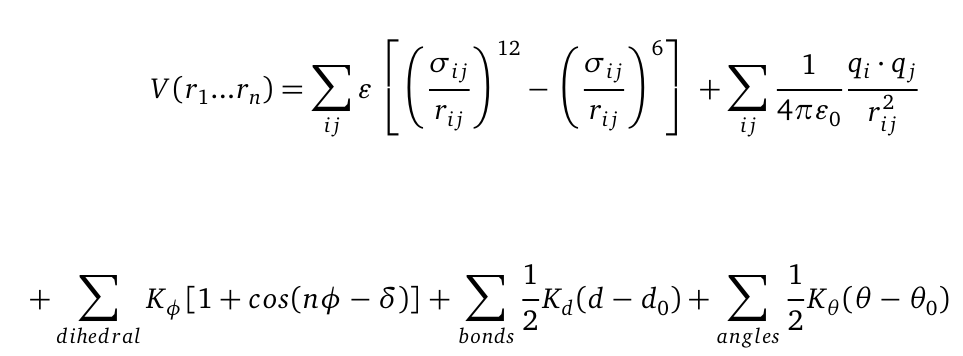Team:TU Darmstadt/Modeling MD
From 2012.igem.org
Contents |
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is one of the most common tools in computational biology. MD simulations solve the classical newton’s equations of motion. For the computation we need to calculate all forces acting in our system. The Forces are described within a potential energy -the Force Field and depends on the atomic coordinates r. For the illustration the potential is computed as follows:
The first term represents a a Lennard-Jones (LJ) potential. It approximates the interaction between a pair of neutral atoms or molecules. The second term is a coulomb potential between a pair of atom I and j. The last terms describe bonds and angles potentials. Due to experimental data and quantum chemical calculations the force-field parameters can be identified.
Goal
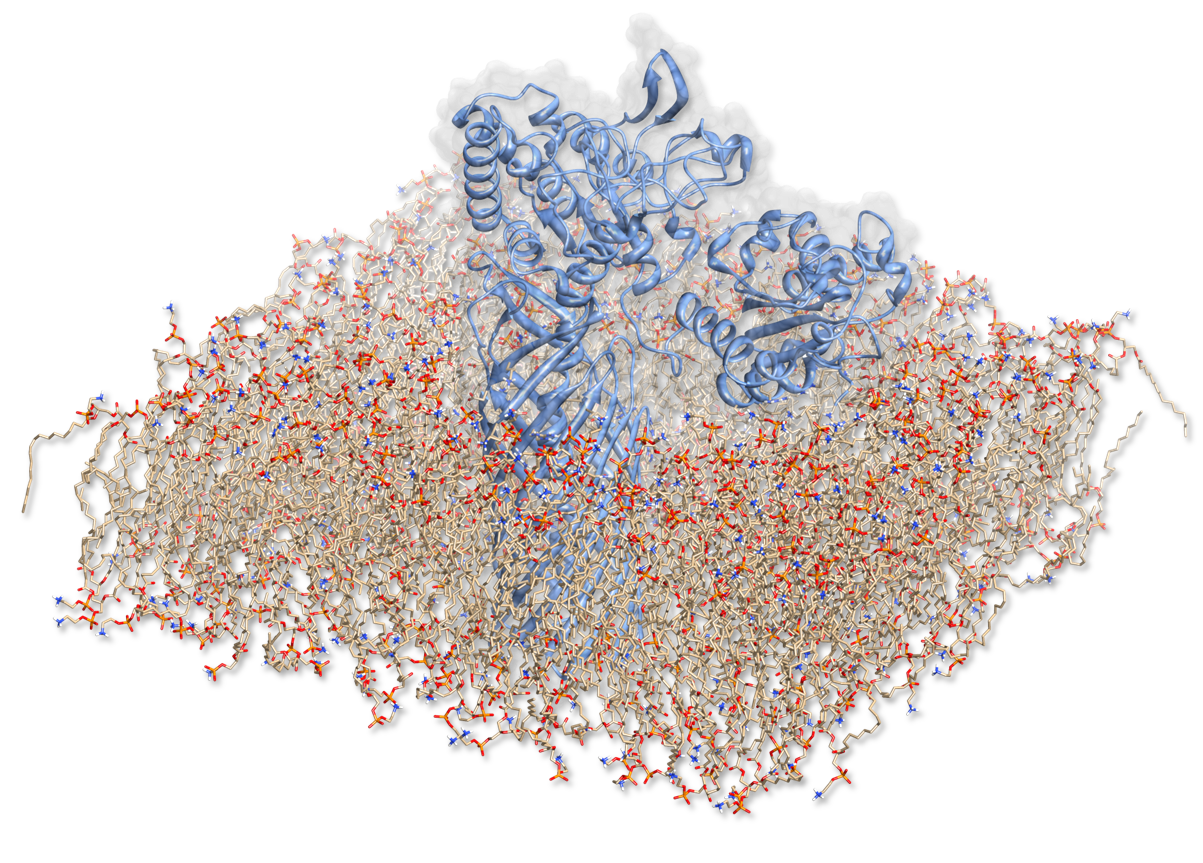
In order to characterize the enzyme construct and to simulate its complex behavior, MD was required to study the interactions. Hence to the degradation of PET, our Team designed a sophisticated protein-construct. This construct is a fusion protein containing a degradation module (PDB :1CEX, pnB) and EstA (PDB id: 3KVN), a membrane bounded beta-beryl. Moreover, this construct is exposed at the outer membrane of our bacteria. Hence, we quantified the dynamic nature of our degradation protein with coarse-grained methods we have to quantify the motion within this construct surrounded by its native environment. We firts have to create a scene were we put our fusion protein and put it into a membran layer. Although simulating this fusion protein was indispensable, it seems to be a complicated task.
 "
"