Team:LMU-Munich/Inverter
From 2012.igem.org
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* To get an explanation of how it works and see the results: [[Team:LMU-Munich/Inverter#Theory and Results|Data and Results]] | * To get an explanation of how it works and see the results: [[Team:LMU-Munich/Inverter#Theory and Results|Data and Results]] | ||
| - | * How to compose your individual Inverter, by fusions PCRs and | + | * How to compose your individual Inverter, by fusions PCRs and 3A assemblies is explained here: [[Team:LMU-Munich/Inverter#Construct your own Inverter|Construct your own Inverter]]</p> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
<p align="justify">The main component of the [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823040 Inverter] is the small RNA RyhB, which natively translationally inhibits the upstream fused region ''uof<sub>CGU</sub>'' of the ''fur'' gene by binding to it and therefore masking Shine Dalgarno sequence. </p> | <p align="justify">The main component of the [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823040 Inverter] is the small RNA RyhB, which natively translationally inhibits the upstream fused region ''uof<sub>CGU</sub>'' of the ''fur'' gene by binding to it and therefore masking Shine Dalgarno sequence. </p> | ||
| + | |||
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | ||
| Line 31: | Line 34: | ||
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="100%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="100%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | ||
|style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | |style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | ||
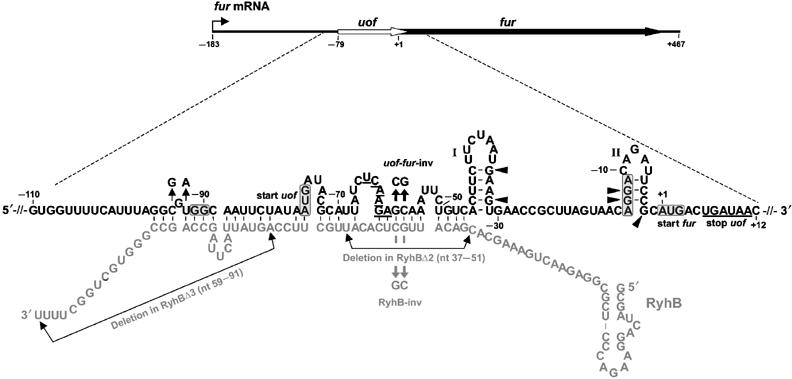
| - | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify"> Fig. 1: Organization of fur mRNA and base-pairing between uof and RyhB. The uof and fur reading frames are depicted by white and black arrows, respectively. The sequence comprising nt −110 to +12 is enlarged. The putative SD sequences and start codons of uof and fur are boxed. The -GG- to -GGAGG- mutation in the putative SD of uof is indicated. </p></font> | + | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify"> '''Fig. 1: Organization of fur mRNA and base-pairing between uof and RyhB.''' The uof and fur reading frames are depicted by white and black arrows, respectively. The sequence comprising nt −110 to +12 is enlarged. The putative SD sequences and start codons of uof and fur are boxed. The -GG- to -GGAGG- mutation in the putative SD of uof is indicated. </p></font> |
