Team:Wellesley HCI/SynBio Search
From 2012.igem.org
| (23 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
<!--Start NavBar--> | <!--Start NavBar--> | ||
<ul id="nav"> | <ul id="nav"> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Team">Team</a></li> | + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Team">Team</a> |
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Team">Team Members</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Notebook">Notebook</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Acknowledgement">Acknowledgement</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Tips_Tricks">Tips & Tricks</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Social">Fun</a></li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Project_Overview">Project</a> | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Project_Overview">Project</a> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 83: | Line 91: | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href=" | + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Human_Practices">Human Practices</a> |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Human_Practices"> | + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Human_Practices">User Research</a></li> |
| - | + | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Methodology">Methodology</a></li> | |
<li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Safety">Safety</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Safety">Safety</a></li> | ||
| - | |||
<li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Outreach">Outreach</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Outreach">Outreach</a></li> | ||
| - | |||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Gold">Medal Fulfillment</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Wellesley_HCI/Gold">Medal Fulfillment</a></li> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
<!--End NavBar--> | <!--End NavBar--> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 119: | Line 121: | ||
<h1>Tool Overview</h1> | <h1>Tool Overview</h1> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | <a href="http://www.synbiosearch.org">SynBio Search</a> is an online tool that generates data sheets for over 2700 biological parts by aggregating data from various publicly available resources. It integrates and links information from various data sources, including the <a href="http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page">Registry of Standard Biological Parts</a>, the iGEM Archive, Google Scholar, and <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/">PubMed</a>. SynBio Search builds on the collected sources by providing a structured view that relates heterogeneous information, links back to original data sources, and allows users to customize and organize the display. It enables researchers to discover the most comprehensive view of freely available data about biological parts from a single online search. SynBio Search allows users to search by keyword (e.g. | + | <a href="http://www.synbiosearch.org">SynBio Search</a> is an online tool that generates data sheets for over 2700 biological parts by aggregating data from various publicly available resources. It integrates and links information from various data sources, including the <a href="http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page">Registry of Standard Biological Parts</a>, the iGEM Archive, Google Scholar, and <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/">PubMed</a>. SynBio Search builds on the collected sources by providing a structured view that relates heterogeneous information, links back to original data sources, and allows users to customize and organize the display. It enables researchers to discover the most comprehensive view of freely available data about biological parts from a single online search. SynBio Search allows users to search by keyword (e.g. qiagen) or by part name. |
</p> | </p> | ||
<h3>Implementation</h3> | <h3>Implementation</h3> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | As a web application, <a href="http://www.synbiosearch.org">SynBio Search</a> was implemented using multiple platforms. Information is gathered by crawling through multiple databases using CGI scripts written in Ruby. | + | As a web application, <a href="http://www.synbiosearch.org">SynBio Search</a> was implemented using multiple platforms. Information is gathered by crawling through multiple databases using CGI scripts written in Ruby. Then, the search results are then outputted into JSON files. After, the files are parsed, and the information is displayed in a clear and logical format on a web page (using HTML 5.0, CSS 3.0, JavaScript, and JQuery) for the user to access. |
</p> | </p> | ||
<h3>Purpose</h3> | <h3>Purpose</h3> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | While there are already several search engines for synthetic biology, none are exactly what users neither want nor need. For example, many iGEM participants and biology scientists and engineers use the <a href="http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page">Registry of Standard Biological Parts</a> to document their experience on | + | While there are already several search engines for synthetic biology, none are exactly what users neither want nor need. For example, many iGEM participants and biology scientists and engineers use the <a href="http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page">Registry of Standard Biological Parts</a> to document their experience on biological parts. However, the Registry is poorly organized, information is hard to locate, and certain data are missing. Thus, the purpose of our project is to create a resource that is not only qualitatively and quantitatively comprehensive, but also more accessible to users. It collects results from multiple data sources, allowing users to view more complete information in an organized and efficient manner. |
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 135: | Line 137: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| - | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/ | + | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/SBSupdated.PNG" width="450px" height="250"><br><br><center><strong>The home page of SynBio Search where users can query by keyword or by part name.</center></strong></td> |
| - | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/ | + | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/searchKeyword2.png" width="450px" height="250"><br><center><strong>The results page when the keyword "diabetes" is searched.</center></strong></td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| - | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/ | + | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/searchResultInfo3.png" width="450px" height="250"><br><center><strong>The data sheet produced for the part BBa I14018: The part's summary is displayed at the top.</center></strong></td> |
| - | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/ | + | <td><img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/searchResultAuthors2.png" width="450px" height="250"><br><center><strong>The data sheet for part BBa I14018: Users can customize their data sheet to only display the references.</center></strong></td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 163: | Line 165: | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | We conducted a preliminary user study for <a href="http://www.synbiosearch.org">SynBio Search</a> with 14 students | + | We conducted a preliminary user study for <a href="http://www.synbiosearch.org">SynBio Search</a> with 14 Biology students. The students were given various tasks so they could explore every aspect of the web application. The users found it useful to have multiple sources listed in one place; while some students preferred to use Google Scholar and PubMed over the other two sources because they were "more reliable sources" and "more well-known," others liked that they were able to "search between literature databases and parts/iGEM databases" all in one search engine. In addition, there was overwhelming support for the intuitiveness of the application and the ability to link to many other resources. Users suggested displaying a count of entries found by each database source and ordering the results by relevance or top hit. |
| - | + | ||
| + | <p><i>Users were asked to measure the level of difficulty (1 being Very Easy to 5 being Very Difficult) for sub-tasks after the usability study, results shown to the right.</i> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | < | + | |
| - | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/ | + | <div width="450px" style="display:block; float:right; margin: 5px;" > |
| + | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM2012/images/synbiosearch/SBSeaseofuseSmall.png" width="450px" style="display:block; float:right;"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
<h3>Quotes from users</h3> | <h3>Quotes from users</h3> | ||
| Line 174: | Line 179: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>"Fusing search results from multiple sources is very useful. I did not have to retype my query."</li> | <li>"Fusing search results from multiple sources is very useful. I did not have to retype my query."</li> | ||
| - | |||
<li>"count of entries found by each search might be helpful"</li> | <li>"count of entries found by each search might be helpful"</li> | ||
<li>"I liked that I could narrow down the searches based on database source."</li> | <li>"I liked that I could narrow down the searches based on database source."</li> | ||
| Line 183: | Line 187: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h3>Raw user study footage</h3> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <center><iframe width="480" height="360" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/g68VwD8TkIY?rel=0" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></center> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 191: | Line 200: | ||
<h1>Demo Video</h1> | <h1>Demo Video</h1> | ||
| - | <center><iframe width=" | + | <center><iframe width="480" height="360" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/djMv0n6GPEU?rel=0" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></center> |
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 201: | Line 209: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li>Include more information in the data sheet for each part | + | <li>Integrate more databases such as: Clotho, SynBERC, Based on user feedback.</li> |
| - | <li> | + | <li>Include more information in the data sheet for each part.</li> |
| + | <li>Increasing the search engine capabilities by including options for customizable search, such as boolean operators (AND, OR).</li> | ||
<li>Iterate on the design based on user feedback.</li> | <li>Iterate on the design based on user feedback.</li> | ||
<li>Incorporate a sophisticated feedback and experience feature.</li> | <li>Incorporate a sophisticated feedback and experience feature.</li> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:28, 4 October 2012

SynBio Search
Tool Overview
SynBio Search is an online tool that generates data sheets for over 2700 biological parts by aggregating data from various publicly available resources. It integrates and links information from various data sources, including the Registry of Standard Biological Parts, the iGEM Archive, Google Scholar, and PubMed. SynBio Search builds on the collected sources by providing a structured view that relates heterogeneous information, links back to original data sources, and allows users to customize and organize the display. It enables researchers to discover the most comprehensive view of freely available data about biological parts from a single online search. SynBio Search allows users to search by keyword (e.g. qiagen) or by part name.
Implementation
As a web application, SynBio Search was implemented using multiple platforms. Information is gathered by crawling through multiple databases using CGI scripts written in Ruby. Then, the search results are then outputted into JSON files. After, the files are parsed, and the information is displayed in a clear and logical format on a web page (using HTML 5.0, CSS 3.0, JavaScript, and JQuery) for the user to access.
Purpose
While there are already several search engines for synthetic biology, none are exactly what users neither want nor need. For example, many iGEM participants and biology scientists and engineers use the Registry of Standard Biological Parts to document their experience on biological parts. However, the Registry is poorly organized, information is hard to locate, and certain data are missing. Thus, the purpose of our project is to create a resource that is not only qualitatively and quantitatively comprehensive, but also more accessible to users. It collects results from multiple data sources, allowing users to view more complete information in an organized and efficient manner.
