Team:Tokyo Tech/Projects/PHAs/index.htm
From 2012.igem.org
(→4-2 Confirmation of PHB accumulated in cells) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<div class="whitebox"> | <div class="whitebox"> | ||
<div id="tokyotech" style=" font:bold ;left ; font-size: 50px; color: #1E90FF; padding: 10px;"> | <div id="tokyotech" style=" font:bold ;left ; font-size: 50px; color: #1E90FF; padding: 10px;"> | ||
| - | + | P(3HB) Production </div> | |
</div class="whitebox"> | </div class="whitebox"> | ||
<div class="whitebox"> | <div class="whitebox"> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
1.</div> | 1.</div> | ||
=Achivement= | =Achivement= | ||
| - | We made a new biobrick part and succeeded in synthesizing Polyhydroxyalkanoates(PHAs). This is the first Biobrick part to synthesize PHAs. | + | We made a new biobrick part and succeeded in synthesizing Polyhydroxyalkanoates(PHAs). This is the first Biobrick part to synthesize P(3HB), a kind of PHAs. |
| - | In our project, we also drew rose silhouette to produce the balcony scene of “Romeo and Juliet” by the synthesis of | + | In our project, we also drew rose silhouette to produce the balcony scene of “Romeo and Juliet” by the synthesis of P(3HB). |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
<div id="tokyotech" style=" font:bold ;left ; font-size: 30px; color: #0000FF; padding: 2px;"> | <div id="tokyotech" style=" font:bold ;left ; font-size: 30px; color: #0000FF; padding: 2px;"> | ||
2.</div> | 2.</div> | ||
| - | =What is | + | =What is PHAs?= |
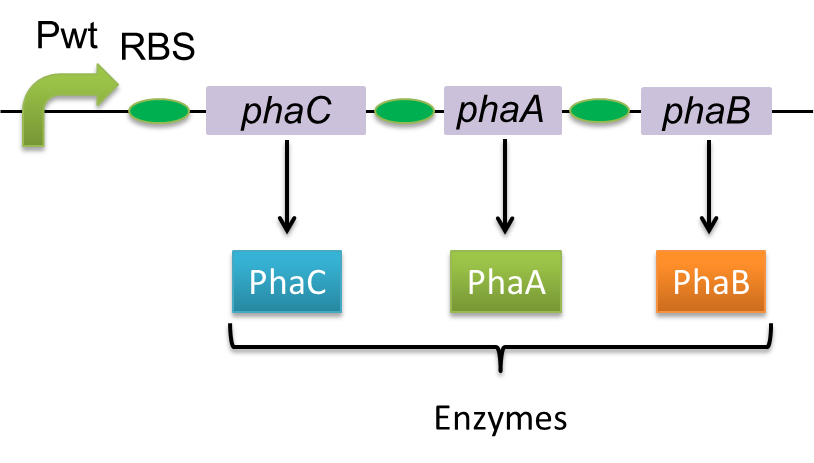
| - | Polyhydroxyalkanoates(PHAs) are biological polyester synthesized by a wide range of bacteria, and can be produced by fermentation from renewable carbon sources such as sugars and vegetable oils. These polyesters are biodegradable thermoplastics and elastomers, which exhibit interesting material properties. PHAs are also a kind of bio plastics, which can be biodegraded a lot faster than fossil-fuel plastics in the environment. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is the most common type of PHAs. P(3HB) is synthesized by the enzymes coded in the gene of PHA synthesis ( | + | Polyhydroxyalkanoates(PHAs) are biological polyester synthesized by a wide range of bacteria, and can be produced by fermentation from renewable carbon sources such as sugars and vegetable oils. These polyesters are biodegradable thermoplastics and elastomers, which exhibit interesting material properties. PHAs are also a kind of bio plastics, which can be biodegraded a lot faster than fossil-fuel plastics in the environment. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is the most common type of PHAs. P(3HB) is synthesized by the enzymes coded in the gene of PHA synthesis (<I>pha C1-A-B1</I>) from <I>Ralstonia eutropha</I> H16. |
