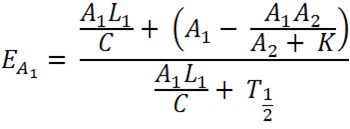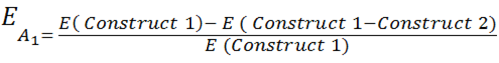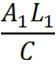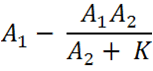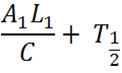Team:NRP-UEA-Norwich/ComparatorCircuit
From 2012.igem.org
Khadijaouadi (Talk | contribs) (→Future Experiments) |
Khadijaouadi (Talk | contribs) (→Introduction) |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{UEANRPProjects}} | {{UEANRPProjects}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
[[File:NRPCompLogo.png | centre]] | [[File:NRPCompLogo.png | centre]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 10: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | In a previous project, the apparent lack of specificity of the promoter BioBrick we looked to improve upon proved to be a minor difficulty that we felt had not been addressed previously in the Registry. Thus we decided to tackle the issue by devising a way of quantitatively measuring the output of NO with the non-specific promoter we were using through a novel gene regulation system. | + | In a previous project, the apparent lack of specificity of the pYear promoter BioBrick we looked to improve upon proved to be a minor difficulty that we felt had not been addressed previously in the Registry. Thus we decided to tackle the issue by devising a way of quantitatively measuring the output of NO with the non-specific promoter we were using through a novel gene regulation system. |
Using pairs of BioBricks that result in the complimentary binding of a pair of otherwise standard promoter and reporter constructs, a subtractive effect can be gained to result in altered translation relative to the availability of various substrates within the chassis environment. | Using pairs of BioBricks that result in the complimentary binding of a pair of otherwise standard promoter and reporter constructs, a subtractive effect can be gained to result in altered translation relative to the availability of various substrates within the chassis environment. | ||
| - | + | This is done via the comparator pairs design, which facilitates complete binding of both mRNAs ribosome binding sites when they are both present in the chassis' transcriptome. | |
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <table width=100% align=center cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td valign=absmiddle width=50%> | ||
| + | Imagine you have two promoter BioBricks, which both have the ability to sense the same substrates, but, critically, one of these promoter BioBricks senses an extra substrate - the substrate you are interested in. The aim of the Comparator Pair of BioBricks we have created is, when each of the pair is ligated to one of the promoter BioBricks, to integrate these promoter outputs to result in a subtractive system that produces a quantitative output of the substrate of interest only. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td valign=absmiddle width=50%><center> | ||
| + | <br><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/e/eb/Different_promoters.png" width=350px align=middle><br> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td valign=absmiddle width=50%> | ||
| + | When these promoter/comparator duplexes are added to different reporter proteins, the translation of these reporters are sequestered when both sequences are transcribed due to the presence of the same substrate. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td valign=absmddle width=50%><center> | ||
| + | <br><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/0/01/Sequester.png" width= 350px align=middle><br> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td valign=absmiddle width=50%> | ||
| + | So, for instance, if one of the promoters produces twice as many mRNA transcripts due to the extra substrate it is sensing... | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td valign=absmiddle width=50%><center> | ||
| + | <br><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/7/7e/Twice_the_reporter.png" width=350px align=middle><br> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td valign=absmiddle width=50%> | ||
| + | ...then only the surplus mRNA transcripts of the second reporter gene will be translated. If the reporter used is a fluorescent protein then a fluorometer can be used to quantitatively determine the exact amount of a particular fluorescence and, as a result, the exact amount of the substrate of interest that was detected by the chassis. | ||
| + | <td valign=absmiddle width=50%><center> | ||
| + | <br><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/1/1f/QuanticareComparator.png" width=350px align=middle><br> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | An important part of the Comparator Circuit idea is the fact that there is potential of other Comparator Pairs being made to result in a family of BioBricks existing on the registry. Different Comparator Pairs could thus be expressed simultaneously in the cell, working with different promoters to quantify a number of different substrates in tandem within the same chassis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The video below describes the project in further detail: | ||
