Team:Peking/Project/Phototaxis/Design
From 2012.igem.org
m |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<div class="floatC"> | <div class="floatC"> | ||
<img src="/wiki/images/8/88/Hposhvposdijpdoigj.png" alt="Figure 1." style="width:600px"/> | <img src="/wiki/images/8/88/Hposhvposdijpdoigj.png" alt="Figure 1." style="width:600px"/> | ||
| - | <p class="description">Figure 1. Gene circuit for Phototaxis.</p> | + | <p class="description" style="text-align:center;width:350px;">Figure 1. Gene circuit for Phototaxis.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<p>After gathering principles and parameters of chemotaxis system, we then simulated the phototaxis system in a stochastic way to reflectively describe the phototaxis mechanism of our system(See <a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Peking/Modeling/Phototaxis">Details Here</a>).</p> | <p>After gathering principles and parameters of chemotaxis system, we then simulated the phototaxis system in a stochastic way to reflectively describe the phototaxis mechanism of our system(See <a href="https://2012.igem.org/Team:Peking/Modeling/Phototaxis">Details Here</a>).</p> | ||
Revision as of 18:45, 26 September 2012
Design
CheZ is dephosphorylase of CheY in chemotaxis pathway. Three main characteristics actuate our consideration of CheZ. First, several experiments indicate that CheZ can effect the movement of bacteria: Increasing levels of CheZ induced by arabinose can enlarge the diameter of swarming colony. CheZ deletion causes cells to tumble incessantly, resulting in a nonmotile phenotype in semisolid agar. Reintroducing CheZ restores cell motility. Second, CheZ is commonly used as motility-control module in synthetic biology. Combination between the CheZ and quorum sensing LuxI/R part forms stripe pattern in colony. Bacteria with CheZ under the control of an atrazine binding riboswitch proves capability of atrazine chemotaxis. CheZ controlled by theophylline riboswitch of upstream random sequence acts as a colony reporter for orthogenesis. Furthermore, CheZ is included in some downsteam locomotive part of bacteria phototaxis such as Halobacterium. On this basis, we decided to use CheZ to control the mobility of the bacteria.
Through rational consideration, we embark on building the circuit. CheZ can only function at a high expression level, so we linked CheZ with strongest RBS B0034 and a high copy plasmid. The circuit of our phototaxis part consists two plasmids containing Luminesensor and CheZ, respectively. Bacteria illuminated by blue light leads to repression of CheZ expression, resulting to lack of cell motility.
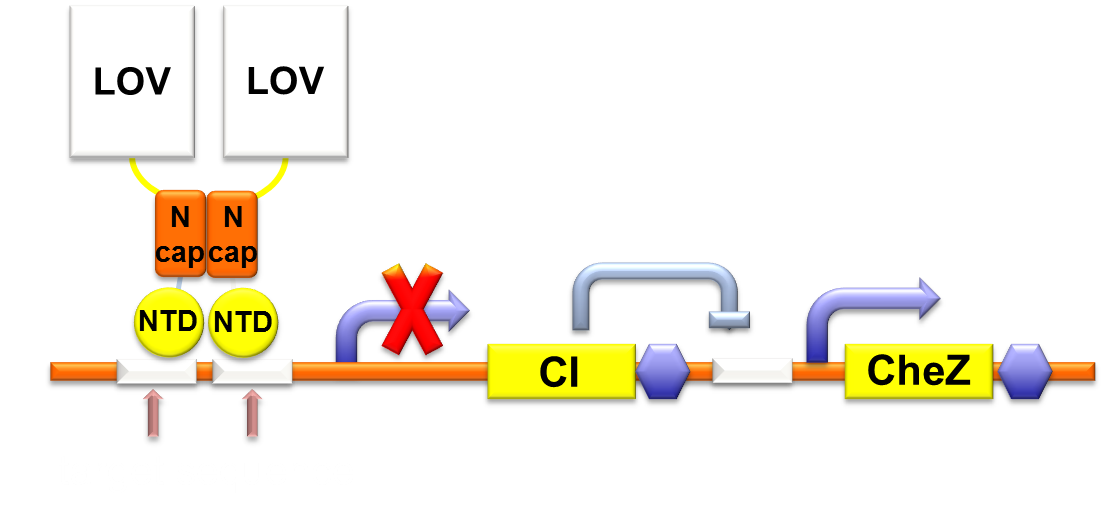
Figure 1. Gene circuit for Phototaxis.
After gathering principles and parameters of chemotaxis system, we then simulated the phototaxis system in a stochastic way to reflectively describe the phototaxis mechanism of our system(See Details Here).
