Team:TU Munich/Project/Constitutive Promoter
From 2012.igem.org
(→Constitutive Promoters) |
(→Constitutive Promoters) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[File:Georg_einzel_TUM12.jpg|200px|thumb||Responsible: Georg Schützinger]] | [[File:Georg_einzel_TUM12.jpg|200px|thumb||Responsible: Georg Schützinger]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
==Background and principles== | ==Background and principles== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:Georg_einzel_TUM12.jpg|200px|thumb||Responsible: Georg Schützinger]] |
| + | For the '''expression of of proteins''' like limonene, thaumatin and others, '''promoters are essential'''. Since gyle from beer is a complex medium, the controlled induction of proteinexpression proves to be a '''nearly impossible task.''' | ||
| + | Therefore '''constitutive promoters''' are the ideal solution for that problem. They offer '''simplicity''', and therefore are the first choice for the introduction of '''new biosynthetic pathways''' in yeast in complex media. | ||
| + | In order to finetune biosynthetic pathways with two or more enzymes, like it is the case with caffeine synthases, we want to use 3 constitutive promoters '''ADH1''', '''TEF1''' and '''TEF2'''. Their strength, and constant expression have been characterized by Partow et al. 2010, Jie Sun et. al. 2011 and many more. | ||
| + | For illustration of their difference in strength TEF1-P and ADH1-P were cloned in front of Renilla Luciferase [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J52008] in pTUM100 [http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K801001] | ||
| + | and the bioluminescence measured. The same experiment shall soon be also made with TEF2-P. | ||
| - | + | ==Background and principles== | |
| + | ---- | ||
| - | + | The promoter '''ADH1''' is one of the most widely used constitutive promoters, for proteinexpression in yeast. It naturally controls the expression of '''Alcohole Dehydrogenase 1''' of ''Saccharomyces Cerevisiae''. This enzyme is part of the | |
| - | + | '''yeast glycolytic pathway''' and is needed for the fermentation of glucose into alcohole. | |
| + | For that reason its natural form (1500 bp) is inhibited by ethanol. To outrun this problem, we used a middle long version (720 bp) [[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K319005]] that was succesfully engineered and tested by Ruohonen et al. 1995 and that is not susceptible to ethanol repression, thus providing '''constant expression''' throughout the brewing process. | ||
| - | + | The promoter '''TEF1''' controls the expression of '''translation elongaton factor EF1 alpha'''. The most important characteristics of this promoter for brewing is his '''high expression strength''' that is 5x above ADH1-P, and its insensitivity to repression by ethanol which often occurs with constitutive promoters from the '''yeast glycolytic pathway''' (Partow et al. 2010). During the brewing process expression even becomes stronger due a slight repression by Glucose at the beginning. | |
| + | |||
| + | The promoter '''TEF2''' controls the expression of a second gene for translation elongation factor EF1 alpha. Since TEF2 proteine alone can keep mutants, lacking TEF1, growing, it is believed that it is an identical of nearly identical version of TEF1 proteine (Schirmaier et al. 1984) . | ||
| - | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
==General remarks and issues== | ==General remarks and issues== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | + | For '''comparison of the promoter strength''' 3 timepoints were chosen. After '''12''' hours, after '''24''' hours and '''48''' hours. This way differences in activity due to varying Ethanol- and glucose concentrations can be analyzed. | |
| - | + | This would be the more interesting since the influence of these substances on the activity of TEF2-Promoter has not been analyzed this far. | |