<html><align=center> | <html><align=center> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 72: | ||
</align> | </align> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The Comparator Circuit Family.== | ||
| + | |||
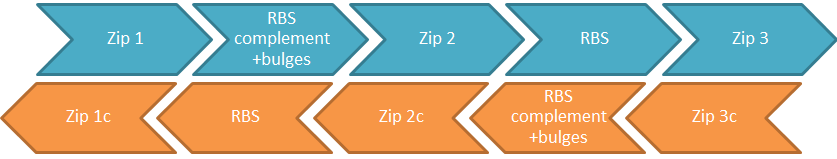
| + | The comparator BioBricks submitted do not stand alone; they are the first of a family of BioBricks. The two that have already been synthesised will complimentary bind to one another but more can be made by following the steps that we have already defined. In the cell they will bind in pairs without interfering with the function of other comparator circuit pairs. This allows for an almost limitless range of combinations of circuits all functioning together in the same cell. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:IGEM_comparator_circuit_familly_diagram_1_12.09.26.png | 600px | centre | thumbnail | '''Figure 1.''' ''Generic make up of comparator circuit BioBricks. “c” indicates reverse complement, so “1c” is reverse complement of “1” etc. Arrows indicate five prime to three prime. This figure represents a pair of BioBricks, blue is one BioBrick and orange is the other."]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Comparator circuit construction''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The BioBricks that make up the comparator circuit consist of a number of complimentary sections of DNA referred to as zips. The generic comparator circuit BioBrick template is shown in figure 1. It is important to note that the two strands are anti-parallel | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Zip 1''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ZIP 1 is at the five prime end of the BioBrick sequence. Because in this BioBrick ZIP 1 is located before the ribosome binding site, it is untranslated. However because the two strands are antiparallel, the reverse complement of ZIP 1 will be translated. This results in the reverse complement of ZIP 1 to form a tag on the synthesised protein. Therefor is is essential that it must encode amino acids that will not disrupt the structure of the protein and be made up of non-rare codons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The ribosome binding site and its reverse complement with bulges''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the two strands to anneal, it it is necessary to have the reverse complement of the ribosome binding site on the other strands. To remove any error caused by different translation rates, it is best to use the same ribosome binding site (RBS) on each strand. However this can cause problems because a strand, that contains both the ribosome binding site and its reverse complement, can complimentary bind it to itself across that sequence causing the RBS to be sequestered. To prevent this problem the RBS reverse complement is made up of alternate codons of complimentary and non-complimentary sections. In addition it is necessary for the binding between the two strands to be entropetically stable. This can be achieved by design of the RBS, its complement and bulges. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This means that it is necessary for sections either side of the ribosome binding site and its complement and bulges to make binding between the two strands entropetically stable | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''ZIP 2''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ZIP 2 forms the complimentary strand between the RBS and the RBS complement on both strands; because it is untranslated it can be as long as is desired. The longer it is, the more stable the construct becomes. To achieve this a high GC content would be advisable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''ZIP 3''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ZIP 3 is downstream of the RBS. It is therefore translated and consequently must contain no rare codons nor code for any amino acids that might affect the function of the protein. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Theoretical modelling''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a final stage, it is necessary to check for internal interactions within the BioBrick. There will always to a degree be formation of secondary structure but as long as the RBS is exposed, it can be expected that the BioBrick will be functional. The efficiency can be increased by decreasing the change in Gibbs free energy caused by formation of 2nd structures. It is possible to use programs such as M-fold or Oligo Analyser to achieve this. | ||
==Planning== | ==Planning== | ||
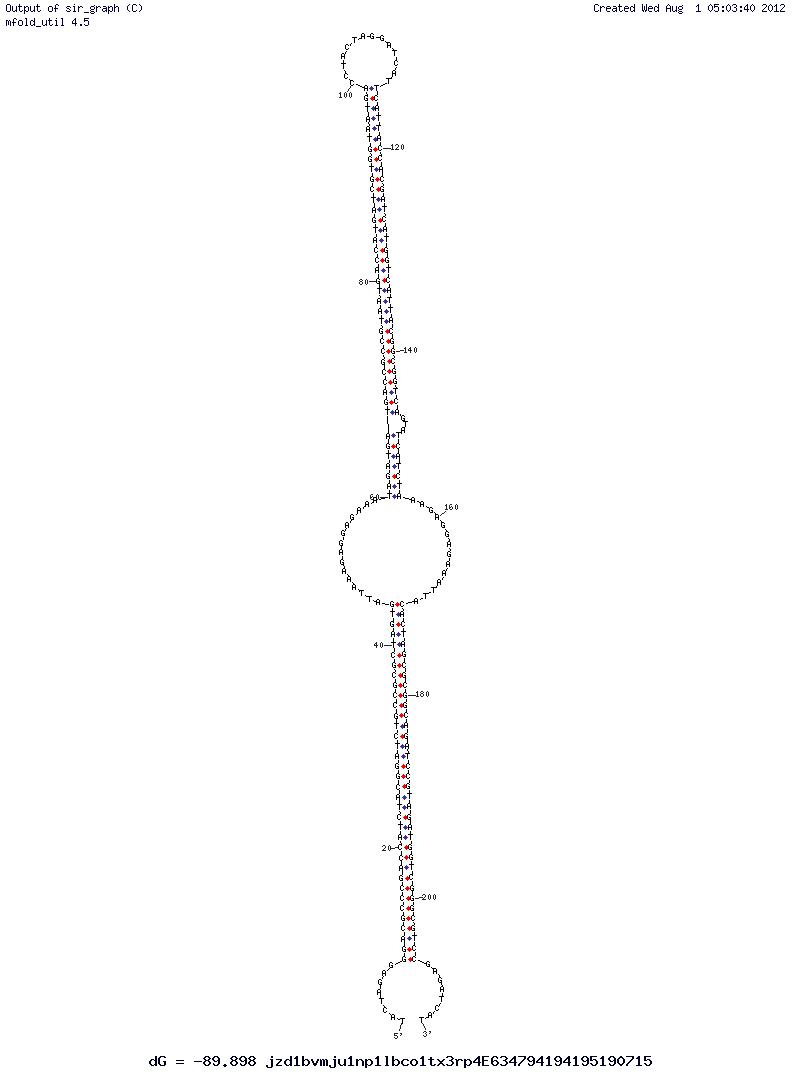
| - | [[File:CombinedMRNA.png | thumb | Figure | + | [[File:CombinedMRNA.png | thumb | Figure 2 - Both BioBricks of a precursor to the Comparator Circuit bound together.]] |