| - | [[File:tokyotech PHA whatsPHA.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig2-2-2-1, Gene of PHA synthesis ( | + | [[File:tokyotech PHA whatsPHA.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig2-2-2-1, Gene of PHA synthesis (<I>pha C1-A-B1</I>) from <I>Ralstonia eutropha</I> H16.]] |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
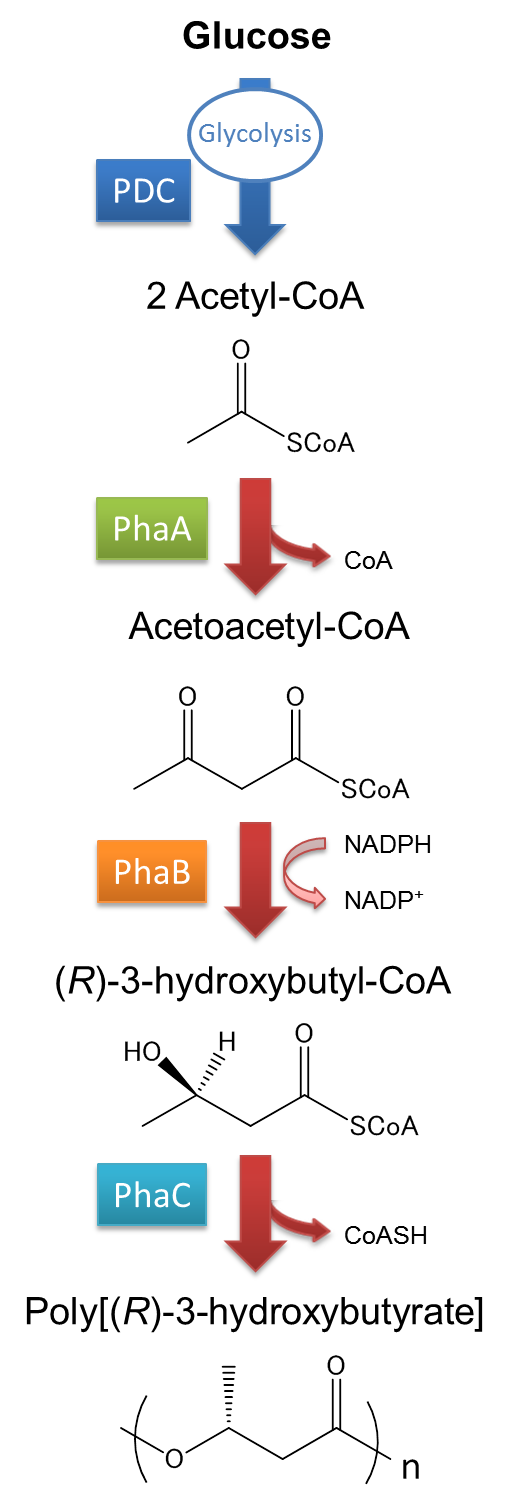
Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is synthesized by three enzymes. | Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is synthesized by three enzymes. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| - | The pathway and regulation of Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], P(3HB) synthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16 is shown in Fig2-2-2-2. Pyruvic acid is metabolized from glucose by glycolysis, and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) transforms pyruvic acid into acetyl-CoA. At first, two molecules of acetyl-CoA are ligated to one molecule acetoacetyl-CoA by the action of 3-ketothiolase (coded in | + | The pathway and regulation of Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], P(3HB) synthesis in <I>Ralstonia eutropha</I> H16 is shown in Fig2-2-2-2. Pyruvic acid is metabolized from glucose by glycolysis, and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) transforms pyruvic acid into acetyl-CoA. At first, two molecules of acetyl-CoA are ligated to one molecule acetoacetyl-CoA by the action of 3-ketothiolase (coded in PhaA). Acetoacetyl-CoA is transformed into (R)-3-hydroxybutyl-CoA by NADPH dependent acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (coded in PhaB). P(3HB) is then synthesized by the polymerization of (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA by the action of PHA synthase (PhaC).([[#Reference|[1][2]]] |
) | ) | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
3.</div> | 3.</div> | ||
| - | =Construction of phaC1-A-B1 in Biobrick format= | + | =Construction of <I>phaC1-A-B1</I> in Biobrick format= |
| - | In this study, we constructed a part containing | + | In this study, we constructed a part containing PHAC1-A-B1 in Biobrick format([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001]).[[https://2012.igem.org/Team:Tokyo_Tech/Projects/PHAs/detail/index.htm#Construction_of_PHA-C1-A-B1_in_Biobrick_format Construction of <I>PHA</I>-C1-A-B1 in Biobrick format]] |
| - | This is the first Biobrick part which worked as expected though some teams had tried to synthesize PHAs in the past iGEM.[[https://2012.igem.org/Team:Tokyo_Tech/Projects/PHAs/detail/index.htm#Production_trial_of_PHAs_by_past_teams Production trial of | + | This is the first Biobrick part which worked as expected though some teams had tried to synthesize PHAs in the past iGEM.[[https://2012.igem.org/Team:Tokyo_Tech/Projects/PHAs/detail/index.htm#Production_trial_of_PHAs_by_past_teams Production trial of <I>PHA</I>s by past teams]] |
