Team:University College London/Module 4/Modelling
From 2012.igem.org
Sednanalien (Talk | contribs) (→Modelling) |
(→Modelling) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{:Team:University_College_London/templates/foot}} | {{:Team:University_College_London/templates/foot}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Conclusion and influence to our experimental work | ||
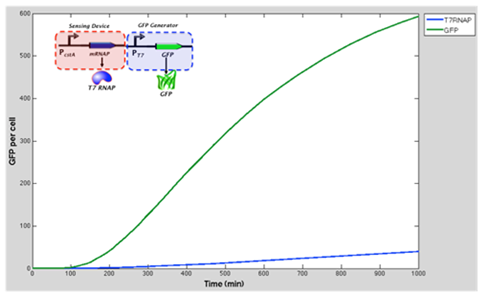
| + | From the results obtained above we can see that our model suggest increase of expression of GFP when the T7 RNA Polymerase as well as T7 promoter are added to the original construct (which was cstA + GFP). | ||
| + | We expect that our experimental data fill follow this. | ||
Revision as of 10:20, 26 September 2012
Module 4: Buoyancy
Description | Design | Construction | Characterisation | Modelling | Results | Conclusions
Modelling
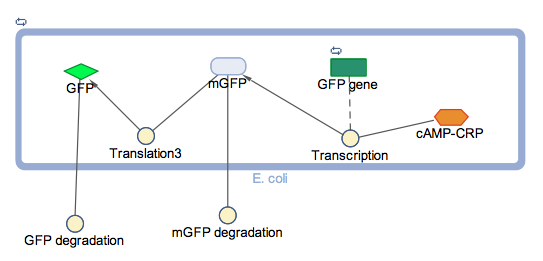
The block diagram shows the module where GFP expression is control by cstA promoter; the expression is triggered under low glucose concentrations.
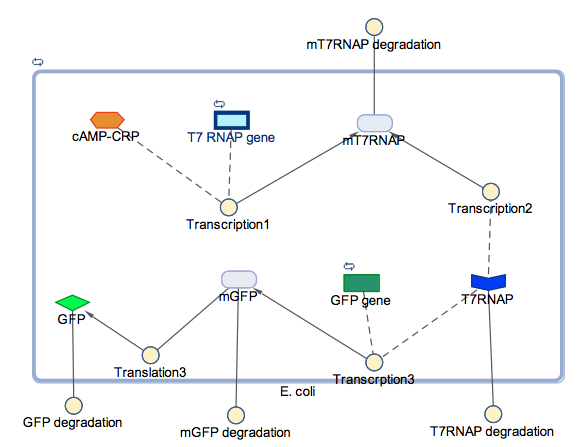
In the models the environmental sensitive promoters (cstA) is activated by carbon starvation stress, then the mRNA encoding T7 RNA polymerase is transcribed, whose protein binds the T7 promoter driving the expression of the the reporter output (GFP).
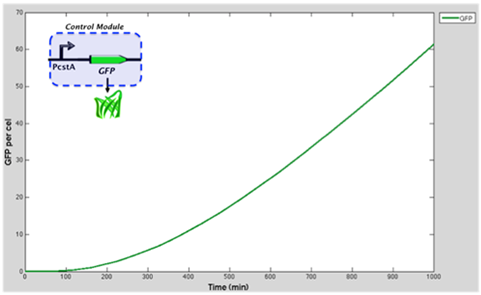
Graph represents the GFP accummulation through time when is controlled by cstA promoter
The green line represents GFP expression levels and the blue line shows the T7 RNAP concentration over time. GFP production is considerably higher than in the previous model.
Conclusion and influence to our experimental work From the results obtained above we can see that our model suggest increase of expression of GFP when the T7 RNA Polymerase as well as T7 promoter are added to the original construct (which was cstA + GFP). We expect that our experimental data fill follow this.
 "
"