Team:ETH Zurich/Modeling
From 2012.igem.org
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
=== Reaction Network ODE model === | === Reaction Network ODE model === | ||
| - | [[Image:ETH UVR8.png|right|thumb|450px|Figure 2: Overall circuit design for UVR8 | + | [[Image:ETH UVR8.png|right|thumb|450px|Figure 2: Overall circuit design for the UVR8 system with feedback via PABA. See all details on [[Team:ETH_Zurich/Modeling/UVR8|UVR8 Circuit]] ]] |
To decode our light receptor input, we created a full deterministic ODE model. As systems of interacting proteins with possibly multiple homodimerisations can grow quickly in size, modelling requires a systematic approach. In order to span the ODE system, we employ rules-based models. For this methodology, we define seed species and rules on how they can interact. In practice the software Ru2ren (to be published by [http://www.csb.ethz.ch/people/cmayer Christian Mayer]) then generates the system of coupled ODEs. | To decode our light receptor input, we created a full deterministic ODE model. As systems of interacting proteins with possibly multiple homodimerisations can grow quickly in size, modelling requires a systematic approach. In order to span the ODE system, we employ rules-based models. For this methodology, we define seed species and rules on how they can interact. In practice the software Ru2ren (to be published by [http://www.csb.ethz.ch/people/cmayer Christian Mayer]) then generates the system of coupled ODEs. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Team:ETH_Zurich/Modeling/UVR8|UVR8-only]] | [[Team:ETH_Zurich/Modeling/UVR8|UVR8-only]] | ||
| - | Having demonstrated a realistic time frame for production of the protecting substance PABA, we continue to | + | Having demonstrated a realistic time frame for production of the protecting substance PABA, we continue to model the decoder in a more complex processing circuit: |
| - | |||
# [[Team:ETH_Zurich/Modeling/Construct2|LovTAP-Cph8]] | # [[Team:ETH_Zurich/Modeling/Construct2|LovTAP-Cph8]] | ||
| - | + | The circuit is described in further detail on the individual page. | |
{{:Team:ETH_Zurich/Templates/Footer}} | {{:Team:ETH_Zurich/Templates/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 21:44, 26 October 2012
Contents |
Overview
To support our colleagues in the lab, we outlined different models for different parts of our project.
Photoinduction
To calculate the activity of light receptors, we devised a model that takes emission spectra of different light sources and absorption spectra, quantum yield and extinction coefficients of the receptors from literature as an input and returns the activation and deactivation constants for the given light conditions.
This model can be used to calculate the activity of a light receptor in a light condition. Together with an mechanistical model of the receptor, it gives an estimate of the transcriptional activation due to light input.
See all the details in Photoinduction model.
Sun Protection Factor
The sun protection factor (SPF) model gives the sun protection factor we can achieve with a given amount of PABA and also what amount of PABA we need to get to a SPF.
See how much our E.colipse protects you from sun radiation in the Sun Protection Factor model!
Reaction Network ODE model
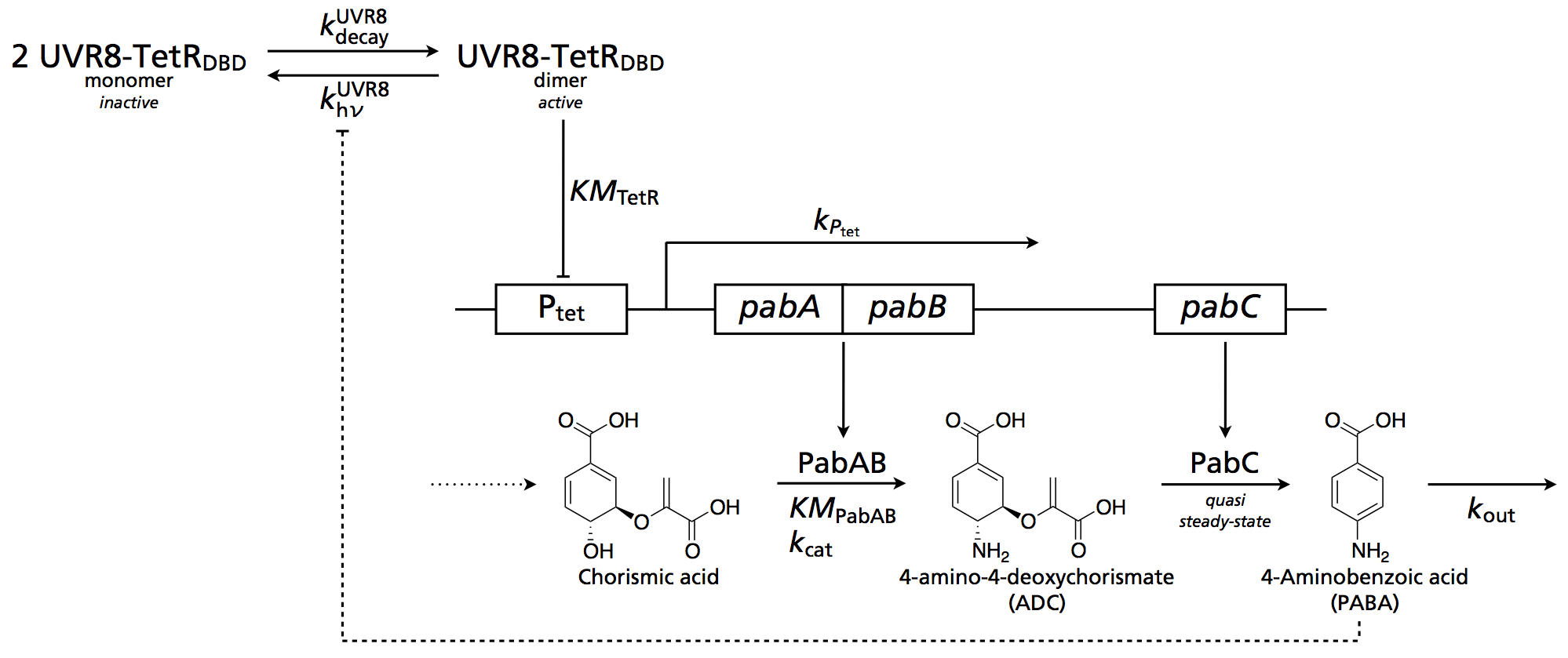
