Team:KAIT Japan/Project
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→E.coli which kill cancer cells.) |
(→E.coli which kill cancer cells.) |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
:Such a mechanism make lose the capital components of immune response towards tumor compromise.(fig1) | :Such a mechanism make lose the capital components of immune response towards tumor compromise.(fig1) | ||
:Natural killer cell is a kind of immune cells participating in an immune system. NK cells have some receptor on the membrane surface, and one of those is the membrane protein called NKG2D. NKG2D can receive stress protein which is called MICA. MICA express the membrane of cancer cells. | :Natural killer cell is a kind of immune cells participating in an immune system. NK cells have some receptor on the membrane surface, and one of those is the membrane protein called NKG2D. NKG2D can receive stress protein which is called MICA. MICA express the membrane of cancer cells. | ||
| - | :<div align="right"><div style="margin-right:183px">'''fig1'''</div></div> | + | :<div align="right"><div style="margin-right:183px"> '''fig1,attracted regulatory T cells '''</div></div> |
:NKG2D is a receptor of MICA which is a stress protein. MICA exist on the surface of the membrane cancer cells. | :NKG2D is a receptor of MICA which is a stress protein. MICA exist on the surface of the membrane cancer cells. | ||
:We thought that E.coli could be combined with a cancer cell by recombinant NKG2D in E.coli. | :We thought that E.coli could be combined with a cancer cell by recombinant NKG2D in E.coli. | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
<p>[[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-04.png|left|366px]] | <p>[[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-04.png|left|366px]] | ||
[[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-05.png|center|367px]]</p> | [[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-05.png|center|367px]]</p> | ||
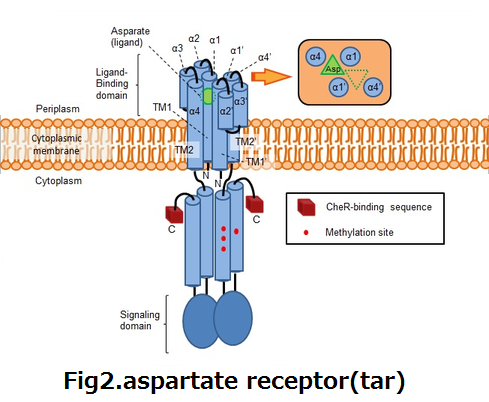
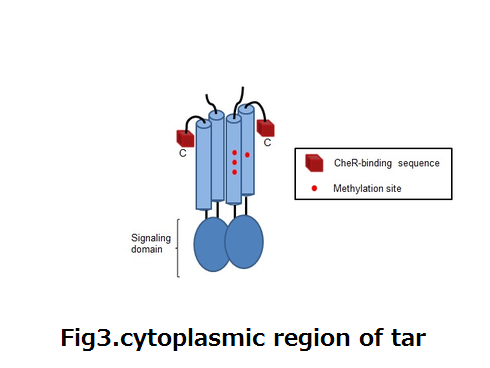
| - | :<p><div align="left"><div style="margin-left:120px">'''fig2'''</div></div><div align="right"><div style="margin-right:300px">'''fig3'''</div></div></p> | + | :<p><div align="left"><div style="margin-left:120px">'''fig2.aspartate receptor(tar)'''</div></div><div align="right"><div style="margin-right:300px">'''fig3.cytoplasmic region of tar'''</div></div></p> |
[[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-07.png|right|366px]] | [[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-07.png|right|366px]] | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
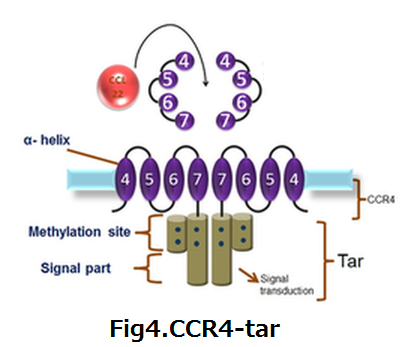
