Team:Peking
From 2012.igem.org
m |
m |
||
| Line 805: | Line 805: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="floatL" style="margin:0 10px 5px 0;"><table class="title_block" style="background-image:url('/wiki/images/6/68/Peking2012_Color_Title_AquaBlue_ADDMODE.jpg');"><tr><td style="height:262px;"><p style="font-size:36px;">Abstract</p></td></tr></table></div> | <div class="floatL" style="margin:0 10px 5px 0;"><table class="title_block" style="background-image:url('/wiki/images/6/68/Peking2012_Color_Title_AquaBlue_ADDMODE.jpg');"><tr><td style="height:262px;"><p style="font-size:36px;">Abstract</p></td></tr></table></div> | ||
| - | |||
<div class="floatC"><p style="height:30px;"></p></div> | <div class="floatC"><p style="height:30px;"></p></div> | ||
<div class="floatL"> | <div class="floatL"> | ||
Revision as of 12:23, 22 October 2012
O
ptogenetic tools have made a significant impact on life sciences and beyond. However, several serious issues remain: cytotoxicity, narrow dynamic range, and dependency on laser, and exogenous chromophores. To unblock the bottleneck, 2012 Peking-ECUST iGEM has rationally constructed and optimized an ultra-sensitive sensor of luminescence -- the Luminesensor. Amazingly, the Luminesensor was proven to be so sensitive as to be able to detect natural light and even bioluminescence. With this sensor, spatiotemporal control of cellular behavior, such as high-resolution 2D and 3D bio-printing using dim light and even the luminescence of iPad were shown to be very easy. What’s more, we successfully implemented cell-cell signaling using light for the very first time in synthetic biology, which will be of great importance for biotechnological use.
Abstract |

The Luminesensor is able to respond to very low light, which encouraged us to explore the possibility of cell-cell communication through light. We have successfully implemented, for the very first time, light-communication among cells without direct physical contact.

3D printing is a new technology that has been rising for many years. But in the realm of synthetic biology, it is far from developed. We exploited the ultra-sensitive Luminesensor to implement 3D printing that can be utilized in many medical or manufacturing applications.
"Phototatic" bacteria can be built by programming the chemotaxis system in E. coli through light. By controlling the expression level of the CheZ protein with the Luminesensor, the tumbling frequency is coupled to the intensity of light signals.
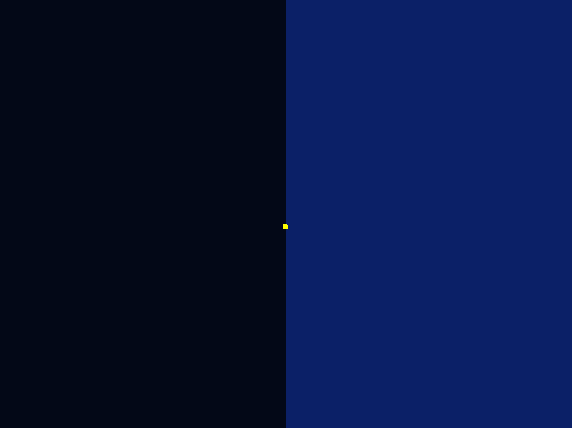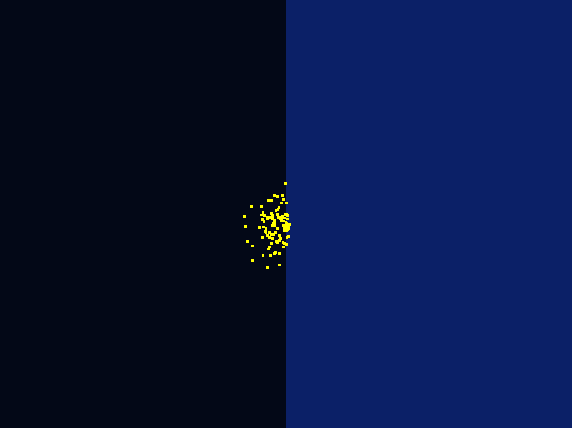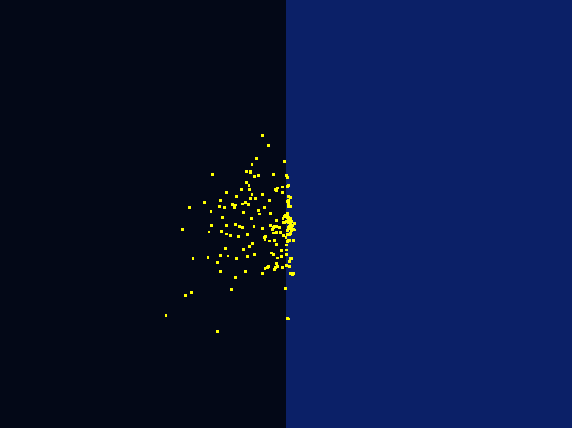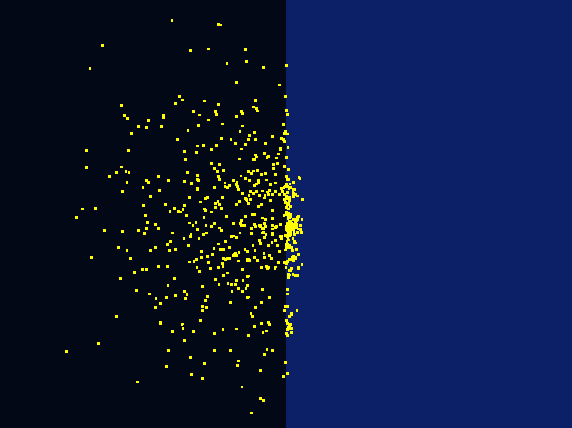
To design our photo-taxis model, we developed a hexagonal-coordinate environment for dynamic simulation of “on-plate" system. Those who focus on cell motility will find it useful and inspirational.

We have done a remarkable job in motivating high school students to study synthetic biology and guiding them towards future participation in the iGEM high school division. Besides, we presented all fresh iGEMers with a collection of praise for historic iGEM projects to share and learn from each other!

Peking-ECUST iGEM team consists 15 undergraduate students from Peking University and 3 graduate students from ECUST who are enjoying synthetic biology.
 "
"