<!-- The uof codons UCA6 and AGA7 involved in iron-responsive decoding (see text) and the two consecutive stop codons of uof in the proximal--> | <!-- The uof codons UCA6 and AGA7 involved in iron-responsive decoding (see text) and the two consecutive stop codons of uof in the proximal--> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 53: | ||
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="100%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="100%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | ||
|style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | |style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | ||
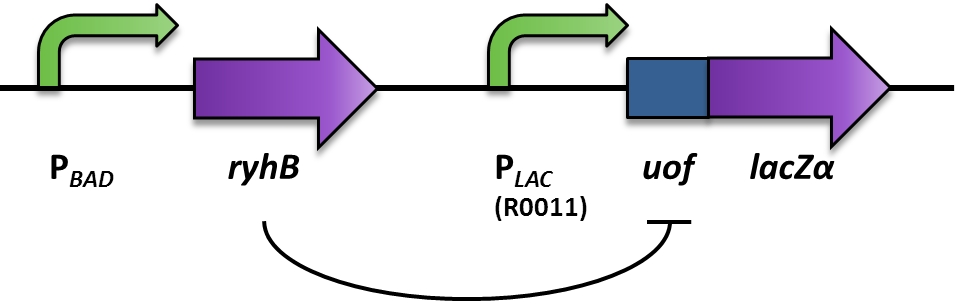
| - | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify"> Fig. 2:Design and functional principle of the Inverter switch. </p></font> | + | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify"> '''Fig. 2: Design and functional principle of the Inverter switch.''' </p></font> |
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 61: | Line 64: | ||
<p align="justify">In order to use the Inverter for the promoters and output of choice, it has to be constructed by fusion PCR (see next section).</p> | <p align="justify">In order to use the Inverter for the promoters and output of choice, it has to be constructed by fusion PCR (see next section).</p> | ||
| + | |||
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="3" width="70%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:left;" | ||
| Line 70: | Line 74: | ||
{| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="100%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | {| style="color:black;" cellpadding="0" width="100%" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="text-align:center;" | ||
|style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | |style="width: 70%;background-color: #EBFCE4;" | | ||
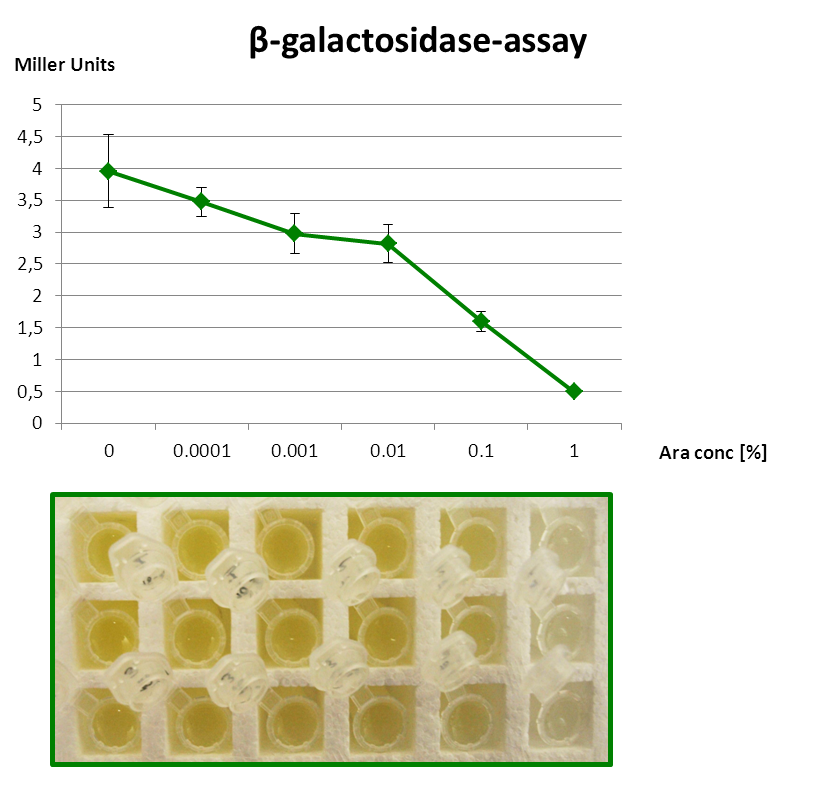
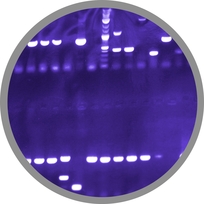
| - | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify"> Fig. 3: β-Galactosidase assay of Inverter with ''lacZα'' as reporter. The higher the arabinose concentration, the higher the translational repression of ''uof<sub>CGU</sub>-lacZα'' </p></font> | + | <font color="#000000"; size="2"><p align="justify"> '''Fig. 3: β-Galactosidase assay of Inverter with ''lacZα'' as reporter.''' The higher the arabinose concentration, the higher the translational repression of ''uof<sub>CGU</sub>-lacZα'' </p></font> |
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
====Construct your own Inverter==== | ====Construct your own Inverter==== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:11, 26 October 2012
The LMU-Munich team is exuberantly happy about the great success at the World Championship Jamboree in Boston. Our project Beadzillus finished 4th and won the prize for the "Best Wiki" (with Slovenia) and "Best New Application Project".
