Team:British Columbia/Pathway
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
The study of environmental genomics attempts to capture the taxonomic and functional diversity of natural microbial communities. Our host at UBC, the Hallam lab, designs novel tools for analyzing the gene content in the context of distributed metabolism. Recently, a pipeline has been developed for the automated construction and visualizing of metabolic pathways from genomic data by integrating software such as Pathway Tools, Pathologic and Metacyc [1]. This provided us an opportunity to model pathway compartmentalization and distribution amongst microbes in the natural environment as it applies to our project. </br></br> | The study of environmental genomics attempts to capture the taxonomic and functional diversity of natural microbial communities. Our host at UBC, the Hallam lab, designs novel tools for analyzing the gene content in the context of distributed metabolism. Recently, a pipeline has been developed for the automated construction and visualizing of metabolic pathways from genomic data by integrating software such as Pathway Tools, Pathologic and Metacyc [1]. This provided us an opportunity to model pathway compartmentalization and distribution amongst microbes in the natural environment as it applies to our project. </br></br> | ||
| - | <h2>Summary of the pipeline for community-level metabolic analysis (Figure 1):</h2> First, open reading frames predicted from sequence data | + | <h2><b>Summary of the pipeline for community-level metabolic analysis (Figure 1):</b></h2> First, open reading frames are predicted from sequence data with Prodigal, are then annotated by protein BLAST, and later summarized in a GenBank file. Pathway/genome databases (PGDBs) are generated from sequence data in a manner which does not constrain predictions within the scope of model organisms. This produces a community-based analysis that can be visualized using Pathway Tools. |
<p align=center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/9/9c/UbcigemSlide1.jpg"></p> | <p align=center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/9/9c/UbcigemSlide1.jpg"></p> | ||
| - | <b>Modeling Metabolism:</b> <i>Rhodococcus erythropolis</i> and <i>Pseudomnas fluorescens</i> are often both prevalent in similar niches. With a high likelihood that these organisms encounter each other, studies have been conducted to assess their metabolic properties in co-culture. In a study by Kayser et al, it was shown that the | + | <h2><b>Modeling Metabolism:</b></h2> <i>Rhodococcus erythropolis</i> and <i>Pseudomnas fluorescens</i> are often both prevalent in similar niches. With a high likelihood that these organisms encounter each other, studies have been conducted to assess their metabolic properties in co-culture. In a study by Kayser et al, it was shown that the 4S biodesulferization pathway in <i>R. erythropolis</i> demonstrated higher activity the presence of <i>P. fluorescens</i> [2]. As <i>P. fluorescens</i> does not biodesulferize DBT and sulfate is known to repress the 4S pathway, we looked to analyze the genomes of the two organisms in the context of sulfur metabolism. </br></br> |
| - | The | + | The 4S pathway releases sulfite, which is toxic to the cell, and therefore genomes were analyzed with the aforementioned pipeline for pathways involved in metabolizing sulfite. It was found that both organisms have annotated genes which convert sulfite into sulfate via a reductase, however the organisms differ in downstream metabolism of sulfate. While both organisms contain a pathway for assimilatory sulfate metabolism, only <i>P. fluorescens</i> has the capability for dissimilatory sulfate metabolism (Figure 2, 3). Based on these findings, we can hypothesize that <i>R. erythropolis</i> and <i>P. fluorescens</i> likely excrete and catabolize any excess sulfate. This provides an explanation for the improved desulfurization found in co-culture conditions. <i>P. fluorescens</i> potentially removes sulfate from the environment, allowing increased secretion by <i>R. erythropolis</i>, and thereby derepressing 4S pathway. The prediction of distributed sulfite metabolism to improve biodesulferization in the environment provides both a testable hypothesis, as well as a grounds for improving biodesulferization through synthetic pathway distribution. </br></br> |
