Team:Freiburg/Project/Experiments
From 2012.igem.org
| (41 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Team:Freiburg}} | {{Template:Team:Freiburg}} | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| - | = | + | = ''In vitro'' testing = |
---- | ---- | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <br> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== The Toolkit == | == The Toolkit == | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | <br> | + | <br>Admittedly, our GATE assembly kit is a little larger than the kit published from the Zhang group in Nature this year<sup>1</sup> (the latter comprises 78 parts). But considering that future iGEM teams can easily combine the parts to form more than 67 million different effectors, we believe that it was worth the effort. Now, to get from the toolbox to the finished TAL effector, you only need a few components: six direpeats, one effector backbone plasmid, two enzymes and one buffer. If you mix these components and incubate in your thermocycler for 2.5 hours, you get your custom TAL effector. To put this in perspective: The average turnaround time for TALE construction with conventional kits is about two weeks! In the following sections, we want to show you the efficiency of our GATE assembly platform.<br> |
| - | The creation of a toolkit with 96 different parts not only means a lot of labwork but also a lot of organisational tasks, sequencing and analysis. We don't want to bore you with the 96 sequences of our finished | + | The creation of a toolkit with 96 different parts not only means a lot of labwork but also a lot of organisational tasks, sequencing and analysis. We don't want to bore you with the 96 sequences of our finished BioBricks, but we want to give you one example of a finished BioBrick and highlight some of the interesting and important strips in its sequence. If you are interested in the other sequences, just have a look at our [[Team:Freiburg/Parts|parts section]] or go to the [http://partsregistry.org Registry of Standard Biological Parts]. |
| Line 40: | Line 16: | ||
| - | In this sequence of our | + | In this sequence of our BioBrick AA1, the main features of all our BioBricks are highlighted. As pointed out in the [[Team:Freiburg/Project/Golden#GGC|Golden Gate Standard section]] of our project description, all direpeat plasmids are submitted in the Golden Gate Standard, that was developed by us and which is fully compatible with existing iGEM standards. In yellow, you can see the direpeat gene fragment itself, the green parts are iGEM restriction sites (a requirement for all BioBricks), the sequence written in red is part of the psb1C3 vector, the blue sequences are recognition sites for BsmB1 and the red boxes are the cutting sites of BsmB1. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Varying Cycle number of GATE assembly has limited effect == | == Varying Cycle number of GATE assembly has limited effect == | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | Golden Gate protocols published so far for multistep TALE assembly differ significantly in the number of digestion-ligation cycles performed. To | + | Golden Gate protocols published so far for multistep TALE assembly differ significantly in the number of digestion-ligation cycles performed. To assess, whether the cycle number significantly affects outcome, we performed 4 different GATE assemblies, each with three different cycle numbers (50, 25 and 13 cycles). We did not see significant differences in the number of colonies for the three cycle numbers. Consequently, from that point on, we performed GATE assembly with only 13 cycles (which only take approximately 2.5 hours instead of 8.5 hours for 50 cycles).<br><br> |
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|[[Image:colonies.png|400px|no frame|link=]] | |[[Image:colonies.png|400px|no frame|link=]] | ||
| Line 61: | Line 31: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| - | <div align="justify">To assess if the direpeats have indeed been successfully cloned into our expression vector, we have accomplished colony PCR with a variety of samples. To this end, we have designed primers which bind to both ends of the direpeat region and thus amplify the | + | <div align="justify">To assess if the direpeats have indeed been successfully cloned into our expression vector, we have accomplished colony PCR with a variety of samples. To this end, we have designed primers which bind to both ends of the direpeat region and thus amplify the direpeat array of our TAL protein. |
The original vector contains a kill cassette which kills bacteria unless it is replaced by the direpeats during the Golden Gate Cloning reaction. | The original vector contains a kill cassette which kills bacteria unless it is replaced by the direpeats during the Golden Gate Cloning reaction. | ||