To decode our light receptor input, we created a full deterministic ODE model. As systems of interacting proteins with possibly multiple homodimerisations can grow quickly in size, modelling requires a systematic approach. In order to span the ODE system, we employ rules-based models. For this methodology, we define seed species and rules on how they can interact. In practice the software Ru2ren (to be published by Christian Mayer) then generates the system of coupled ODEs.
As an input to the decoder, we use a combination of ab initio constants from our photoconversion model and a mechanistical model of the receptor mode of action, parameters from literature and assumed respectively desired parameters. Given such models and parameters, the biological implementation can then be optimised.
We first analyse the separation (dynamic range) and timescale of UVR8 dimerisation/dissociation: UVR8-only
Having demonstrated a realistic time frame for production of the protecting substance PABA, we continue to model the decoder in a more complex processing circuit:
The circuit is described in further detail on the individual page.
References
- Brown, B. a, Headland, L. R., & Jenkins, G. I. (2009). UV-B action spectrum for UVR8-mediated HY5 transcript accumulation in Arabidopsis. Photochemistry and photobiology, 85(5), 1147–55.
- Christie, J. M., Salomon, M., Nozue, K., Wada, M., & Briggs, W. R. (1999): LOV (light, oxygen, or voltage) domains of the blue-light photoreceptor phototropin (nph1): binding sites for the chromophore flavin mononucleotide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96(15), 8779–83.
- Christie, J. M., Arvai, A. S., Baxter, K. J., Heilmann, M., Pratt, A. J., O’Hara, A., Kelly, S. M., et al. (2012). Plant UVR8 photoreceptor senses UV-B by tryptophan-mediated disruption of cross-dimer salt bridges. Science (New York, N.Y.), 335(6075), 1492–6.
- Cloix, C., & Jenkins, G. I. (2008). Interaction of the Arabidopsis UV-B-specific signaling component UVR8 with chromatin. Molecular plant, 1(1), 118–28.
- Cox, R. S., Surette, M. G., & Elowitz, M. B. (2007). Programming gene expression with combinatorial promoters. Molecular systems biology, 3(145), 145. doi:10.1038/msb4100187
- Drepper, T., Eggert, T., Circolone, F., Heck, A., Krauss, U., Guterl, J.-K., Wendorff, M., et al. (2007). Reporter proteins for in vivo fluorescence without oxygen. Nature biotechnology, 25(4), 443–5
- Drepper, T., Krauss, U., & Berstenhorst, S. M. zu. (2011). Lights on and action! Controlling microbial gene expression by light. Applied microbiology, 23–40.
- EuropeanCommission (2006). SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE ON CONSUMER PRODUCTS SCCP Opinion on Biological effects of ultraviolet radiation relevant to health with particular reference to sunbeds for cosmetic purposes.
- Elvidge, C. D., Keith, D. M., Tuttle, B. T., & Baugh, K. E. (2010). Spectral identification of lighting type and character. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 10(4), 3961–88.
- GarciaOjalvo, J., Elowitz, M. B., & Strogatz, S. H. (2004). Modeling a synthetic multicellular clock: repressilators coupled by quorum sensing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(30), 10955–60.
- Gao Q, Garcia-Pichel F. (2011). Microbial ultraviolet sunscreens. Nat Rev Microbiol. 9(11):791-802.
- Goosen N, Moolenaar GF. (2008) Repair of UV damage in bacteria. DNA Repair (Amst).7(3):353-79.
- Heijde, M., & Ulm, R. (2012). UV-B photoreceptor-mediated signalling in plants. Trends in plant science, 17(4), 230–7.
- Hirose, Y., Narikawa, R., Katayama, M., & Ikeuchi, M. (2010). Cyanobacteriochrome CcaS regulates phycoerythrin accumulation in Nostoc punctiforme, a group II chromatic adapter. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(19), 8854–9.