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
4.</div> | 4.</div> | ||
| - | = | + | =P(3HB) production by <I>E.coli</I> & Confirmation of P(3HB)= |
| - | To synthesize | + | To synthesize P(3HB) by <I>E.coli</I>, we transformed <I>E.coli</I> JM109 with the constructed <I>pha C1-A-B1</I> part on pSB1C3 ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001]). <I>E.coli</I> JM109 is used to synthesize P(3HB), because it tends to have a high density accumulation of P(3HB)([[#Reference|[5]]] |
). As a negative control, we transformed <I>E.coli</I> JM109 with PlasI-gfp on pSB1C3. | ). As a negative control, we transformed <I>E.coli</I> JM109 with PlasI-gfp on pSB1C3. | ||
| - | ==4-1 Confirmation of | + | ==4-1 Confirmation of P(3HB) synthesized on colonies== |
| - | We observed the accumulation of | + | We observed the accumulation of P(3HB) in the <I>E.coli</I> colonies on Nile red positive medium under UV. Nile red has been widely used to stain colonies and distinguish between PHA-accumulating and non-accumulating colonies. Nile red in the agar medium doesn’t affect the growth of the cells, and the accumulation of PHAs in the colonies can be directly monitored([[#Reference|[3][4][5]]] |
| - | ). We cultured the transformant on LB agar medium plates with Nile red. After several days, colonies storing | + | ). We cultured the transformant on LB agar medium plates with Nile red. After several days, colonies storing P(3HB) were stained orange by Nile red when observed under UV. This result indicates that transformant synthesized and stored P(3HB). |
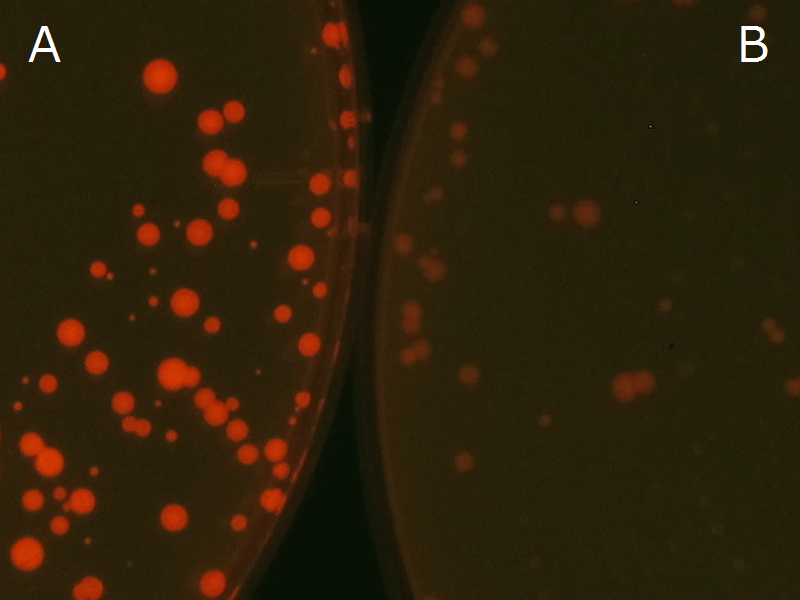
| - | Fig2-2-4-1 is the photographs of <I>E.coli</I> colonies on Nile red positive medium taken under UV. The orange colonies in Fig2-2-4-1A show that the accumulated | + | Fig2-2-4-1 is the photographs of <I>E.coli</I> colonies on Nile red positive medium taken under UV. The orange colonies in Fig2-2-4-1A show that the accumulated P(3HB) in cells was stained by Nile red. This result indicates that part [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] synthesized P(3HB). Fig2-2-4-1B is the photograph of negative control cells. In this figure we observed that there were no remarkable colored colonies. Fig2-2-4-1-2 shows the difference between cells storing P(3HB) and those not storing P(3HB) on one plate. The cells in blue rectangle area are the cells with P(3HB) synthesis gene and the cells in green rectangle area are the cells with PlasI-gfp gene as a negative control. Using the cells storing P(3HB), we drew a rose silhouette on the LB agar plate containing Nile red (Fig2-2-4-1-3).[[https://2012.igem.org/Team:Tokyo_Tech/Projects/PHAs/detail/index.htm#A_.PHB_production_on_colonies_and_preparation_before_confirmation_with_Nile_red_under_UV Protocol]] |