[ more news ]


Last year, the LMU-Munich iGEM team designed a metal-sensing device. This device links metal sensing promoters to a visual output. However, it turned out that some of the promoters that respond to metal ions are negatively regulated. For this purpose, the LMU-Munich 2011 Team started a project to convert a positive input signal into a negative output or vice versa.
Since such a genetic part would be a very beneficial tool, Julia, who also participated in iGEM 2011, continued the work from last year and got some great results.
- To get an explanation of how it works and see the results: Data and Results
- How to compose your individual Inverter, by fusions PCRs and 3A assemblies is explained here: Construct your own Inverter
Theory and Results
The main component of the [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K823040 Inverter] is the small RNA RyhB, which natively translationally inhibits the upstream fused region uofCGU of the fur gene by binding to it and therefore masking Shine Dalgarno sequence.
|
We aimed at using this system to build our inverter (Fig. 2). For a proof of principle, the promoter to be inverted, was the arabionose-inducible PBAD (PCR of [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_I0500 BBa_I0500]), which regulates the expression of the small RNA RyhB (PCR of pURyhB) ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1852835/ Vecerek B., Bläsi U., 2007]). RyhB itself translationally inhibits uofCGU (upstream of fur) (PCR of pRuofCGU-lacZ) ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1852835/ Vecerek B., Bläsi U., 2007]) by binding and masking the Shine Dalgarno sequence. If uofCGU is translationally fused to a reporter, in this case lacZα (PCR from pRuofCGU-lacZ from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1852835/ Vecerek B., Bläsi U., 2007]), expression of the β-galactosidase is translationally repressed. The repression of the reporter is dependent on the concentration of RyhB, and therefore the induction of the PBAD promoter. consequently, the induction of the PBAD promoter is inverted to a negative output of the reporter.
|
The β-galactosidase assay below shows the function of this Inverter. 1 mM IPTG is always present, so that the Reporter is fully induced. When grown with increasing amounts of arabinose in the medium, RyhB is produced and inhibits uofCGU and consequently the fused reporter in a concentration-dependent manner.
But since the PBAD promoter lacks the repressor binding sites, it is leaky and always produces a bit RyhB. Therefore there is always a repression of the reporter. Consequently, we got only a small signal without Arabinose (minimal repression) and the PBAD promoter is generally poorly titratable.
In order to use the Inverter for the promoters and output of choice, it has to be constructed by fusion PCR (see next section).
|
Construct your own Inverter
1. Primer design:
- Promoter (which you would like to invert): BB-suffix + Promoter primer forward (a), GTCTTCCTGATCGCGAGACA + Promoter reverse primer from -10 (b)
- RyhB: TGTCTCGCGATCAGGAAGAC (RyhB fwd) (c), BB-suffix + AAAGCCAGCACCCGGCTGGCTAAG (RyhB rev) (d)
- uof: BB-prefix + GTGGTTTTCATTTAGGCGTG (Uof fwd) (e), Output/Reporter forward primer + GTTATCAGTCATGCGGAATC (uof rev) (f)
- Output/Reporter: Forward primer without BB-prefix (g), Reverse primer with BB-suffix (h)
- basic PCRs: Promoter (a+b), RyhB (c+d), uof (e+f), Output/Reporter (g+h)
- Fusion PCRs: ~ 200 ng equimolar with forward primer of the front and reverse primer of the back fusion part: promoter to RyhB (a+d) and uof to Output/Reporter (e+h)
- 3A assembly of Output/Reporter with a constitutive/inducible promoter like [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_R0011 BBa_R0011]
- 3A assembly of promoter + RyhB with product of step above
 "
"