| - | This cassette will also be amplified by the designed primers. A distinction between the amplification of the kill cassette and that of direpeats can be made upon the amplicon length: if the kill cassette is amplified, the resulting amplicon will contain 1527bp, while direpeat amplification will produce amplicons of 1276bp length. The difference between these two amplicons is 251bp, and can be detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. | + | This cassette will also be amplified by the designed primers. A distinction between the amplification of the kill cassette and that of direpeats can be made upon the amplicon length: if the kill cassette is amplified, the resulting amplicon will contain 1527bp, while direpeat amplification will produce amplicons of 1276bp length. The difference between these two amplicons is 251bp, and can be detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. |
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/0/04/Direpeat_amp.jpg" align="right" width="400px" hspace="20" vspace="20" alt="Direpeat amplification by colony PCR"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/0/04/Direpeat_amp.jpg" align="right" width="400px" hspace="20" vspace="20" alt="Direpeat amplification by colony PCR"/> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 39: | ||
The figure clearly demonstrates the difference in size between the amplicons of negative control (kill cassette still in the vector) and positive (direpeats have replaced the cassette) samples. While lane 2 shows a negative result with a single band of bigger size, all the other samples yielded amplicons of smaller length and thus are considered as positive due to amplification of direpeats. | The figure clearly demonstrates the difference in size between the amplicons of negative control (kill cassette still in the vector) and positive (direpeats have replaced the cassette) samples. While lane 2 shows a negative result with a single band of bigger size, all the other samples yielded amplicons of smaller length and thus are considered as positive due to amplification of direpeats. | ||
Nevertheless, it is obvious that the colony PCR did not produce one single product when amplifying the direpeats, but rather a smear consisting of amplicons with varying lengths. | Nevertheless, it is obvious that the colony PCR did not produce one single product when amplifying the direpeats, but rather a smear consisting of amplicons with varying lengths. | ||
| - | This effect is due to numerous homologies within the direpeats and has previously been described by Briggs et al.<sup> | + | This effect is due to numerous homologies within the direpeats and has previously been described by Briggs et al.<sup>2</sup> . |
| - | To eliminate those homologies to the greatest extent possible, we changed codon usage within our direpeats. Nevertheless, as the results of our colony PCR demonstrate, there is still a profound amount of homologies left, which imposes difficulties on the amplification of the | + | To eliminate those homologies to the greatest extent possible, we changed codon usage within our direpeats. Nevertheless, as the results of our colony PCR demonstrate, there is still a profound amount of homologies left, which imposes difficulties on the amplification of the direpeat array by PCR and instead results in a smear. |
| - | Thus, the existence of this smear indicates the presence of direpeats within the expression vector. Moreover, the light bands at 1276 bp indicates, that the right number of direpeats have been inserted into the vector. We performed 30 colony PCRs from colonies of different GATE assemblies and had no negative results (but in some cases, we could not determine the hight of the light band). Since positive results in colony PCR of TALEs do not exclude wrong order of direpeats, we sequenced | + | Thus, the existence of this smear indicates the presence of direpeats within the expression vector. Moreover, the light bands at 1276 bp indicates, that the right number of direpeats have been inserted into the vector. We performed 30 colony PCRs from colonies of different GATE assemblies and had no negative results (but in some cases, we could not determine the hight of the light band). Since positive results in colony PCR of TALEs do not exclude wrong order of direpeats, we sequenced 33 clones of different GATE assemblies and analyzed the results: In 32 of the 33 clones, sequencing results entirely matched the right sequence. So the efficiency of GATE assembly is approximately 97 %. |
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | == | + | = ''In vivo'' testing = |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | == Gene activation == | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| - | < | + | <p><br> |
| - | < | + | |