[[File:tokyotech PHA Nilered1.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig2-2-4-1-1 <br>Fig2-2-4-1-1A: <I>E.coli</I> JM109 colonies with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] gene, PHB accumulation | [[File:tokyotech PHA Nilered1.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig2-2-4-1-1 <br>Fig2-2-4-1-1A: <I>E.coli</I> JM109 colonies with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] gene, PHB accumulation | ||
| - | <br>Fig2-2-4-1-1B: <I>E.coli</I> JM109 colonies with PlasI-gfp gene, no | + | <br>Fig2-2-4-1-1B: <I>E.coli</I> JM109 colonies with PlasI-gfp gene, no P(3HB) accumulation]] |
| - | [[File:tokyotech PHA Nilered3.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig2-2-4-1-2, Difference between cells storing | + | [[File:tokyotech PHA Nilered3.png|300px|thumb|left|Fig2-2-4-1-2, Difference between cells storing P(3HB) and cells not storing P(3HB). <br>Blue rectangle: with [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] gene, PHB accumulation. <br>Green rectangle: with PlasI-gfp gene, no PHB accumulation]] |
[[File:tokyotech PHA make rose.png|150px|thumb|right|Fig2-2-4-1-3, Rose silhouette on the LB agar plate containing Nile red.]] | [[File:tokyotech PHA make rose.png|150px|thumb|right|Fig2-2-4-1-3, Rose silhouette on the LB agar plate containing Nile red.]] | ||
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| - | ==4-2 Confirmation of | + | ==4-2 Confirmation of P(3HB) accumulated in cells== |
| - | To confirm the accumulation condition of | + | To confirm the accumulation condition of P(3HB) in <I>E.coli</I> with a microscope, we stained the P(3HB) with Nile blue A reagent. Nile blue A is also used to detect the existence of P(3HB) and has no toxicity to the cells([[#Reference|[5]]]). Before the observation, we stained the dried cells with Nile blue A solution. We then took photographs of the sample under fluorescence microscope. |
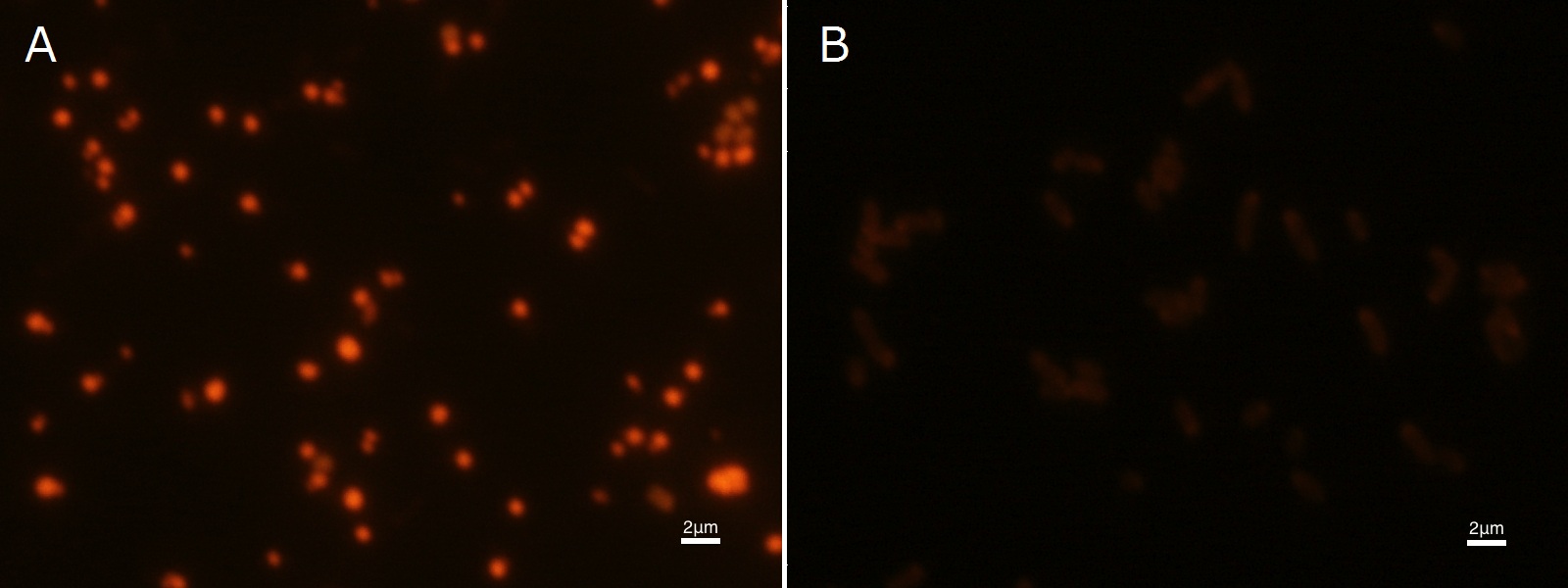
| - | Fig2-2-4-2-1 is the photograph of dried <I>E.coli</I> (with | + | Fig2-2-4-2-1 is the photograph of dried <I>E.coli</I> (with <I>pha C1-A-B1</I> gene) cells dyed with Nile blue A solution taken by fluorescence microscope. The fluorescent areas in Fig2-2-4-2-1A are the accumulated P(3HB) in the cells. This result also indicates that part [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] synthesized P(3HB). In the photograph of negative control (Fig2-2-4-2-1B), no remarkable fluorescent area was observed.[[https://2012.igem.org/Team:Tokyo_Tech/Projects/PHAs/detail/index.htm#B.PHB_production_in_cells_and_preparation_before_the_confirmation_with_Nile_blue_A Protocol]] |
[[File:tokyotech PHA Nileblue1.png|500px|thumb|center| | [[File:tokyotech PHA Nileblue1.png|500px|thumb|center| | ||
| - | Fig2-2-4-2-1A, <I>E.coli</I> JM109 dried cells with | + | Fig2-2-4-2-1A, <I>E.coli</I> JM109 dried cells with P(3HB) accumulation stained by Nile blue A |