| - | :<div align="right"><div style="margin-right:200px">'''fig4'''</div></div> | + | :<div align="right"><div style="margin-right:200px">'''fig4.CCR4-tar'''</div></div> |
:'''3-3 When MICA is recepted by NKG2D , How E.coli product Azurin?''' | :'''3-3 When MICA is recepted by NKG2D , How E.coli product Azurin?''' | ||
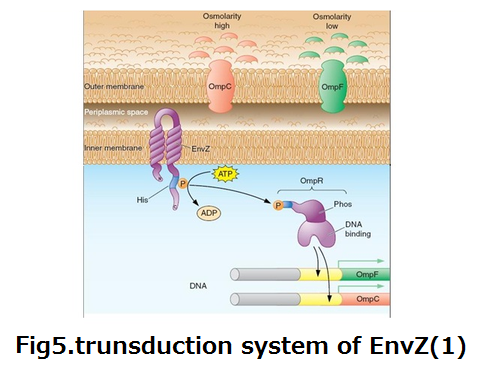
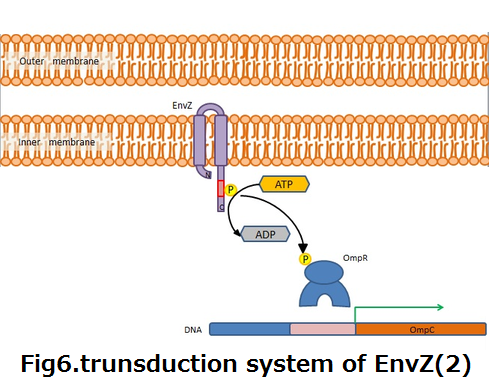
::Membrane protein EnvZ cascade, E.coli has it orijinall, as a osmolality sensor was used for the system what product Azurin by a signal for NKG2D. | ::Membrane protein EnvZ cascade, E.coli has it orijinall, as a osmolality sensor was used for the system what product Azurin by a signal for NKG2D. | ||
::EnvZ perceive osmolality shift, and control expression of membrane protein OmpF and OmpC on the gene level.(fig5,6) | ::EnvZ perceive osmolality shift, and control expression of membrane protein OmpF and OmpC on the gene level.(fig5,6) | ||
| - | ::Histidine which intracellular part of EnvZ is phosphorylated by ATP when the factor of osmolality shift is receptived to EnvZ. Then OmpR that is activator enhance OmpC. | + | ::Histidine which intracellular part of EnvZ is phosphorylated by ATP when the factor of osmolality shift is receptived to EnvZ. Then OmpR that is activator enhance OmpC. |
::We applied the cascade to produce Azurin. | ::We applied the cascade to produce Azurin. | ||
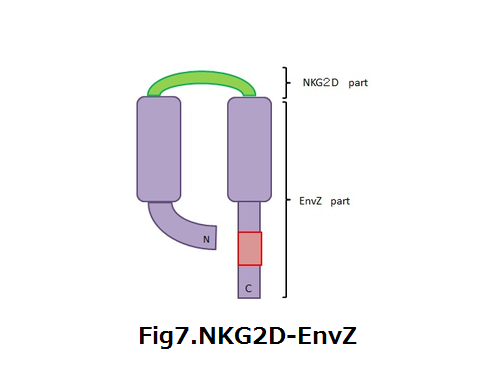
| - | ::We designed that azurin is produced by converting OmpC part to gene of azurin when MICA bond with NKG2D-EnvZ. | + | ::We designed that azurin is produced by converting OmpC part to gene of azurin when MICA bond with NKG2D-EnvZ(fig7). |
<p>[[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-01.png|left|366px]] | <p>[[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-01.png|left|366px]] | ||
[[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-02.png|center|366px]]</p> | [[file:KAIT_JAPAN-Project-emvz-02.png|center|366px]]</p> | ||
| - | :<p><div align="left"><div style="margin-left:120px">'''fig5'''</div></div><div align="right"><div style="margin-right:300px">'''fig6'''</div></div></p> | + | :<p><div align="left"><div style="margin-left:120px">'''fig5.trunsduction system of EnvZ(1)'''</div></div><div align="right"><div style="margin-right:300px">'''fig6.trunsduction system of EnvZ(2)'''</div></div></p> |
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
| - | + | :<div align="right"><div style="margin-right:200px">'''fig7.NKG2D-EnvZ'''</div></div> | |
| - | :<div align="right"><div style="margin-right:200px">'''fig7'''</div></div> | + | |
Revision as of 01:34, 27 September 2012
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E.coli which kill cancer cells.http://partsregistry.org/wiki/images/1/1d/Biosafety_Level1.png Biosafety Level 1
|
 "
"