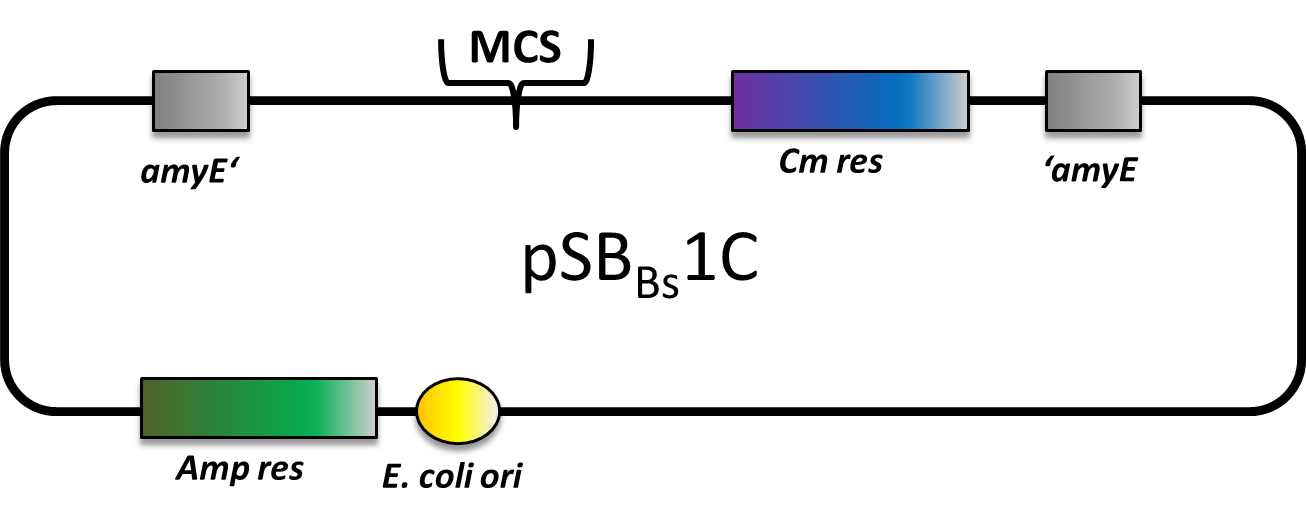Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus BioBricks
From 2012.igem.org
(Promoter Box) |
(Reporter Box) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
{| "width=100%" style="align:right"| | {| "width=100%" style="align:right"| | ||
| | | | ||
| - | <p align="justify">To provide a set of promoters of different strength we characterized several promoters in ''Bacillus subtilis''. | + | <p align="justify">To provide a set of promoters of different strength we characterized several promoters in ''Bacillus subtilis''. Both constitutive and inducible promoters are covered.</p> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| | | | ||
[[File:Promoters overview.png|200px|right|link=Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus BioBricks/Promoters]] | [[File:Promoters overview.png|200px|right|link=Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus BioBricks/Promoters]] | ||
| Line 78: | Line 75: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | <div class="box"> | |
==''Bacillus'' Reporters [[File:LMU Reporter.png|50px]]== | ==''Bacillus'' Reporters [[File:LMU Reporter.png|50px]]== | ||
| - | + | {| "width=100%" style="align:right"| | |
| - | <p align="justify"> | + | | |
| - | We designed and codon-optimized a set of reporters that are commonly used in ''B. subtilis'' | + | <p align="justify">We designed and codon-optimized a set of reporters that are commonly used in ''B. subtilis''.</p> |
| - | + | | | |
| - | + | [[File:LMU GFP.jpg|200px|right|link=Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus BioBricks/Reporters]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| - | + | ! colspan="2" |[[File:LMU Arrow purple.png|40px|link=Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus BioBricks/Reporters]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | | | + | |
| - | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | </div> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | < | + | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Revision as of 20:55, 24 October 2012

The LMU-Munich team is exuberantly happy about the great success at the World Championship Jamboree in Boston. Our project Beadzillus finished 4th and won the prize for the "Best Wiki" (with Slovenia) and "Best New Application Project".
[ more news ]