| - | <img src=" | + | <div align="justify">To show the functionality of our TAL protein as well as the impact of the VP 64 transcription factor fusion protein, we used a TAL-VP64 fusion construct targeting a minimal promotor coupled with the secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP). The product of the reporter gene SEAP is - as the name tells - a phosphatase that is secreted by the cells into the surrounding media. The existence of SEAP and therefore the activity of the promotor can be measured by the addition of para-Nitrophenylphosphate (pNPP). The SEAP enzyme catalyzes the reaction from pNPP to para-Nitrophenol, this new product absorbs light at 405 nm and can be measured via photometry. |
| + | This reporter system gives us a couple of advantages over standard EGFP or luciferase systems. First of all, the SEAP is secreted into the cell culture media, therefore we don't have to lyse our cells for measuring, but just take a sample from the supernatant. <br><img src="http://imageshack.us/a/img189/6140/seapplasmid.png" align="right" padding:0px width="450px" hspace="20"/><br> We are also able to measure one culture multiple times, e.g. at two different points in time. Another advantage is the measurement via photometry which makes the samples quantitively comparable. Interestingly, we did not have to clone a TALE binding site upstream of the minimal promoter (which would be required for other DNA binding proteins) but simply produced a TALE that specifically bound to the given sequence. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <img src="http://imageshack.us/a/img268/53/exp1design2.png" align="left" padding:0px width="250px" hspace="20" /> | ||
| + | The experiment was done with four different transfections, either no plasmid, only the TAL vector, only the SEAP plasmid or a cotransfection of both plasmids. The cells were seeded on a twelve well plate the day before in 500µl culture media per well. The transfection was done with CaCl2 after a cell culture course protocol written by the lab of Professor Weber. | ||
| - | In theory, the TAL domain should bring the fused VP64 domain in close proximity to the minimal promotor to activate the transcription of the repoter gene SEAP. The phosphatase is secreted an acummulates in the cell culture media. After 24 and 48 hours, we took samples from the media, stored them at -20°C, and subjected them | + | <div align="justify">To show that our TAL effectors are actually working, we used our completed toolkit to produce a TAL protein which is fused to a VP64 transcription factor. With this TAL-TF construct we targeted a sequence upstream of a minimal promotor that controls transcription of the enzyme secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP). In theory, the TAL domain should bring the fused VP64 domain in close proximity to the minimal promotor to activate the transcription of the repoter gene SEAP. The phosphatase is secreted an acummulates in the cell culture media. After 24 and 48 hours, we took samples from the media, stored them at -20°C, and subjected them to photometric analysis.<br> |
| - | <br>< | + | |
| - | As it is observable in the graph, co-transfection of cells with TAL and SEAP plasmids (++) yielded a high increase in SEAP activity, compared to the control samples. The graph shows the average value of three biological replicates with its standard deviation. We further performed a t-test (Table) to prove if our experiment is statistically significant | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/8/84/IGEMres4.png" width="400px" hspace="20" vspace="20" alt="SEAP essay using the TAL transcription factor plasmid targeting a minimal promotor coupled to a SEAP reporter gene" style="margin-left:170px"/> |
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | As it is observable in the graph, co-transfection of cells with TAL and SEAP plasmids(++) yielded a high increase in SEAP activity, compared to the control samples. Also the control experiment with a TAL-VP64 targeting a random sequence shows the specificity of our system. The graph shows the average value of three biological replicates with its standard deviation. We further performed a t-test (Table) to prove if our experiment is statistically significant. As it is clearly observable, the p-values range below a value of 0,05, which indicates that our TAL transcription factor is able to elevate the transcription of the SEAP gene in a statistically significant manner. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/ | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/a/a6/Igemres-p.png" width="400px" hspace="20" vspace="20" alt="SEAP assay using the TAL transcription factor plasmid targeting a minimal promotor coupled to a SEAP reporter gene" style="margin-left:170px"/> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | After addition of pNPP, the substrate of SEAP, the activity of SEAP was measured over | + | After addition of pNPP, the substrate of SEAP, the activity of SEAP was measured over time. In the next image, the results of the first nine minutes of this measurement are shown. After this time, the OD of the double transfection (++) rose too high to be measured by our photometer. As it is clearly visible, the sample with the double transfection shows a profound increase in the OD. This points to the fact that great amounts of SEAP have been secreted into the cell culture media due to elevated gene expression. In the other samples almost no SEAP activity was measureable. The sample transfected with only the SEAP plasmid showed the highest OD but this effect was not statistically significant (p-value:0,25/0,51). |
