Contents[hide] |
Transfections
To test whether our transfections worked, we have cotransfected control cell cultures with 5% pOri-eGFP (i.e. 5% of the inserted DNA is GFP). Over multiple experiments, we have found the transfection efficiency to vary between 20 and 50% (measured using a flow cytometer), which means the transfections are working very well. The following image was taken with a fluorescence microscope. The fluorescence clearly colocalizes with the cells (mouse-over to switch between normal and fluorescent microscopy images):


Also note that the fluorescence intensity isn't uniform in all cells. This is a side-effect of transient transfection: it's a lot faster (it takes a few days instead of a few months to have transfected cells), but every cell is different in its uptake of the plasmid.
Flowcytometry
Detecting LovTAP
The Lov domain contained in LovTAP has certain fluorescent properties (Kasahara2002). It has excitation peaks around 380nm and 480nm and an emission spectrum with a peak at 500nm. We tried to use this property to detect the presence and the localization of LovTAP.
Using fluorescence microscopy, we looked at the fluorescence at 500nm
when excited at 380nm (blue in the image) and at 488nm (green in the
image). While the green fluorescence has a certain amount of specificity
(it seems to appear consistently around the nucleus), there is no significant
difference between LovTAP transfected cells and cells transfected with other
plasmids or non-transfected cells.
Characterizing LovTAP
We used our lighting system to test if there was a detectable difference in dsRed (the read-out protein) expression between lit and unlit cells. There was no detectable difference, which means that either the difference is so small it disappears in the noise from transient transfections or that LovTAP is not being folded or even expressed correctly (as there is no difference between cells with and without LovTAP either, this seems to be the most likely result). To sum it up in a sentence:
Non-leakage dsRed, where art thou?
Melanopsin
Melanopsin Pathway
Transfections in CHO cells of the full system described by Prof. Fussenegger were performed, but didn't exhibit any significant reaction to light input. The tests were also performed on HEK cells, with the same results. This is probably due to the fact that, due to time constraints, we couldn't form a stable melanopsin-expressing cell line as in Prof. Fussenegger's experiments.
Melanopsin Calcium Imaging
By using timelapse photography and fluorescence microscopy we were able to study the influx of calcium into CHO cells. The cells were stained with a calcium activated dye that fluoresces green, oregon green (OGB-1/AM), and exposed to blue light under the microscope ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K838002:Experience more details on the experimental setup]). Here is a sample picture (mouse-over to switch to fluorescence microscopy view:


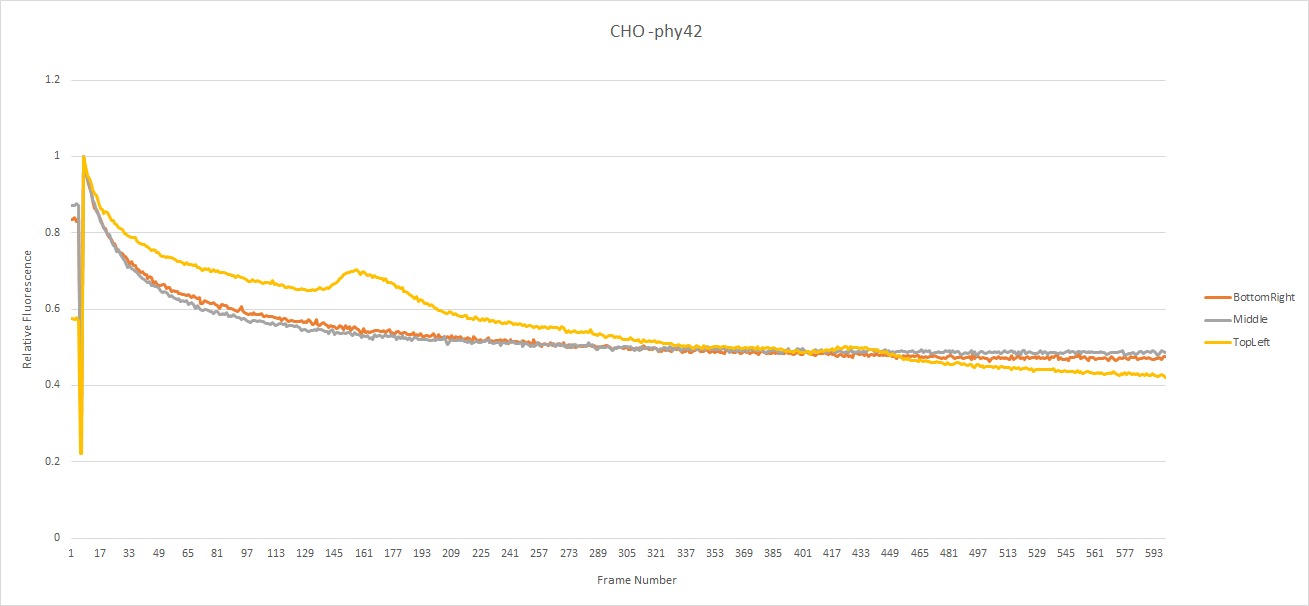
The CHO seed cells show the expected response to light exposure. The dye's intensity gradually decreases along an exponential curve over time. This would seem to indicate the concentration of calcium in the cell remained constant during light exposure. Note: The yellow line seems to go up a bit at certain points, this is due to a cell passing over (out of focus), which increased the local brightness but didn't change the actual fluorescence of the cell. Notice that on all of the graphs the intensity was normalized with respect to the value of the first frame after the switch to fluorescent mode.
The CHO cells transfected with pHY42 contain human melanopsin. The cells show a slow linear looking decrease in dye intensity. This indicates that the calcium concentration in the cell is increasing which partly counter-acts the loss of fluorescence.
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K838002 Melanopsin Biobrick]
Part assembly
We planned to clone several parts we used into pSB1C3, which is the standard backbone plasmid in which parts are shipped to the [http://partsregistry.org/Main_Page Registry]. Four parts were successfully inserted based on colony PCR results followed by successful sequencing.
LovTAP-VP16: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K838000 BBa_K838000]
Successfully cloned on the 4th of September.
LovTAP readout (RO): [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K838001 BBa_K838001]
Successfully cloned on the 18th of September
Melanopsin: [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K838002 BBa_K838002]
Successfully cloned on the 12th of September
 "
"