B4 - 22 core parts for Bacillus subtilis
A major goal of our iGEM project is to introduce B. subtilis as a new chassis for BioBrick-based Synthetic Biology. For that purpose, we created a toolbox of Bacillus BioBricks to contribute to the registry to make it accessible to many more future iGEM-Teams! This Bacillus BioBrick Box (B4) contains the following Bacillus specific parts:
| Vectors | Promoters | Reporters | Affinity tags |

| 
| 
| |
|
pSBBs1C |
Anderson |
gfp |
Flag |
Since Bacillus subtilis is not an organism commonly used in iGEM, please check out our Introduction.
Bacillus Vectors 
Bacillus Promoters 
|
To provide a set of promoters of different strength we characterized several promoters in Bacillus subtilis. Both constitutive and inducible promoters are covered. | |
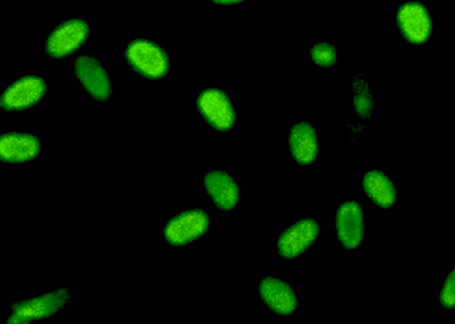
Bacillus Reporters 
|
We designed and codon-optimized a set of reporters that are commonly used in B. subtilis. | |
Affinity Tags 
All our tags have been synthesized by [http://de-de.invitrogen.com/site/de/de/home/Products-and-Services/Applications/Cloning/gene-synthesis.html GeneArt]. They are designed in Freiburg standard with an optimized ribosome binding site upstream. We have not yet tested our tags.
Find out more about the design of our prefix with ribosome binding site.
prefix: GAATTCCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATAAGGAGGAACTACTATGGCCGGC
suffix: ACCGGTTAATACTAGTAGCGGCCGCTGCAGT
- 3x Flag-tag [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K823034 (BioBrick:BBa_K823034)]
The Flag-tag was the first epitope tag to be published ([http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v6/n10/full/nbt1088-1204.html Hopp, Prickett et al. (1988)]). It consists of eight hydrophobic amino acids: DYKDDDDK. To enhence senstitivity in Western blots, it is routinely used as a 3x Flag tag in B. subtilis [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=wiegert%20flag (Kaltwasser et al., 2002)]. Its sequence is: DYKDHDGDYKDHDIDYKDDDDK. There are a variety of monoclonal antibodies against this tag, N-terminal as well as position insensitive.
- HA - tag [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K823035 (BioBrick:BBa_K823035)]
The HA-tag is an epitope derived from the HA-virus. There was first an antibody against it and then the epitope was characterized ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6204768 Wilson, I.A. et al. (1984)]). It was then furthermore used as a tag for protein purification and recognition ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2455217 Field et al. (1988)]). The amino acid sequence is: YPYDVPDYA.
- cMyc - tag [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K823036 (BioBrick:BBa_K823036)]
The cMyc-tag is derived from the cMyc gene product. Antibodies were generated from the immunization with synthetic peptides from the cMyc sequence ([http://mcb.asm.org/content/5/12/3610.short Evan, Bishop et al.(1985)]). The amino acid sequence is EQKLISEEDL.
- His - tag [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K823037 (BioBrick:BBa_K823037)]
The His-tag is a metal chelating peptide ([http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v6/n11/full/nbt1188-1321.html Hochul,Stüber et al. (1988)]) consisting of at least 6 histidin residues. It can be used for protein purification by metal2+ion-containing columns (nickel). There are also antibodies against this tag, or nickel/cobalt containing fluorescent probes can be used for detection. Moreover, an immobilization is possible in nickel/cobalt coated plastikware. The aminoacid sequence is:HHHHHHHHHH
- Strep - tag [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K823038 (BioBrick:BBa_K823038)]
The Strep-tag is a mimicry peptide of biotin which binds to Streptavidin ([http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1050386299000339 Skerra, Schmidt (1999)]). Its sequence is WSHPQFEK. It can be used for protein purification, immobilization with streptavidin or strep-tactin ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9415448 Voss, Skerra (1997)]) or detection with Strep-tactin or antibodies.
| 
| 
| 
|
| Bacillus Intro | Bacillus BioBrickBox | Sporobeads | Germination STOP |
 "
"