Team:Amsterdam/project/features and applications
From 2012.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<div id="sub-menu" class="content-block"> | <div id="sub-menu" class="content-block"> | ||
| - | <h1> | + | <h1>Features and Applications</h1> |
| - | + | __NOTOC__ | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
The Cellular Logbook regards quite unexplored and fundamental based research. Our projects holds a platform for new technology. But there are already some applications that are feasible in the near future. | The Cellular Logbook regards quite unexplored and fundamental based research. Our projects holds a platform for new technology. But there are already some applications that are feasible in the near future. | ||
<div class='clear'></div> | <div class='clear'></div> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 22: | ||
<h4>Time Indicator</h4> | <h4>Time Indicator</h4> | ||
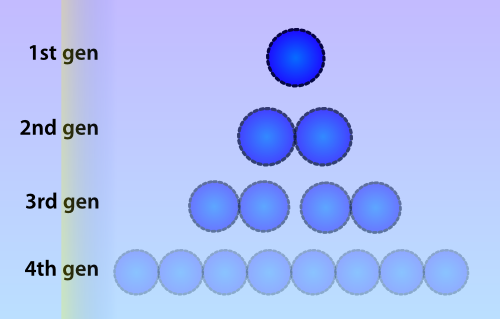
| - | [[File:Celldivision.png|thumb|right|300px|Due to cell division, the amount of methylated plasmids will be approximately halved during each division cycle. In this picture a lower opacity indicates a lower amount of methylated plasmids]] | + | [[File:Celldivision.png|thumb|right|300px|Figure 1: Due to cell division, the amount of methylated plasmids will be approximately halved during each division cycle. In this picture a lower opacity indicates a lower amount of methylated plasmids]] |
Numerous identical plasmids are often present in single cells and plasmids replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome (Scott 1984). A plasmid copy number (PCN) has been determined for all plasmids in the Parts Registry, which indicates a likely amount of copies of the plasmid to be present in each cell. Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes do not copy DNA methylation patterns to the newly synthesized strand during DNA replication. This will lead to a dilution of the amount of ‘written’-plasmids over time, mostly due to cell replication and the ensuing binomial division of the plasmids in the parent cell among the two daughter cells. | Numerous identical plasmids are often present in single cells and plasmids replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome (Scott 1984). A plasmid copy number (PCN) has been determined for all plasmids in the Parts Registry, which indicates a likely amount of copies of the plasmid to be present in each cell. Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes do not copy DNA methylation patterns to the newly synthesized strand during DNA replication. This will lead to a dilution of the amount of ‘written’-plasmids over time, mostly due to cell replication and the ensuing binomial division of the plasmids in the parent cell among the two daughter cells. | ||
Latest revision as of 03:52, 27 September 2012
 "
"