| - | Fig2-2-4-2-1B, <I>E.coli</I> JM109 dried cells without | + | Fig2-2-4-2-1B, <I>E.coli</I> JM109 dried cells without P(3HB) accumulation stained by Nile blue A |
]] | ]] | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
=Possible Synbio research area by using our achievement= | =Possible Synbio research area by using our achievement= | ||
| - | [[File:tokyotech PHA perspective.png|200px|thumb|right|Fig2-2-5-1, PHA gene expression spatially manipulated]] | + | [[File:tokyotech PHA perspective.png|200px|thumb|right|Fig2-2-5-1, PHA synthesis gene expression spatially manipulated]] |
The achievement of our project “PHAs Production” is that we registered available PHA synthetic gene in Biobrick parts. | The achievement of our project “PHAs Production” is that we registered available PHA synthetic gene in Biobrick parts. | ||
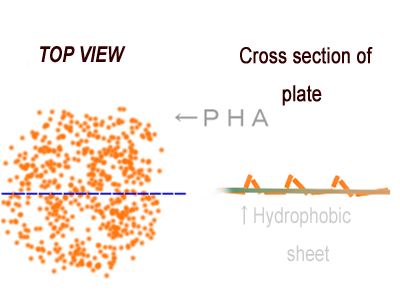
We can control the expression of the PHA synthetic gene spatially by using combination of Biobrick parts. What we want to claim as an example of the spatial manipulation of gene expression is water-repellent. A stronger water-repellent requires hydrophobicity as well as the increase in real surface area that can be achieved as ruggedness of PHA adsorbed on particular surface. If we can control the expression of the PHA synthetic gene spatially by using genetic parts which are registered in Biobrick parts, the application of a super water-repellent sheet will become available. We note this as to the future prospects of our project. | We can control the expression of the PHA synthetic gene spatially by using combination of Biobrick parts. What we want to claim as an example of the spatial manipulation of gene expression is water-repellent. A stronger water-repellent requires hydrophobicity as well as the increase in real surface area that can be achieved as ruggedness of PHA adsorbed on particular surface. If we can control the expression of the PHA synthetic gene spatially by using genetic parts which are registered in Biobrick parts, the application of a super water-repellent sheet will become available. We note this as to the future prospects of our project. | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
[6] Vladimir K. Vanag, Cross-diffusion and pattern formation in reaction–diffusion systems, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics(2009), vol 11.897-912 | [6] Vladimir K. Vanag, Cross-diffusion and pattern formation in reaction–diffusion systems, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics(2009), vol 11.897-912 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [7] Pohlmann A, et al, Genome sequence of the bioplastic-producing "Knallgas" bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16, Nat Biotechnol 24:1257-62 (2006) | ||