| - | Assembling the various gene constructs was not without its challenges. Due to the fact that complimentary ‘zips’ within the sequence were designed to surround the ribosome binding site it was often the case that the DNA sequence would form unwanted secondary structures that could serve to inhibit the translation of the mRNA in its uncoupled state. | + | Assembling the various gene constructs was not without its challenges. Due to the fact that complimentary ‘zips’ within the sequence were designed to surround the ribosome binding site, it was often the case that the DNA sequence would form unwanted secondary structures that could serve to inhibit the translation of the mRNA in its uncoupled state. |
| - | Therefore, when designing the DNA, care was taken to avoid these | + | Therefore, when designing the DNA, care was taken to avoid these structure obstructing sequences required for translation of the mRNA. Simultaneously only common codons for the chassis of interest, ''E. coli'', could be used and these codon had to code for amino acids that were unlikely to change the function of the protein product. This is required since the zip sequences extend past the translational start codon. Thus our construct will add a small N-terminal tag to any reporter protein it was attached to. |
| - | Using IDT's very helpful online tool, Oligo Analyser, we were able to | + | Using IDT's very helpful online tool, Oligo Analyser, we were able to design sequences of both constructs that fulfilled these requirements. These sequences theoretically bind together when transcribed in the same chassi, yet leave the RBS open and very importantly unfold when either stand of mRNA lacks its counterpart it could complementary bind to. |
| - | Due to the stop codon present in the scars of Assembly Standard 10 BioBricks, we decided that our constructs would have to be an Assembly Standard 23 BioBrick. Although the use of Bioscaffolds produced by previous iGEM teams was considered, time constraints meant that changing the Assembly Standard we | + | The software produced figures demonstrating the likely secondary structure of the constructs made and their Gibbs Free Energy value at specific temperatures. From this, trial and error eventually resulted in the construction of two BioBricks that have free ribosome binding sites when in isolation, but bind to sequester translation of both mRNAs when bound together (''Figure 2.''). |
| + | |||
| + | Due to the stop codon present in the scars of Assembly Standard 10 BioBricks, we decided that our constructs would have to be an Assembly Standard 23 BioBrick. Although the use of Bioscaffolds produced by previous iGEM teams was considered, time constraints meant that changing the Assembly Standard we would use for assembly of our BioBricks would be the most convenient solution. | ||
==Experiments== | ==Experiments== | ||
| - | Due to the limited time we had available, it was decided fairly early on that the comparator circuit BioBricks could only be characterised theoretically. However, our confidence in the system meant that we felt obliged to synthesise these BioBricks and submit them to the registry. It is our hope that we will be granted lab space after the regional jamboree to characterise these BioBricks and submit our findings | + | Due to the limited time we had available, it was decided fairly early on that the comparator circuit BioBricks could only be characterised theoretically. However, our confidence in the system meant that we felt obliged to synthesise these BioBricks and submit them to the registry. It is our hope that we will be granted lab space after the regional jamboree to characterise these BioBricks and submit our findings on their respective registry experience page in due course. In preparation for this, the team have devised a provisional experimentation design for these characterisation studies. |
==Future Experiments== | ==Future Experiments== | ||
| - | Further cloning experiments hope to be carried out, ligating each comparator circuit | + | Further cloning experiments hope to be carried out, ligating each comparator circuit BioBrick with a different reporter and promoter. Initially, for proof of concept, the promoters used would be simple promoters that have overlapping specificity, but one substance will only act as an inducer for one of these promoters (e.g. the pYEAR and SoxR promoters, which both sense small nitrogen species, but SoxR also senses superoxides). |
| - | Reporter | + | Reporter BioBricks would also be ligated, with these reporters being as far apart in wavelength of the florescence produced as possible. Both DNA sequences, each containing one half of the comparator circuit system, with be transformed into an E. coli chassis and the amount of either fluorophore (as seen via fluorometer studies) would indicate the translation of either sequences. It is hoped that in simulated environments containing higher levels of, using the example above, superoxides, the corresponding fluorescent protein will be translated over its counterpart. |