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| - | We then | + | We then scanned the literature for more evidence of shared metabolism between both <i>R. erythropolis</i> and <i>P. fluorescens</i> in order to further analyze gene content in the context of co-culture experiments. In a study by Goswami et al., the metabolism of chlorinated aromatic compounds and phenol was compared in monoculture versus co-culture using <i>R. erythropolis</i> and <i>P. fluorescens</i> [3]. This study showed that the growth rate of pure cultures of <i>R. erythropolis</i> was higher than <i>P. fluorescens</i> on chlorinated aromatics, however in mixed culture, <i>P. fluorescens</i> showed a higher growth rate. For the degradation of phenol, <i>R. erythropolis</i> showed higher growth rates in both pure and mixed culture. The authors of this study suggested that these results were likely a product of substrate competition. We attempted to analyze the genomes of both <i>R. erythropolis</i> and <i>P. fluorescens</i>, separately and together in an attempt to offer an alternate interpretation of the co-culture results. The first pathways assessed were those involved in chlorinated aromatic degradation. It was found that <i>P. fluorescens</i> contains a higher diversity of genes involved in catabolizing chlorinated aromatics; however, only <i>R. erythropolis</i> seems to be able to degrade phenol (Figure 4, 5). This suggests the possibility of the compartmentalization of different components of these metabolic processes, leading to the different growth kinetics observed in co-culture. For example, while <i>R. erythropolis</i> may be more efficient at degrading certain chlorinated aromatics, in co-culture, the diversity of catabolism of chlorinated aromatics allows <i>P. fluorescens</i> to grow more rapidly. Chlorinated aromatic degradation by <i>P. fluorescens</i>, however, would result in the accumulation of downstream products, such as phenol, that only <i>R. erythropolis</i> can catabolism. This provides a metabolic network which could both select and sustain both microbes in the presence of diverse chlorinated aromatics. </br> |
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
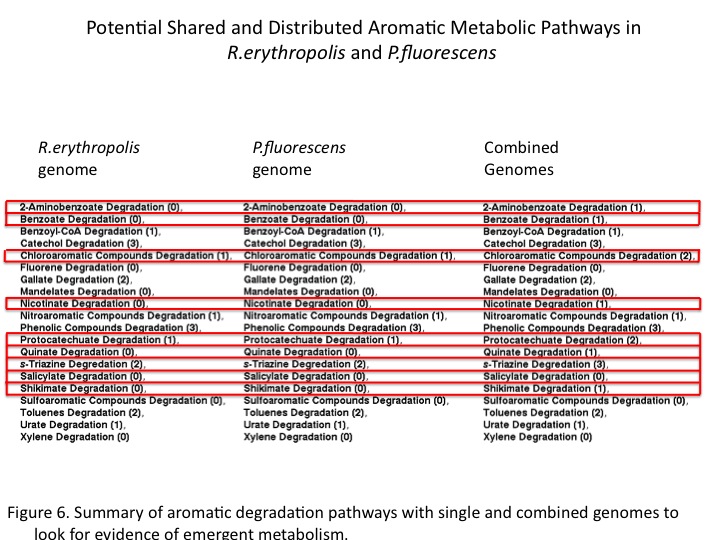
| - | + | The sums of general aromatic degradation pathways were compared for the organisms genomes separately and together (Figure 6). This resulted in emergent predicted pathways in combination as well as combinatorial increases araomatic degradation potential. <br /> | |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | Ultimately, gene annotation-based models for distributed metabolism in the environment may help to engineer and optimize complex metabolism through synthetic consortia. </br> | ||
<p align=center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/a/aa/UbcigemSlide6.jpg"></p></br></br> | <p align=center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/a/aa/UbcigemSlide6.jpg"></p></br></br> | ||
| + | <h2><b>References</b></h2><br /> | ||
[1] Hanson, N.W; Page, A.P; Konwar, K.M; Howes, C.G; Hallam, S.J. Metabolic interaction networks for the whole community, 2012. Unpublished.</br></br> | [1] Hanson, N.W; Page, A.P; Konwar, K.M; Howes, C.G; Hallam, S.J. Metabolic interaction networks for the whole community, 2012. Unpublished.</br></br> | ||
| - | [2] Kayser, K.J; Biolaga-Jones, B.A.; Jackowski, K; Odusan, O; Kildane, J.J. Utilzation of organosulfur compounds by anexic and mixed culture of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IGTS8, 1993. Journal of General Microbioology, 139: 3123-3129.</br></br> | + | [2] Kayser, K.J; Biolaga-Jones, B.A.; Jackowski, K; Odusan, O; Kildane, J.J. Utilzation of organosulfur compounds by anexic and mixed culture of <i>Rhodococcus rhodochrous</i> IGTS8, 1993. Journal of General Microbioology, 139: 3123-3129.</br></br> |