Revision as of 06:36, 21 October 2012
Contents |
Achivement
We made a new biobrick part and succeeded in synthesizing Polyhydroxyalkanoates(PHAs). This is the first Biobrick part to synthesize P(3HB), a kind of PHAs.
In our project, we also drew rose silhouette to produce the balcony scene of “Romeo and Juliet” by the synthesis of P(3HB).
What is PHAs?
Polyhydroxyalkanoates(PHAs) are biological polyester synthesized by a wide range of bacteria, and can be produced by fermentation from renewable carbon sources such as sugars and vegetable oils. These polyesters are biodegradable thermoplastics and elastomers, which exhibit interesting material properties. PHAs are also a kind of bio plastics, which can be biodegraded a lot faster than fossil-fuel plastics in the environment. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is the most common type of PHAs. P(3HB) is synthesized by the enzymes coded in the gene of PHA synthesis (pha C1-A-B1) from Ralstonia eutropha H16.
Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, P(3HB) is synthesized by three enzymes.
The A gene encodes for the 393 amino acids protein, 3-ketothiolase (PhaA)
The B gene encodes for the 246 amino acids protein, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (PhaB)
The C gene encodes for the 589 amino acids protein, PHA Synthase (PhaC)
The pathway and regulation of Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], P(3HB) synthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16 is shown in Fig2-2-2-2. Pyruvic acid is metabolized from glucose by glycolysis, and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) transforms pyruvic acid into acetyl-CoA. At first, two molecules of acetyl-CoA are ligated to one molecule acetoacetyl-CoA by the action of 3-ketothiolase (coded in PhaA). Acetoacetyl-CoA is transformed into (R)-3-hydroxybutyl-CoA by NADPH dependent acetoacetyl-CoA reductase (coded in PhaB). P(3HB) is then synthesized by the polymerization of (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA by the action of PHA synthase (PhaC).([1][2]
)
Construction of phaC1-A-B1 in Biobrick format
In this study, we constructed a part containing PHAC1-A-B1 in Biobrick format([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001]).[Construction of PHA-C1-A-B1 in Biobrick format]
This is the first Biobrick part which worked as expected though some teams had tried to synthesize PHAs in the past iGEM.[Production trial of PHAs by past teams]
P(3HB) production by E.coli & Confirmation of P(3HB)
To synthesize P(3HB) by E.coli, we transformed E.coli JM109 with the constructed pha C1-A-B1 part on pSB1C3 ([http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001]). E.coli JM109 is used to synthesize P(3HB), because it tends to have a high density accumulation of P(3HB)([5] ). As a negative control, we transformed E.coli JM109 with PlasI-gfp on pSB1C3.