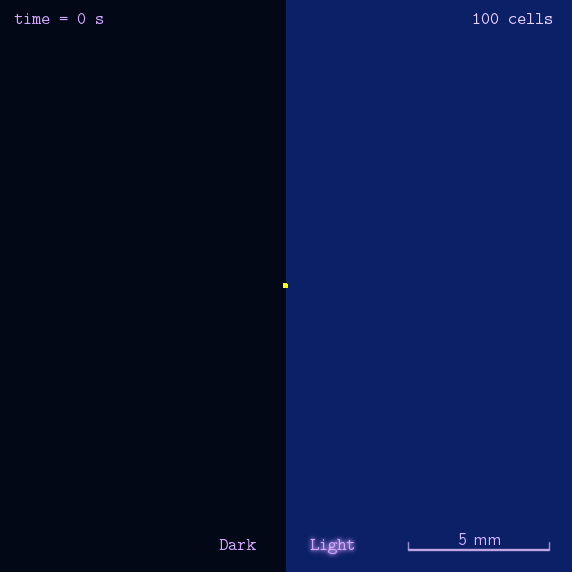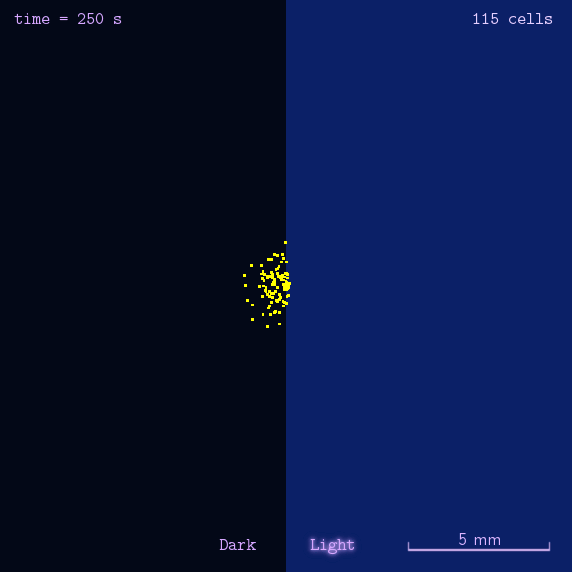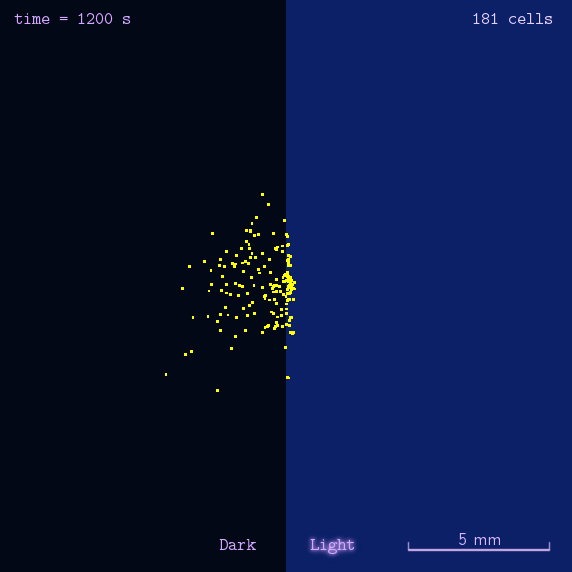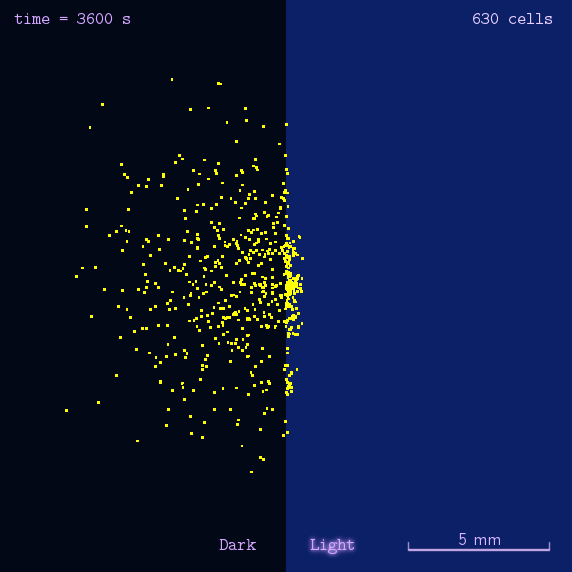
Figure 2. Modeling result of phototaxis behavior.
As the modeling indicated, we designed several experiments to realize phototaxis. Firstly, we have to verify the function of CheZ. Two experiments were designed: the measurement of diameter of mobile (MG1655) and immobile (DH5 α and ΔCheZ MG1655) bacteria and the bacteria with CheZ under different strength of promoters: BBa_J23112, BBa_J23113, and BBa_J23114, whose relative expression levels of downstream gene are expected to be 1, 21, and 256, respectively. Sceondly, plates pasted polaroid of different transmittance are used to measure CheZ expression under different light strength. Thirdly, plot the bacteria in the center of the plate whose half is opaque. These experiments together are expected to have different diameter of colony or oval shape of colony to show the phototaxis.
Reference
- 1. Kuo, S.C., and Koshland, D.E.(1987) Roles of che Y and cheZ Gene Products in Controlling Flagellar Rotation in Bacterial Chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol., 3:1307:1313
- 2. Bren, A., Welch, M., Blat, Y., Eisenbeach, M.(1996) Signal termination in bacterial chemotaxis: CheZ mediates dephosphorylation of free rather than switch-bound CheY. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93: 10090: 10093
- 3. Bren, A., and Eisenbeach, M.(2000) How Signals Are Heard during Bacterial Chemotaxis: Protein-Protein Interactions in Sensory Signal Propagation. J. Bacteriol., 182: 6865: 6873
- 4. Sanna, M. G., and Simon, M.I.(1996) in vivo and in vitro Characterization of Escherichia coli Protein CheZ Gain- and Loss-of-Function Mutants. J. Bacteriol., 178: 6275: 6280
- 5. Liu, C., et al.(2012) Sequential Establishment of Stripe Patterns in an Expanding Cell Population. Science, 334: 238: 241
- 6. Lee, S.H., Butler, S.M., and Camilli, A.(2001) Selection for in vivo regulators of bacterial virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98: 6889: 6894
- 7. sinha, J., Reyes, S.J., Gallivan, J.P.(2010) Reprogramming bacteria to seek and destroy an herbicide. Nat. Chem. Biol., 464:468
- 8. Topp, S., and Gallivan. J.P.(2008) Random Walks to Synthetic Riboswitches — A High-Throughput Selection Based on Cell Motility. Chem. Biol., 9:210:213
 "
"