Team:University College London/Module 4/Results
From 2012.igem.org
Module 4: Buoyancy
Description | Design | Construction | Characterisation | Modelling | Results | Conclusions
Characterisation of Starvation Promoter BBa_K118011
Normalized expression levels were plotted as relative fluorescent units per optical density at 600 nm. E. coli carrying BBa_K200018 was grown in minimal M9 media supplemented with different glucose concentrations (0%, 0.2%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 3%, 5%).
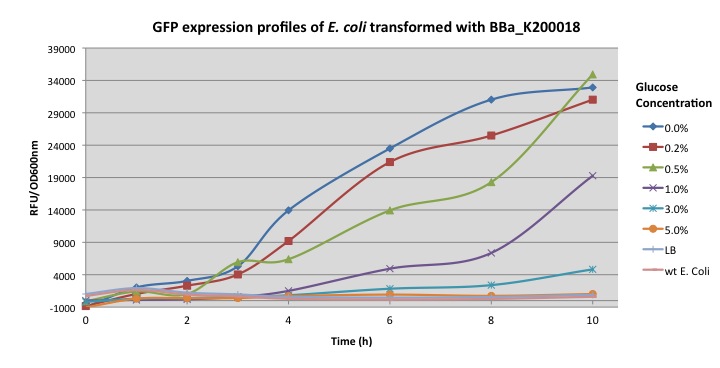 We carried out further characterization of the pcstA fused with GFP (BBa_K200018) built by Imperial College's 2009 iGem team. Fluorescence was measured from overnight cultures and data collected shows significant higher expression for cultures with 0%, 0.2%, 0.5% glucose concentration, this essay also shows how glucose represses cstA promoter.
We carried out further characterization of the pcstA fused with GFP (BBa_K200018) built by Imperial College's 2009 iGem team. Fluorescence was measured from overnight cultures and data collected shows significant higher expression for cultures with 0%, 0.2%, 0.5% glucose concentration, this essay also shows how glucose represses cstA promoter.
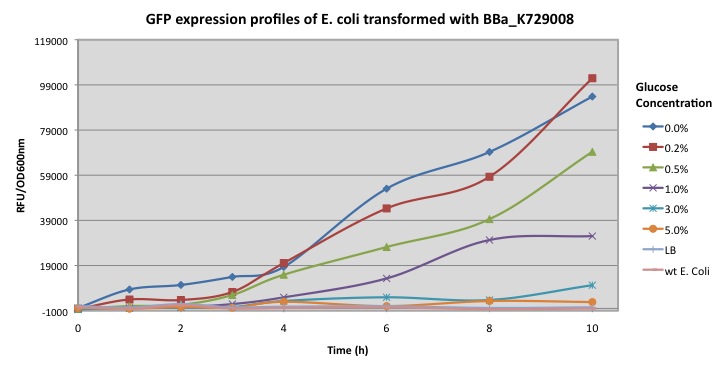 Our module (BBa_K729008) integrates the T7 RNA polymerase and T7 promoter in order to increase the expression of the reporter gene. Once the bacteria is exposed to carbon starvation stress, cstA promoter is activated, as a results it can be seen from the chart that GFP was expressed reaching higher accumulation in cultures with M9 media supplemented with less than 0.5% of glucose.
Our module (BBa_K729008) integrates the T7 RNA polymerase and T7 promoter in order to increase the expression of the reporter gene. Once the bacteria is exposed to carbon starvation stress, cstA promoter is activated, as a results it can be seen from the chart that GFP was expressed reaching higher accumulation in cultures with M9 media supplemented with less than 0.5% of glucose.
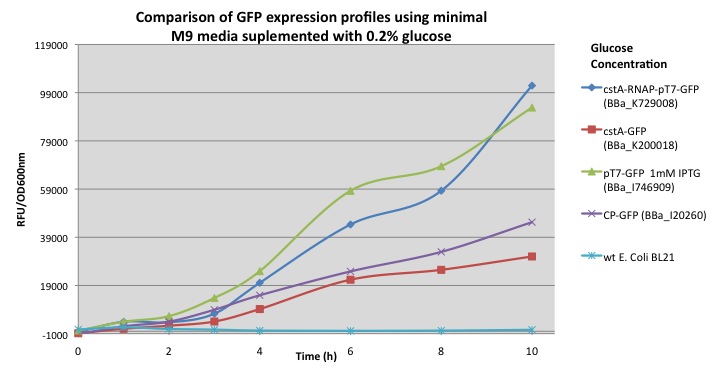 In order to demonstrate that our new biobrick increases the output production when using the cstA promoter and T7 RNA polymerase, we compared our results with other modules using minimal M9 media supplemented with 0.2% glucose: pcstA-GFP (BBa_K200018), pT7-GFP (BBa_I746909) and a constitutive promoter fused with GFP (BBa_I20260). E. coli transformed with our module (BBa_K729008) demonstrated a 3 fold increase in GFP expression over the BBa_K200018 (pcstA-GFP) developed by Imperial College’s 2009 iGem team.
In order to demonstrate that our new biobrick increases the output production when using the cstA promoter and T7 RNA polymerase, we compared our results with other modules using minimal M9 media supplemented with 0.2% glucose: pcstA-GFP (BBa_K200018), pT7-GFP (BBa_I746909) and a constitutive promoter fused with GFP (BBa_I20260). E. coli transformed with our module (BBa_K729008) demonstrated a 3 fold increase in GFP expression over the BBa_K200018 (pcstA-GFP) developed by Imperial College’s 2009 iGem team.
 "
"