| - | Ultimately it is hoped that we would be able to ligate our comparator circuit BioBricks to NO-sensing promoters and | + | Ultimately it is hoped that we would be able to ligate our comparator circuit BioBricks to NO-sensing promoters and effector enzymes to control NO levels/reporters to detect NO levels quantitatively - which is where our fictitious brand Quanticare comes in. Should we have time, we'd like to investigate if the transfection of mammalian cells with these constructs, as seen in our science-fiction self-diagnostic tattoos, is plausible via the transfection of cancer cell lines with the DNA constructs. |
| - | + | Beyond the addition of promoters and transformation into a bacterial chassis, further experiments which would need to be carried out are: | |
| - | The idea of the comparator circuit is to provide a modular sensor which can specifically and quantitatively measure different chemical species within the cell. Through | + | 1) A growth study into whether the incorporation of the comparator circuits affect the growth of the chassis compared to growth without can be tested |
| + | |||
| + | 2) A fluorescence study into whether the comparator circuit functions as expected. This would involve the use of a fluorometer and FACs to obtain a comprehensive view of the proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3) A cytotoxic study involving a cytotoxic assay similar to the one carried out on BM and MB, however, this will test whether the accumulation of silenced RNA transcripts will affect the cell. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4) Study into the sensitivity of the promoters- this be a measure of threshold levels of a promoter before it expresses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Theoretical Characterisation== | ||
| + | The idea of the comparator circuit is to provide a modular method of signal integration that can produce a sensor which can specifically and quantitatively measure different chemical species within the cell using non specific promoters. Through mathematical modelling, an equation has been assembled which can predict the expression of each of the reporter proteins such as RFP and CFP. | ||
[[File:Equation_7.png| 300px | center]] | [[File:Equation_7.png| 300px | center]] | ||
| - | Figure: Theoretical equation to | + | Figure: Theoretical equation to predict the degree of expression of Construct 1 and 2. |
| - | + | The full equation has been laid out in a way that is relevant only to Construct 1, however, the numbers can be reversed to be relevant to Construct 2. For ease of explanation, everything described will be relevant to Construct 1. | |
| - | E = Proportion of rate | + | E = Proportion of expression rate of Construct 1 when both constructs are transcribed (i.e. there is knockdown of one construct) relative to the non-knocked down expression of Construct 1 when only Construct 1 is expressed. |
| - | A = The rate of transcription of Construct 1 as a proportion of the maximum transcription rate. As a proportion this is measured on a scale of 0 - 1. As an example if the rate of transcription is half of the maximum rate, rate would be 0.5 (arbituary units). It can be assumed the rate of transcription of construct 1 and 2 due to cellular components (e.g. RNA polymerase) is the same, however, the | + | A = The rate of transcription of Construct 1 as a proportion of the maximum transcription rate. As a proportion this is measured on a scale of 0 - 1. As an example if the rate of transcription is half of the maximum rate, rate would be 0.5 (arbituary units). It can be assumed the rate of transcription of construct 1 and 2 due to cellular components (e.g. RNA polymerase) is the same, however, the rate of transcription initiation will dictate the transcription rate. The initiation is reliant on the chemical species interacting with the transcription factor which binds to the promoter (i.e. nitric oxide,nitrates,nitrites to PyeaR). The '1' and '2' refer to the Construct 1 or 2 and hence the promoter and the measured fluorescent protein attached (e.g GFP, RFP, CFP, etc). |
L = The length of the Construct 1 in the DNA form that is transcribed (i.e the leader and protein coding region). | L = The length of the Construct 1 in the DNA form that is transcribed (i.e the leader and protein coding region). | ||
| - | Note: Leader refers to the section of RNA at the start of the mRNA that is not translated but has an | + | Note: Leader refers to the section of RNA at the start of the mRNA that is not translated but has an effect on translation rate. |
C = The rate of transcription. Assuming the rate of transcription of Construct 1 and 2 are the same because the same ribosomes and RBS are involved. | C = The rate of transcription. Assuming the rate of transcription of Construct 1 and 2 are the same because the same ribosomes and RBS are involved. | ||
| Line 78: | Line 164: | ||
| - | The full equation is | + | The full equation is modelled on the basic equation of: |
[[File:Equation_2.png| 400px | center]] | [[File:Equation_2.png| 400px | center]] | ||