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | In the samples | + | In the samples that had been taken 48h after double transfection, the same effects could be demonstrated. |
<br> | <br> | ||
Furthermore, we reapeated the same experiment for a second time. The corresponding data can be viewed here: <html><div style=text-indent:0px><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/9/9c/Second_Essay.pdf">Second Experiment.</a> | Furthermore, we reapeated the same experiment for a second time. The corresponding data can be viewed here: <html><div style=text-indent:0px><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/9/9c/Second_Essay.pdf">Second Experiment.</a> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/5/55/TALTF-SEAP-TIME.png" align="middle" width="500px" hspace="20" vspace="20" alt="SEAP assay using the TAL transcription factor plasmid targeting a minimal promotor coupled to a SEAP reporter gene" style="margin-left:120px"/> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/5/55/TALTF-SEAP-TIME.png" align="middle" width="500px" hspace="20" vspace="20" alt="SEAP assay using the TAL transcription factor plasmid targeting a minimal promotor coupled to a SEAP reporter gene" style="margin-left:120px"/><br><br></html> |
| + | |||
| + | == Precise Gene Knockout == | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <p><br> | ||
| + | TALENs are a very powerful tool for efficient gene knockout. In order to prove that our TALEN construct was functional, we decided to simply knock out a destabilized GFP gene on a plasmid, which we co-transfected with our TALEN plasmids into HEK cells. Moreover, we also transfected our cells with an mCherry vector to normalize for transfection efficiency. TAL constructs were designed to bind to opposite strands of the target plasmid in a way that the FokI monomers of each TALEN construct would be able to dimerize in the spacer region between the TALEN binding sites. 48 hours after transfection, gene knock-out efficiency was evaluated by FACS analysis. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| + | [[Image:xx.png|500px|center|link=]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br> | ||
== Reference == | == Reference == | ||
| - | 1. Briggs, A. W. et al. Iterative capped assembly: rapid and scalable synthesis of repeat-module DNA such as TAL effectors from individual monomers. ''Nucl Acids Res'' (2012).doi:10.1093/nar/gks624 | + | 1. Sanjana, N. E. et al. A transcription activator-like effector toolbox for genome engineering. Nature Protocols 7, 171–192 (2012).<br> |
| + | 2. Briggs, A. W. et al. Iterative capped assembly: rapid and scalable synthesis of repeat-module DNA such as TAL effectors from individual monomers. ''Nucl Acids Res'' (2012).doi:10.1093/nar/gks624 | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
[[#top|Back to top]] | [[#top|Back to top]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:30, 10 November 2012
In vitro testing
The Toolkit
Admittedly, our GATE assembly kit is a little larger than the kit published from the Zhang group in Nature this year1 (the latter comprises 78 parts). But considering that future iGEM teams can easily combine the parts to form more than 67 million different effectors, we believe that it was worth the effort. Now, to get from the toolbox to the finished TAL effector, you only need a few components: six direpeats, one effector backbone plasmid, two enzymes and one buffer. If you mix these components and incubate in your thermocycler for 2.5 hours, you get your custom TAL effector. To put this in perspective: The average turnaround time for TALE construction with conventional kits is about two weeks! In the following sections, we want to show you the efficiency of our GATE assembly platform.
The creation of a toolkit with 96 different parts not only means a lot of labwork but also a lot of organisational tasks, sequencing and analysis. We don't want to bore you with the 96 sequences of our finished BioBricks, but we want to give you one example of a finished BioBrick and highlight some of the interesting and important strips in its sequence. If you are interested in the other sequences, just have a look at our parts section or go to the [http://partsregistry.org Registry of Standard Biological Parts].

