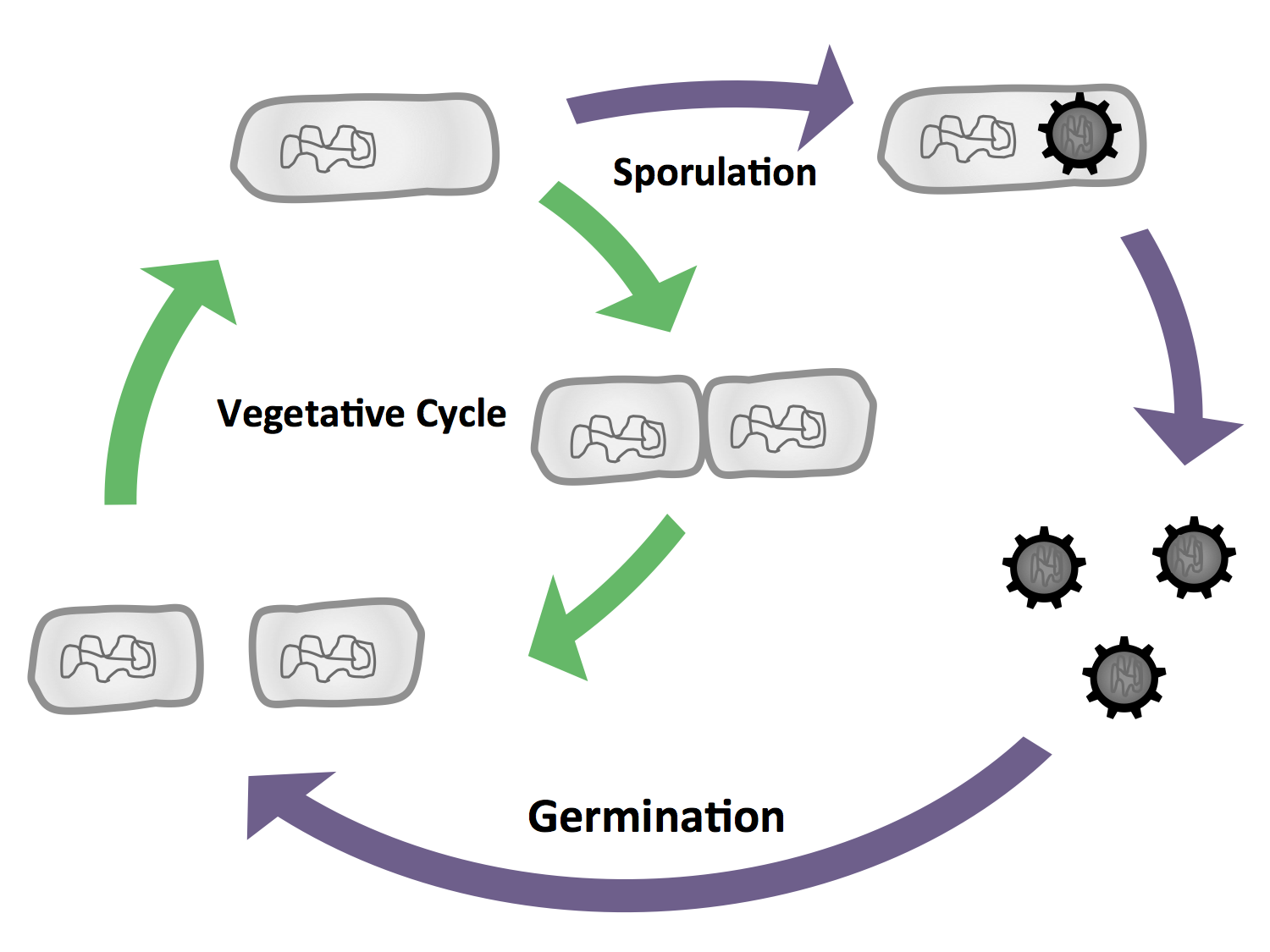
| - | <p align="justify">''B. subtilis'' is able to differentiate into cells with different morphologies and functions ( | + | <p align="justify">''B. subtilis'' is able to differentiate into cells with different morphologies and functions (Fig. 3). The most characteristic form is the endospore, which is produced under nutrient starvation. In our project, we exploited the production of endospores. Because they are extremely stable, spores are perfect vehicles for the display of functional fusion proteins on their surface as illustrated by our [https://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Spore_Coat_Proteins '''Sporo'''bead] module. |
<br> | <br> | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 23: | ||
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="95%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="95%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | ||
|style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | |style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | ||
| - | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify">Fig. 3: The vegetative cycle is very similiar to | + | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify">Fig. 3: The vegetative cycle is very similiar to that of ''E. coli.'' However, in the event of a stressor such as starvation, the cells enter sporulation, where they first undergo a polar cell division, followed by the formation of the endospore. If the environmental conditions are suitable again, the spore will then germinate and reenter the vegetative cycle.</p></font> |
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 36: | Line 34: | ||
| + | {| width="100%" cellpadding="20" | ||
| + | | [[File:LMU Arrow purple BACK.png|center|80px|link=Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus_Introduction]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| - | |||
Latest revision as of 10:49, 26 October 2012

The LMU-Munich team is exuberantly happy about the great success at the World Championship Jamboree in Boston. Our project Beadzillus finished 4th and won the prize for the "Best Wiki" (with Slovenia) and "Best New Application Project".
[ more news ]


Differentiation
B. subtilis is able to differentiate into cells with different morphologies and functions (Fig. 3). The most characteristic form is the endospore, which is produced under nutrient starvation. In our project, we exploited the production of endospores. Because they are extremely stable, spores are perfect vehicles for the display of functional fusion proteins on their surface as illustrated by our Sporobead module.
|
 "
"