| Line 85: | Line 171: | ||
| - | The additional complexity factors in less assumptions, and | + | The additional complexity factors in less assumptions, and mimics a biological system, more closely. Below is a breakdown of the full equation. |
[[File:Equation_3.png| 50px | left]] | [[File:Equation_3.png| 50px | left]] | ||
| - | This refers to the | + | This refers to the number of Construct 1 RNA transcripts undergoing transcription at any one time. The length of DNA is particularly important when the chassis is bacterial. In bacteria, as there is no true nucleus, translation occurs simultaneously with transcription. Transcription affects the probability of interaction between construct 1 and 2 and therefore, they are less likely to be translated. As the measurement of fluorescence is the output directly related to the rate of translation, the overall equation measures translation, however, translation rate iis dependent on rate of transcription and degree of knockdown, and hence transcription is factored in here. L/C is the period of time taken for transcription to take place. It is the time in which translation can be initiated but it is unlikely that the two leaders will bind to one another |
[[File:Equation_5.png| 150px | left]] | [[File:Equation_5.png| 150px | left]] | ||
| - | This part of the equation is the deduction of the knockdown of Construct 1 when there is Construct 2 expression and interaction. The biological constant, k, factors in that not all of construct 2 that is expressed will interact with construct 1 and | + | This part of the equation is the deduction of the knockdown of Construct 1 when there is Construct 2 expression and interaction. The biological constant, k, factors in that not all of construct 2 that is expressed will interact with construct 1 and vice versa. Hence, both exist despite construct 2 existing in small quantities. We believe that depending upon the assembly of the orientation of the two constructs within the plasmid, the interaction and hence the binding efficiency can be altered vastly. If the genes have opposite orientations, so that the termination sites are very close then the reduction of distance will increase the chances of interaction and hence make the sensory system more accurate. |
[[File:Equation_6.png| 120px | left]] | [[File:Equation_6.png| 120px | left]] | ||
| - | This part of the equation encompasses the natural half life of Construct 1 when it alone is expressed (i.e. no expression or interaction | + | This part of the equation encompasses the natural half life of Construct 1 when it alone is expressed (i.e. no expression of or interaction with Construct 2). As described before in the modelling from the basic equation, this is the lower part of the equation and puts it in perspective of Construct 1 and gives expression as a porportion of the maximum transcription. The half life is also Construct 1's half life. |
So to bring it all together; the top half of the equation indicates the degree of translation of the RNA transcribed by the first promoter under any particular transcription rate of the two promoters in arbitrary units. To make this into a meaningful output it is divided by the maximum translation rate at that rate of transcription to equal E(A1); this indicates the degree of attenuation of one RNA from the other. | So to bring it all together; the top half of the equation indicates the degree of translation of the RNA transcribed by the first promoter under any particular transcription rate of the two promoters in arbitrary units. To make this into a meaningful output it is divided by the maximum translation rate at that rate of transcription to equal E(A1); this indicates the degree of attenuation of one RNA from the other. | ||
| Line 102: | Line 188: | ||
==Future Applications== | ==Future Applications== | ||
| - | . | + | The Comparator Circuit has the potential to have real world applications, particularly, as Quanticare shows, in medicine. To give an example, by monitoring blood sugar levels quantitatively via specific promoters, the sequence following the comparator circuit could encode for insulin. This could be transfected into human cells and could be used to alleviate the symptoms associated with type I diabetes. |
| - | + | ||
| - | . | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | . | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ... | + | Moving back to the specific nitrogen sensor, attaching these promoters to the comparator circuit BioBricks and a gene for the synthesis of nitrite reductase could result in a positive feedback loop to result in the tumour reducing in size. Macrophages naturally sense the presence of tumours in the body via their emission of nitric oxide. This could be taken one step further by adding nitrogen reductase to this system, where an excess of nitric oxide in the tumour environment. NO was seen to have cytotoxic properties in large amounts and, thus, a positive feedback loop could result in tumour apoptosis. |
Latest revision as of 00:52, 27 September 2012
 "
"