| + | If you set the activity of TEF1-Promoter for 100%, the activity of ADH1-P should be roughly 20% and keep constant. TEF1-Promoter should reach 150 % during the later The activity of TEF2-P activity should be 40% at the beginning. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
=== Gel picture of finished Constructs === | === Gel picture of finished Constructs === | ||
| - | + | ||
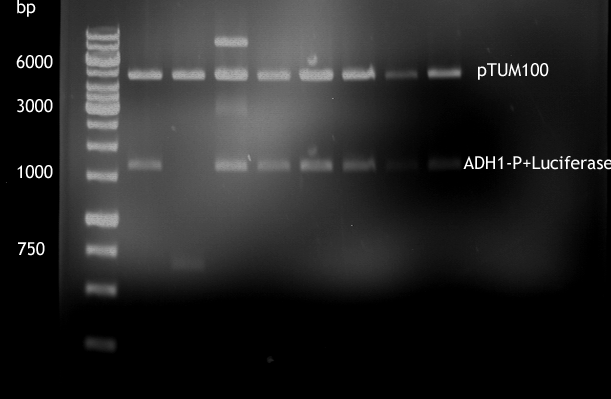
| - | + | [[File:20120918_ADH1-P_und_P791.png]] | |
| + | |||
| + | * Analytical digestion of ADH1-P with luciferase in pTUM100 | ||
| + | |||
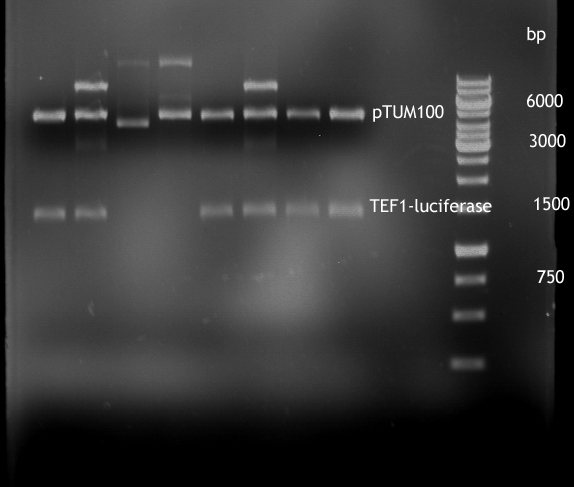
| + | [[File:20120918_TEF1-P_und_P791.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Analytical digestion of TEF1-P with luciferase in pTUM100 | ||
| + | |||
=== Results of luciferase assay === | === Results of luciferase assay === | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 25 September 2012



Contents |
Constitutive Promoters
Background and principles
For the expression of of proteins like limonene, thaumatin and others, promoters are essential. Since gyle from beer is a complex medium, the controlled induction of proteinexpression proves to be a nearly impossible task. Therefore constitutive promoters are the ideal solution for that problem. They offer simplicity, and therefore are the first choice for the introduction of new biosynthetic pathways in yeast in complex media. In order to finetune biosynthetic pathways with two or more enzymes, like it is the case with caffeine synthases, we want to use 3 constitutive promoters ADH1, TEF1 and TEF2. Their strength, and constant expression have been characterized by Partow et al. 2010, Jie Sun et. al. 2011 and many more. For illustration of their difference in strength TEF1-P and ADH1-P were cloned in front of Renilla Luciferase [1] in pTUM100 [2] and the bioluminescence measured. The same experiment shall soon be also made with TEF2-P.
Background and principles
The promoter ADH1 is one of the most widely used constitutive promoters, for proteinexpression in yeast. It naturally controls the expression of Alcohole Dehydrogenase 1 of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. This enzyme is part of the yeast glycolytic pathway and is needed for the fermentation of glucose into alcohole. For that reason its natural form (1500 bp) is inhibited by ethanol. To outrun this problem, we used a middle long version (720 bp) [[3]] that was succesfully engineered and tested by Ruohonen et al. 1995 and that is not susceptible to ethanol repression, thus providing constant expression throughout the brewing process.
The promoter TEF1 controls the expression of translation elongaton factor EF1 alpha. The most important characteristics of this promoter for brewing is his high expression strength that is 5x above ADH1-P, and its insensitivity to repression by ethanol which often occurs with constitutive promoters from the yeast glycolytic pathway (Partow et al. 2010). During the brewing process expression even becomes stronger due a slight repression by Glucose at the beginning.
The promoter TEF2 controls the expression of a second gene for translation elongation factor EF1 alpha. Since TEF2 proteine alone can keep mutants, lacking TEF1, growing, it is believed that it is an identical of nearly identical version of TEF1 proteine (Schirmaier et al. 1984) .
</div>
General remarks and issues
For comparison of the promoter strength 3 timepoints were chosen. After 12 hours, after 24 hours and 48 hours. This way differences in activity due to varying Ethanol- and glucose concentrations can be analyzed. This would be the more interesting since the influence of these substances on the activity of TEF2-Promoter has not been analyzed this far. If you set the activity of TEF1-Promoter for 100%, the activity of ADH1-P should be roughly 20% and keep constant. TEF1-Promoter should reach 150 % during the later The activity of TEF2-P activity should be 40% at the beginning.
Gel picture of finished Constructs
- Analytical digestion of ADH1-P with luciferase in pTUM100
- Analytical digestion of TEF1-P with luciferase in pTUM100
Results of luciferase assay
</div>
 "
"