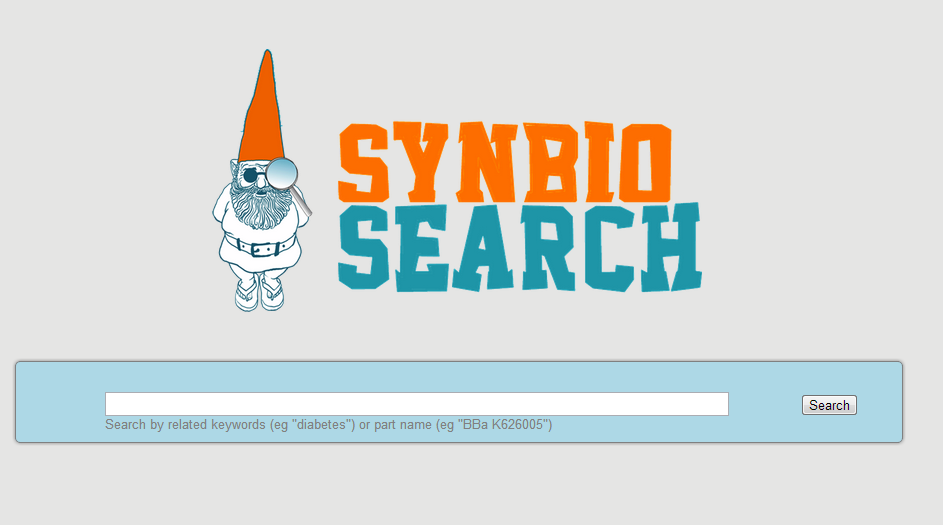 |
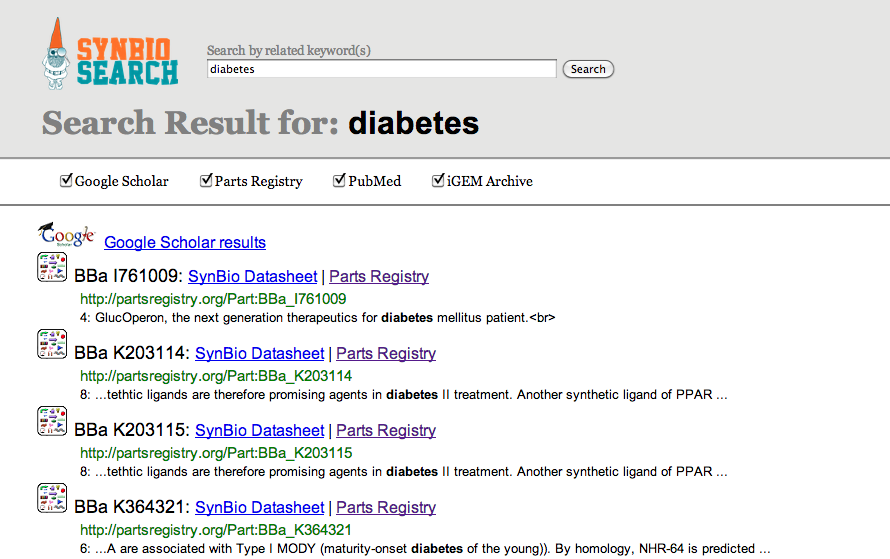 |
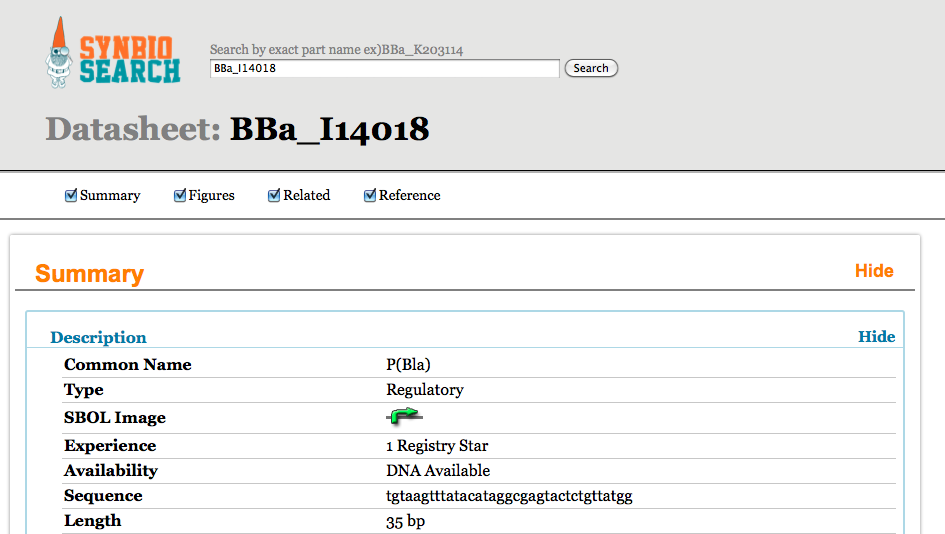 |
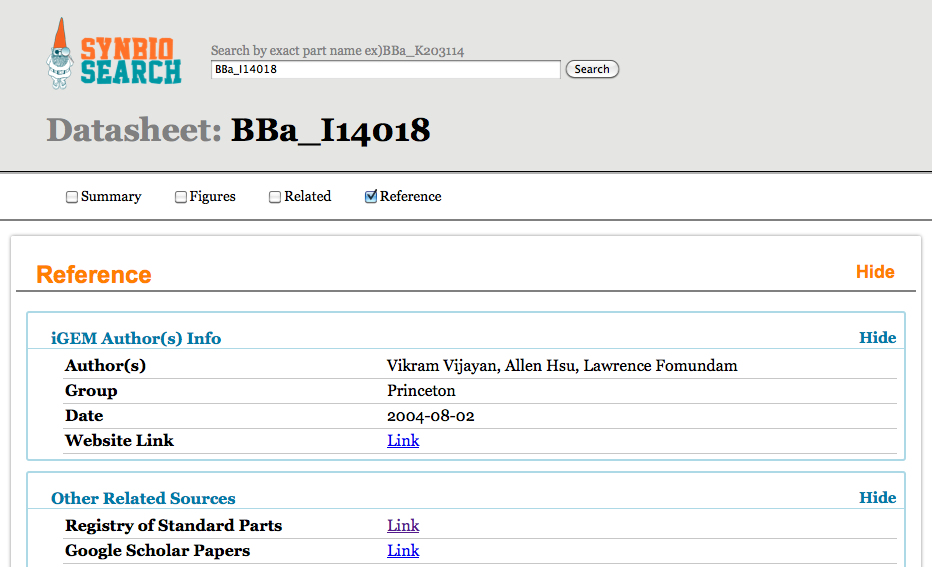 |
Results
We conducted a preliminary user study for SynBio Search with 14 Biology students. The students were given various tasks so they could explore every aspect of the web application. The users found it useful to have multiple sources listed in one place; while some students preferred to use Google Scholar and PubMed over the other two sources because they were "more reliable sources" and "more well-known," others liked that they were able to "search between literature databases and parts/iGEM databases" all in one search engine. In addition, there was overwhelming support for the intuitiveness of the application and the ability to link to many other resources. Users suggested displaying a count of entries found by each database source and ordering the results by relevance or top hit.
Users were asked to measure the level of difficulty (1 being Very Easy to 5 being Very Difficult) for sub-tasks after the usability study, results shown to the right.
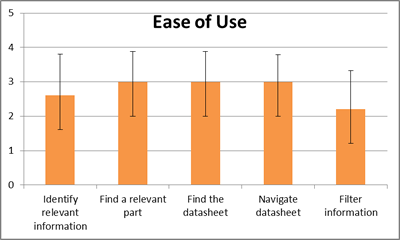
Quotes from users
- "Fusing search results from multiple sources is very useful. I did not have to retype my query."
- "count of entries found by each search might be helpful"
- "I liked that I could narrow down the searches based on database source."
- "It's intuitive to use and seems to gather all related data into one place, which is very helpful for project design purposes. I particularly like being able to filter out publications and just search for protocols/ lab notebooks."
- "I think its useful because instead of having to search in 100 different places for resources on one topic, all I had to do was look at one page."
- "I found the ability to search between literature databases and parts/ iGEM databases in one search engine very helpful. It was nice to be able to limit my search to only literature or only parts/ lab notebooks, depending on the stage of the research project I might be in. I also liked how hyperlinked everything was - I could navigate from the datasheet to the lab notebooks describing that part, or to publications that might be related. It was very nice to have everything laid out in one place."
Raw user study footage
Demo Video
Future Work
- Integrate more databases such as: Clotho, SynBERC, Based on user feedback.
- Include more information in the data sheet for each part.
- Increasing the search engine capabilities by including options for customizable search, such as boolean operators (AND, OR).
- Iterate on the design based on user feedback.
- Incorporate a sophisticated feedback and experience feature.
 "
"