4-1 Confirmation of P(3HB) synthesized on colonies
We observed the accumulation of P(3HB) in the E.coli colonies on Nile red positive medium under UV. Nile red has been widely used to stain colonies and distinguish between PHA-accumulating and non-accumulating colonies. Nile red in the agar medium doesn’t affect the growth of the cells, and the accumulation of PHAs in the colonies can be directly monitored([3][4][5] ). We cultured the transformant on LB agar medium plates with Nile red. After several days, colonies storing P(3HB) were stained orange by Nile red when observed under UV. This result indicates that transformant synthesized and stored P(3HB). Fig2-2-4-1 is the photographs of E.coli colonies on Nile red positive medium taken under UV. The orange colonies in Fig2-2-4-1A show that the accumulated P(3HB) in cells was stained by Nile red. This result indicates that part [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] synthesized P(3HB). Fig2-2-4-1B is the photograph of negative control cells. In this figure we observed that there were no remarkable colored colonies. Fig2-2-4-1-2 shows the difference between cells storing P(3HB) and those not storing P(3HB) on one plate. The cells in blue rectangle area are the cells with P(3HB) synthesis gene and the cells in green rectangle area are the cells with PlasI-gfp gene as a negative control. Using the cells storing P(3HB), we drew a rose silhouette on the LB agar plate containing Nile red (Fig2-2-4-1-3).[Protocol]
4-2 Confirmation of P(3HB) accumulated in cells
To confirm the accumulation condition of P(3HB) in E.coli with a microscope, we stained the P(3HB) with Nile blue A reagent. Nile blue A is also used to detect the existence of P(3HB) and has no toxicity to the cells([5]). Before the observation, we stained the dried cells with Nile blue A solution. We then took photographs of the sample under fluorescence microscope. Fig2-2-4-2-1 is the photograph of dried E.coli (with pha C1-A-B1 gene) cells dyed with Nile blue A solution taken by fluorescence microscope. The fluorescent areas in Fig2-2-4-2-1A are the accumulated P(3HB) in the cells. This result also indicates that part [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K934001 BBa_K934001] synthesized P(3HB). In the photograph of negative control (Fig2-2-4-2-1B), no remarkable fluorescent area was observed.[Protocol]
Possible Synbio research area by using our achievement
The achievement of our project “PHAs Production” is that we registered available PHA synthetic gene in Biobrick parts.
We can control the expression of the PHA synthetic gene spatially by using combination of Biobrick parts. What we want to claim as an example of the spatial manipulation of gene expression is water-repellent. A stronger water-repellent requires hydrophobicity as well as the increase in real surface area that can be achieved as ruggedness of PHA adsorbed on particular surface. If we can control the expression of the PHA synthetic gene spatially by using genetic parts which are registered in Biobrick parts, the application of a super water-repellent sheet will become available. We note this as to the future prospects of our project.
Reference
[1] Jumiarti Agus, Altered expression of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene and its effect on poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] synthesis in recombinant Escherichia coli, Polymer Degradation and Stability(2006) 91:1645-1650
[2] Joanne Stubbe and Jiamin Tian, Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) homeostasis: the role of the PHA synthase, 2003, Nat. Prod. Rep.,20, 445–457.
[3] Stanley D. Fowler and Phillip Greenspan, Application of Nile red, a fluorescent hydrophobic probe, for the detection of neutral lipid deposits in tissue sections, Histochemistry & Cytochemistry(1985), vol 33.No 8, 833-836
[4] Pinzon NM, Nile red detection of bacterial hydrocarbons and ketones in a high-throughput format, mBio (2011),vol 2. issue 4.e-00109-11
[5] Patricia Spiekermann, A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds, Arch Microbiol (1999), 171:73–80
[6] Vladimir K. Vanag, Cross-diffusion and pattern formation in reaction–diffusion systems, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics(2009), vol 11.897-912
[7] Pohlmann A, et al, Genome sequence of the bioplastic-producing "Knallgas" bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16, Nat Biotechnol 24:1257-62 (2006) "
"