Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Project/Appoach
From 2012.igem.org
KevinJarosch (Talk | contribs) (→Approach) |
KevinJarosch (Talk | contribs) (→Approach) |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | == | + | == Immobilization and the final Development of the Filter== |
| + | |||
| + | The last step to realize our project is to immobilize the produced laccasses with the highes potentials. To generate a filtersystem with a high yield of active and immobilized enzymes different approaches are tested. One the one hand we try to immobilize the enzyme with a chemical immobilization protocol to bind covalent the laccases on specific silica-beads | ||
Revision as of 17:21, 15 August 2012
Contents |
Approach
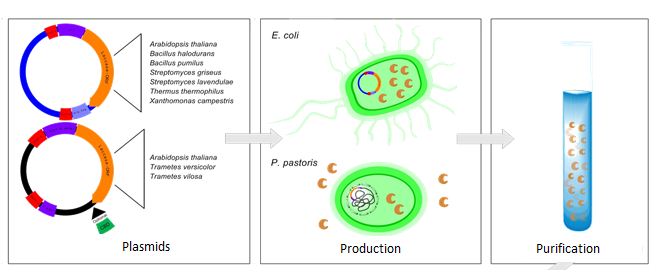
The conventional methods in sewage treatment plants are unable to treat waste water sufficiently because the most frequently used micro contaminants like estrogen, Bisphenol A, Dicolfenac etc. are very difficult to break down. The goal of Bielefeld’s iGEM team is to develop a biological filtersystem using immobilized laccases to purify municipal and industrial wastewater from synthetic estrogens and other aromatic compounds. Laccases are copper-containing oxidase enzymes found in many organisms, and one of their properties is the ability to break down a wide range of aromatic and phenolic compounds. For this purpose, genes of various bacterial and eukaryotic laccases should be isolated and expressed in Escherichia coli and Pichia pastoris. The choice of the expressionsystem depends on the glycosylation status of the enzyme.
Isolation and Generating of new BioBricks
The first step for Step of our project is to isolate the specific gene sequences and to generate new BioBricks for the iGEM competition. The Laccases of the following organisms are isolated:
bacterial laccases:- Escherichia Coli
- Baccilus Halodurans
- Baccilus Pumilus
- Streptomyces griseus
- Streptomyces lavendulae
- Thermus thermophilus
- Xanthomonas campestris
Eukaryota laccases:
- Arabidopsis thaliana
- Tramestes versicolor
- Trametes villosa
For more information about the Organisms click here.
These BioBricks are used to design new plasmids and vector-systems. The diffenten parts to realise a functional Plasmid btw. Shuttle-Vector-System are shwon in the following table:
Parts of the E.coli Expressionvector and the P.Pastoris Shuttle-Vector
| Plasmid Characteristics | Shuttlevector Characteristics |
|---|---|
| T7 Promotorregion | AOX-Promotor |
| His-Tag-Sequence | alpha-factor |
| Chloramphenicol Resistance | Zeocin Resistance |
The Choice which expression system is used depends on the folding and glycosylation of the different laccases. The genetically modified organisms are used to produce different laccases. Further down the line, these laccases are isolated and purified.
Determining Activity and Potential of The Different Laccases
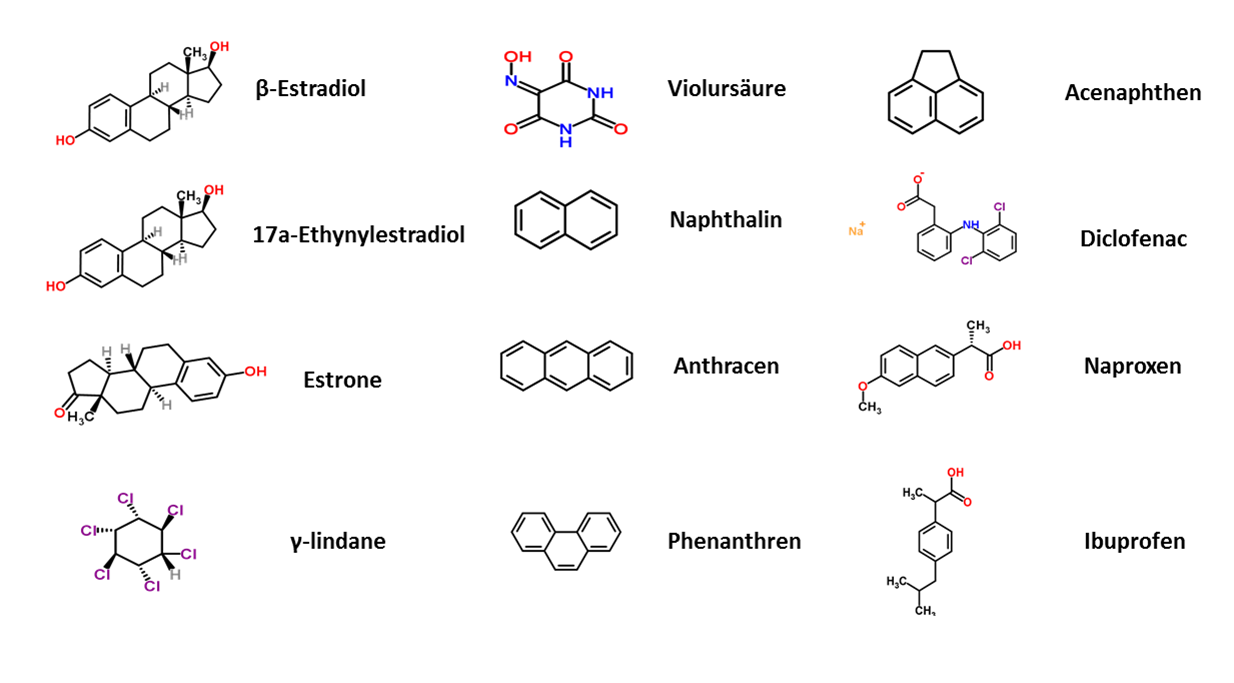
| The next step to generate a effeciantally filter system is to characterize different produced and purified laccases. To identify the potential of different laccases, the enzyme are examined on their activity and the potential to degrade different substances. The degradation potential of different laccases are investigate for representative substances from different chemical areas like analgetics, endocrine substances, pesticides, poly aromatic hydrocarbons and bleaching agents.
In this case we analyses the efficiency of the laccase degradation and investigate different parameters like temperature, pH, and Buffer-systems. A great concern of our team is to guarantee the Safety of the generated filter system. Besides the degradation potential, a very important aspect is an analyzing of the degradated substances to guarantee, that the degradation with laccases don't generate any toxic or dangerous substances. These analyses realized by HPLC-massspectorscopy. With this knowledge we want to identify these laccase which show the highes potential for a functional filter system. |
Immobilization and the final Development of the Filter
The last step to realize our project is to immobilize the produced laccasses with the highes potentials. To generate a filtersystem with a high yield of active and immobilized enzymes different approaches are tested. One the one hand we try to immobilize the enzyme with a chemical immobilization protocol to bind covalent the laccases on specific silica-beads
 "
"