Team:Colombia/Project/Problem
From 2012.igem.org
m (→References) |
m (→References) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
#Arneson, P. A. (2000). Coffee rust. The Plant Health Instructor. doi:10.1094/PHI-I-2000-0718-02 | #Arneson, P. A. (2000). Coffee rust. The Plant Health Instructor. doi:10.1094/PHI-I-2000-0718-02 | ||
| - | |||
#USDA. 2011. National Agricultural Library. Research; Special Note: NAL Catalog Search | #USDA. 2011. National Agricultural Library. Research; Special Note: NAL Catalog Search | ||
Revision as of 19:53, 15 July 2012
Template:Https://2012.igem.org/User:Tabima
Contents |
The Problem
Coffee rust (Hemileia vastatrix)
Coffee rust is the most economically important coffee disease in the world, and in monetary value, coffee is the most important agricultural product in international trade. Even a small reduction in coffee yields or a modest increase in production costs caused by the rust has a huge impact on the coffee producers, the support services, and even the banking systems in those countries whose economies are absolutely dependent on coffee export (Arneson, 2000).
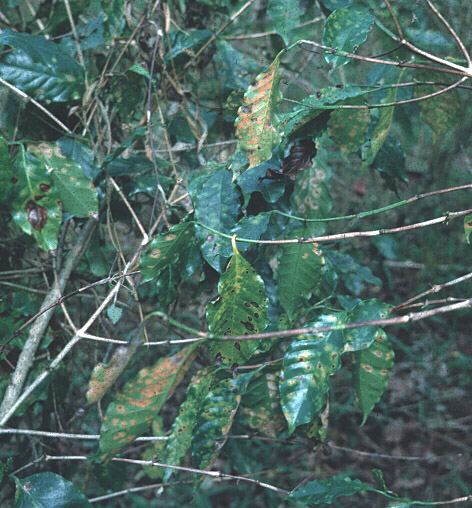
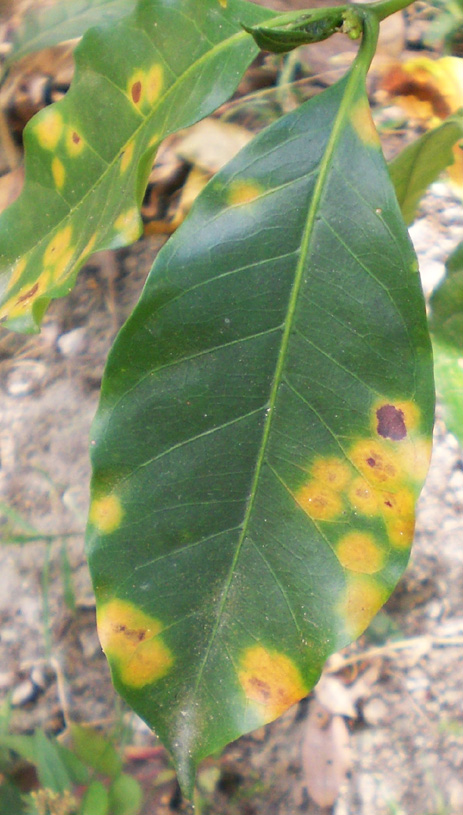
The fungus responsible of the “coffee leaf disease” Hemileia vastatrix belongs to the class Basidiomycetes, the order Uredinales, and family Pucciniaceae. Even though it is capable of producing urediniospores and basidiospores, only the former infect the coffee plant while the latter have no known susceptible host. Urediniospores infect usually during rainy seasons, since germination requires a 24 to 48 hour continuous presence of free water (rain or heavy dew). Infection occurs over a wide range of temperature: from 15°C to 28°C with an optimum of 22°C, and only occurs through stomata on the underside of the leaf, so it does not form the pustules typical of many rusts. The infected leaves drop prematurely, which reduces photosynthetic capacity and weakens the plant (as seen in the following pictures), altogether reducing next season’s berry yield (as much as 10-fold) (Arneson, 2000).
Bacterial Wilt (Ralstonia solanacearum)
Ralstonia solanacearum attack almost 200 plant species in 33 different plant families. This constitutes one of the largest known host ranges for any plant pathogenic bacterium. The disease it causes is known as Southern wilt, bacterial wilt, and brown rot of potato. Although Solanaceae (potato family) contains the greatest number of susceptible species, many other dicot and a few monocot plants are also susceptible. The important agricultural crops attack by this phytopathogen includes: Potato (Solanum tuberosum); Tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum); Aubergine (egg plant) (Solanum melongena); Banana, (Musa spp); Geranium (common name) (Pelargonium); Ginger (Zingiber officinale); Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum); Sweet pepper (Capsicum spp); Olive (Olea europea) (USDA,2011). According to the USDA is considered an invasive organism and plants infected must be erradicare.
References
- Arneson, P. A. (2000). Coffee rust. The Plant Health Instructor. doi:10.1094/PHI-I-2000-0718-02
- USDA. 2011. National Agricultural Library. Research; Special Note: NAL Catalog Search
 "
"