- Hirose, Y., Shimada, T., Narikawa, R., Katayama, M., & Ikeuchi, M. (2008). Cyanobacteriochrome CcaS is the green light receptor that induces the expression of phycobilisome linker protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(28), 9528–33.
- Kast, Asif-Ullah & Hilvert (1996) Tetrahedron Lett. 37, 2691 - 2694., Kast, Asif-Ullah, Jiang & Hilvert (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 5043 - 5048
- Kiefer, J., Ebel, N., Schlücker, E., & Leipertz, A. (2010). Characterization of Escherichia coli suspensions using UV/Vis/NIR absorption spectroscopy. Analytical Methods, 9660. doi:10.1039/b9ay00185a
- Kinkhabwala, A., & Guet, C. C. (2008). Uncovering cis regulatory codes using synthetic promoter shuffling. PloS one, 3(4), e2030.
- Krebs in Deutschland 2005/2006. Häufigkeiten und Trends. 7. Auflage, 2010, Robert Koch-Institut (Hrsg) und die Gesellschaft der epidemiologischen Krebsregister in Deutschland e. V. (Hrsg). Berlin.
- Lamparter, T., Michael, N., Mittmann, F., & Esteban, B. (2002). Phytochrome from Agrobacterium tumefaciens has unusual spectral properties and reveals an N-terminal chromophore attachment site. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(18), 11628–33.
- Levskaya, A. et al (2005). Engineering Escherichia coli to see light. Nature, 438(7067), 442.
- Mancinelli, A. (1986). Comparison of spectral properties of phytochromes from different preparations. Plant physiology, 82(4), 956–61.
- Nakasone, Y., Ono, T., Ishii, A., Masuda, S., & Terazima, M. (2007). Transient dimerization and conformational change of a BLUF protein: YcgF. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 129(22), 7028–35.
- Orth, P., & Schnappinger, D. (2000). Structural basis of gene regulation by the tetracycline inducible Tet repressor-operator system. Nature structural biology, 215–219.
- Parkin, D.M., et al., Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 2005. 55(2): p. 74-108.
- Rajagopal, S., Key, J. M., Purcell, E. B., Boerema, D. J., & Moffat, K. (2004). Purification and initial characterization of a putative blue light-regulated phosphodiesterase from Escherichia coli. Photochemistry and photobiology, 80(3), 542–7.
- Rizzini, L., Favory, J.-J., Cloix, C., Faggionato, D., O’Hara, A., Kaiserli, E., Baumeister, R., et al. (2011). Perception of UV-B by the Arabidopsis UVR8 protein. Science (New York, N.Y.), 332(6025), 103–6.
- Roux, B., & Walsh, C. T. (1992). p-aminobenzoate synthesis in Escherichia coli: kinetic and mechanistic characterization of the amidotransferase PabA. Biochemistry, 31(30), 6904–10.
- Strickland, D. (2008). Light-activated DNA binding in a designed allosteric protein. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(31), 10709–10714.
- Sinha RP, Häder DP. UV-induced DNA damage and repair: a review. Photochem Photobiol Sci. (2002). 1(4):225-36
- Sambandan DR, Ratner D. (2011). Sunscreens: an overview and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011 Apr;64(4):748-58.
- Tabor, J. J., Levskaya, A., & Voigt, C. A. (2011). Multichromatic Control of Gene Expression in Escherichia coli. Journal of Molecular Biology, 405(2), 315–324.
- Thibodeaux, G., & Cowmeadow, R. (2009). A tetracycline repressor-based mammalian two-hybrid system to detect protein–protein interactions in vivo. Analytical biochemistry, 386(1), 129–131.
- Tschowri, N., & Busse, S. (2009). The BLUF-EAL protein YcgF acts as a direct anti-repressor in a blue-light response of Escherichia coli. Genes & development, 522–534.
- Tschowri, N., Lindenberg, S., & Hengge, R. (2012). Molecular function and potential evolution of the biofilm-modulating blue light-signalling pathway of Escherichia coli. Molecular microbiology.
- Tyagi, A. (2009). Photodynamics of a flavin based blue-light regulated phosphodiesterase protein and its photoreceptor BLUF domain.
- Vainio, H. & Bianchini, F. (2001). IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention: Volume 5: Sunscreens. Oxford University Press, USA
- Quinlivan, Eoin P & Roje, Sanja & Basset, Gilles & Shachar-Hill, Yair & Gregory, Jesse F & Hanson, Andrew D. (2003). The folate precursor p-aminobenzoate is reversibly converted to its glucose ester in the plant cytosol. The Journal of biological chemistry, 278.
- van Thor, J. J., Borucki, B., Crielaard, W., Otto, H., Lamparter, T., Hughes, J., Hellingwerf, K. J., et al. (2001). Light-induced proton release and proton uptake reactions in the cyanobacterial phytochrome Cph1. Biochemistry, 40(38), 11460–71.
- Wegkamp A, van Oorschot W, de Vos WM, Smid EJ. (2007 )Characterization of the role of para-aminobenzoic acid biosynthesis in folate production by Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. Apr;73(8):2673-81.
 "
"