|
In this sequence of our BioBrick AA1, the main features of all our BioBricks are highlighted. As pointed out in the Golden Gate Standard section of our project description, all direpeat plasmids are submitted in the Golden Gate Standard, that was developed by us and which is fully compatible with existing iGEM standards. In yellow, you can see the direpeat gene fragment itself, the green parts are iGEM restriction sites (a requirement for all BioBricks), the sequence written in red is part of the psb1C3 vector, the blue sequences are recognition sites for BsmB1 and the red boxes are the cutting sites of BsmB1.
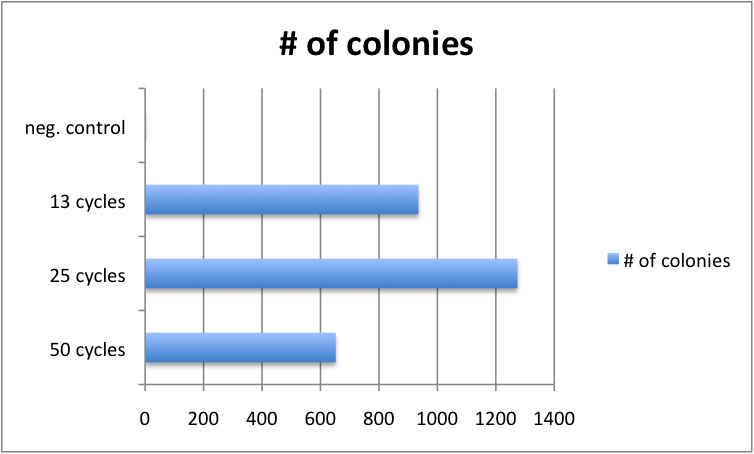
Varying Cycle number of GATE assembly has limited effect
Golden Gate protocols published so far for multistep TALE assembly differ significantly in the number of digestion-ligation cycles performed. To assess, whether the cycle number significantly affects outcome, we performed 4 different GATE assemblies, each with three different cycle numbers (50, 25 and 13 cycles). We did not see significant differences in the number of colonies for the three cycle numbers. Consequently, from that point on, we performed GATE assembly with only 13 cycles (which only take approximately 2.5 hours instead of 8.5 hours for 50 cycles).
|
Direpeat Amplification by Colony PCR
 The figure clearly demonstrates the difference in size between the amplicons of negative control (kill cassette still in the vector) and positive (direpeats have replaced the cassette) samples. While lane 2 shows a negative result with a single band of bigger size, all the other samples yielded amplicons of smaller length and thus are considered as positive due to amplification of direpeats.
Nevertheless, it is obvious that the colony PCR did not produce one single product when amplifying the direpeats, but rather a smear consisting of amplicons with varying lengths.
This effect is due to numerous homologies within the direpeats and has previously been described by Briggs et al.2 .
To eliminate those homologies to the greatest extent possible, we changed codon usage within our direpeats. Nevertheless, as the results of our colony PCR demonstrate, there is still a profound amount of homologies left, which imposes difficulties on the amplification of the direpeat array by PCR and instead results in a smear.
Thus, the existence of this smear indicates the presence of direpeats within the expression vector. Moreover, the light bands at 1276 bp indicates, that the right number of direpeats have been inserted into the vector. We performed 30 colony PCRs from colonies of different GATE assemblies and had no negative results (but in some cases, we could not determine the hight of the light band). Since positive results in colony PCR of TALEs do not exclude wrong order of direpeats, we sequenced 33 clones of different GATE assemblies and analyzed the results: In 32 of the 33 clones, sequencing results entirely matched the right sequence. So the efficiency of GATE assembly is approximately 97 %.
The figure clearly demonstrates the difference in size between the amplicons of negative control (kill cassette still in the vector) and positive (direpeats have replaced the cassette) samples. While lane 2 shows a negative result with a single band of bigger size, all the other samples yielded amplicons of smaller length and thus are considered as positive due to amplification of direpeats.
Nevertheless, it is obvious that the colony PCR did not produce one single product when amplifying the direpeats, but rather a smear consisting of amplicons with varying lengths.
This effect is due to numerous homologies within the direpeats and has previously been described by Briggs et al.2 .