| - | [3] Goswami, M; Shivaraman, N; Singh, R.P. Microbial metabolism of 2-chlorophenol, phenol and p-cresol by Rhodococcus erythropolis M1 and co-culture with Pseudomonas fluorescens P1, 2005. Microbiological Research, 160: 101-109.</br></br> | + | [3] Goswami, M; Shivaraman, N; Singh, R.P. Microbial metabolism of 2-chlorophenol, phenol and p-cresol by <i>Rhodococcus erythropolis</i> M1 and co-culture with <i>Pseudomonas fluorescens</i> P1, 2005. Microbiological Research, 160: 101-109.</br></br> |
Latest revision as of 03:26, 4 October 2012

Our Pathway Model
The study of environmental genomics attempts to capture the taxonomic and functional diversity of natural microbial communities. Our host at UBC, the Hallam lab, designs novel tools for analyzing the gene content in the context of distributed metabolism. Recently, a pipeline has been developed for the automated construction and visualizing of metabolic pathways from genomic data by integrating software such as Pathway Tools, Pathologic and Metacyc [1]. This provided us an opportunity to model pathway compartmentalization and distribution amongst microbes in the natural environment as it applies to our project.Summary of the pipeline for community-level metabolic analysis (Figure 1):
First, open reading frames are predicted from sequence data with Prodigal, are then annotated by protein BLAST, and later summarized in a GenBank file. Pathway/genome databases (PGDBs) are generated from sequence data in a manner which does not constrain predictions within the scope of model organisms. This produces a community-based analysis that can be visualized using Pathway Tools.
Modeling Metabolism:
Rhodococcus erythropolis and Pseudomnas fluorescens are often both prevalent in similar niches. With a high likelihood that these organisms encounter each other, studies have been conducted to assess their metabolic properties in co-culture. In a study by Kayser et al, it was shown that the 4S biodesulferization pathway in R. erythropolis demonstrated higher activity the presence of P. fluorescens [2]. As P. fluorescens does not biodesulferize DBT and sulfate is known to repress the 4S pathway, we looked to analyze the genomes of the two organisms in the context of sulfur metabolism. The 4S pathway releases sulfite, which is toxic to the cell, and therefore genomes were analyzed with the aforementioned pipeline for pathways involved in metabolizing sulfite. It was found that both organisms have annotated genes which convert sulfite into sulfate via a reductase, however the organisms differ in downstream metabolism of sulfate. While both organisms contain a pathway for assimilatory sulfate metabolism, only P. fluorescens has the capability for dissimilatory sulfate metabolism (Figure 2, 3). Based on these findings, we can hypothesize that R. erythropolis and P. fluorescens likely excrete and catabolize any excess sulfate. This provides an explanation for the improved desulfurization found in co-culture conditions. P. fluorescens potentially removes sulfate from the environment, allowing increased secretion by R. erythropolis, and thereby derepressing 4S pathway. The prediction of distributed sulfite metabolism to improve biodesulferization in the environment provides both a testable hypothesis, as well as a grounds for improving biodesulferization through synthetic pathway distribution.



Ultimately, gene annotation-based models for distributed metabolism in the environment may help to engineer and optimize complex metabolism through synthetic consortia.
References
[1] Hanson, N.W; Page, A.P; Konwar, K.M; Howes, C.G; Hallam, S.J. Metabolic interaction networks for the whole community, 2012. Unpublished. [2] Kayser, K.J; Biolaga-Jones, B.A.; Jackowski, K; Odusan, O; Kildane, J.J. Utilzation of organosulfur compounds by anexic and mixed culture of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IGTS8, 1993. Journal of General Microbioology, 139: 3123-3129. [3] Goswami, M; Shivaraman, N; Singh, R.P. Microbial metabolism of 2-chlorophenol, phenol and p-cresol by Rhodococcus erythropolis M1 and co-culture with Pseudomonas fluorescens P1, 2005. Microbiological Research, 160: 101-109.
 "
"