To eliminate those homologies to the greatest extent possible, we changed codon usage within our direpeats. Nevertheless, as the results of our colony PCR demonstrate, there is still a profound amount of homologies left, which imposes difficulties on the amplification of the direpeat array by PCR and instead results in a smear.
Thus, the existence of this smear indicates the presence of direpeats within the expression vector. Moreover, the light bands at 1276 bp indicates, that the right number of direpeats have been inserted into the vector. We performed 30 colony PCRs from colonies of different GATE assemblies and had no negative results (but in some cases, we could not determine the hight of the light band). Since positive results in colony PCR of TALEs do not exclude wrong order of direpeats, we sequenced 33 clones of different GATE assemblies and analyzed the results: In 32 of the 33 clones, sequencing results entirely matched the right sequence. So the efficiency of GATE assembly is approximately 97 %.
In vivo testing
Gene activation

We are also able to measure one culture multiple times, e.g. at two different points in time. Another advantage is the measurement via photometry which makes the samples quantitively comparable. Interestingly, we did not have to clone a TALE binding site upstream of the minimal promoter (which would be required for other DNA binding proteins) but simply produced a TALE that specifically bound to the given sequence.
 The experiment was done with four different transfections, either no plasmid, only the TAL vector, only the SEAP plasmid or a cotransfection of both plasmids. The cells were seeded on a twelve well plate the day before in 500µl culture media per well. The transfection was done with CaCl2 after a cell culture course protocol written by the lab of Professor Weber.
The experiment was done with four different transfections, either no plasmid, only the TAL vector, only the SEAP plasmid or a cotransfection of both plasmids. The cells were seeded on a twelve well plate the day before in 500µl culture media per well. The transfection was done with CaCl2 after a cell culture course protocol written by the lab of Professor Weber.

As it is observable in the graph, co-transfection of cells with TAL and SEAP plasmids(++) yielded a high increase in SEAP activity, compared to the control samples. Also the control experiment with a TAL-VP64 targeting a random sequence shows the specificity of our system. The graph shows the average value of three biological replicates with its standard deviation. We further performed a t-test (Table) to prove if our experiment is statistically significant. As it is clearly observable, the p-values range below a value of 0,05, which indicates that our TAL transcription factor is able to elevate the transcription of the SEAP gene in a statistically significant manner.

After addition of pNPP, the substrate of SEAP, the activity of SEAP was measured over time. In the next image, the results of the first nine minutes of this measurement are shown. After this time, the OD of the double transfection (++) rose too high to be measured by our photometer. As it is clearly visible, the sample with the double transfection shows a profound increase in the OD. This points to the fact that great amounts of SEAP have been secreted into the cell culture media due to elevated gene expression. In the other samples almost no SEAP activity was measureable. The sample transfected with only the SEAP plasmid showed the highest OD but this effect was not statistically significant (p-value:0,25/0,51).
In the samples that had been taken 48h after double transfection, the same effects could be demonstrated.
Furthermore, we reapeated the same experiment for a second time. The corresponding data can be viewed here:

Precise Gene Knockout
TALENs are a very powerful tool for efficient gene knockout. In order to prove that our TALEN construct was functional, we decided to simply knock out a destabilized GFP gene on a plasmid, which we co-transfected with our TALEN plasmids into HEK cells. Moreover, we also transfected our cells with an mCherry vector to normalize for transfection efficiency. TAL constructs were designed to bind to opposite strands of the target plasmid in a way that the FokI monomers of each TALEN construct would be able to dimerize in the spacer region between the TALEN binding sites. 48 hours after transfection, gene knock-out efficiency was evaluated by FACS analysis.
Reference
1. Sanjana, N. E. et al. A transcription activator-like effector toolbox for genome engineering. Nature Protocols 7, 171–192 (2012).
2. Briggs, A. W. et al. Iterative capped assembly: rapid and scalable synthesis of repeat-module DNA such as TAL effectors from individual monomers. Nucl Acids Res (2012).doi:10.1093/nar/gks624
 "
"
